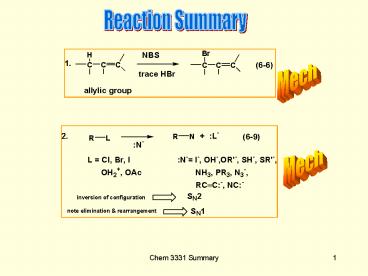
Reaction Summary - PowerPoint PPT Presentation
1 / 24
Title:
Reaction Summary
Description:
1. Structure of alkanes - staggered, eclipsed, gauche, Newman diagrams ... cyclohexane - axial versus equatorial, ring flips. mono and disubstituted cyclohexanes ... – PowerPoint PPT presentation
Number of Views:39
Avg rating:3.0/5.0
Title: Reaction Summary
1
Reaction Summary
Mech
Mech
2
Mech
Mech
Mech
3
Mech
Mech
Mech
4
Mech
Mech
5
Mech
Mech
6
Mech
Mech
7
(No Transcript)
8
Mech
Mech
Mech
9
Mech
10
Mech
11
Mech (for keto to enol trans.)
12
(No Transcript)
13
Mech
Mech
Mech
14
Mech
15
Mech
16
Mech
Mech
17
(No Transcript)
18
Concepts
Chapter 1
- octet rule - writing Lewis structures
- electronegativity trends
- formal charges - computing them
- resonance - drawing structures
- drawing condensed/line formulas
- Brønsted acidity/bascity - trends
- Lewis acidity/basicity
19
Chapter 2
1. s versus p bonds 2. hybrids number
angle sp3 4 109.5
sp2 3 120 sp
2 180 3. stereoisomers a.
constitutional isomers b. geometric isomers 4.
intermolecular forces 5. functional groups and
names
20
Chapter 3
- 1. Structure of alkanes - staggered, eclipsed,
gauche, - Newman diagrams
- 2. Structure of cycloalkanes
- cyclohexane - axial versus equatorial, ring flips
- mono and disubstituted cyclohexanes
Chapter 4
- 1. kinetics
- a. rate constants
- b. activation energies (DG, DH, DS)
- c. rate determining step
- 2. thermodynamics
- a. equilibrium constants
- b. energies (DG, DH, DS)
- c. endothermic/ exothermic
21
- 3. linear free energy relationships
- reactivity versus selectivity
- the Hammond principle
- 4. mechanism of halogenation reactions
- a. initiation, propagation, termination events
- b. energetics - how to compute them from BDEs
- c. selectivity - reactivity
5. reactive intermediates a. carbocations,
carbanions, radicals b. stabilities - resonance,
inductive effects c. drawing resonance
structures, allyl, benzyl, etc. d. carbenes
22
Chapter 5
- Definitions
- a. chiral/ achiral
- b. diastereomer/ enantiomer
- c. configuration/ conformation
- d. mirror plane/ center of inversion
- 2. Absolute configuration know
Cahn-Ingold-Prelog rules - a. determine priority of groups around chiral
center - b. determine R, S configuration
- 3. More than one center of chirality
- a. Fischer projections
- i) manipulations, ie inverting, flipping,
rotating - ii) determining R, S
- b. Diastereomers - resolution of enantiomers
23
Chapter 6
1. Nucleophilic substitution a. mechanisms of
SN1 and SN2 b. rate laws and stereochemistry c
. variation of nucleophile, structure of R group,
solvent and leaving group, L on reaction
rates d. rearrangements in carbocations 2.
Elimination reactions a. mechanisms of E1, E2
and E1cB b. stereochemistry and rate laws c.
orientation - Saytzeff versus Hofmann d. effect
of base, leaving group and alkyl group 3.
Factors favoring substitution versus
elimination
24
Chapter 7
1. Know how to calculate elements of
unsaturation. 2. What the p bond in olefins is
and does - relative stability. 3. Nomenclature
cis/trans and E/Z names
Chapter 8
- Markovnikov versus anti-Markovnikov addition
- Syn versus anti addition
Chapter 9
1. Acidity of terminal alkynes
Chapter 10
1. Property of alcohols - lone pairs acidic H
Chapter 11
1. Techniques in multistep synthesis - pp. 489
-492 2. How to figure out reaction mechanisms -
pp. 480 -484