Reaction Orientation (ortho/meta/para) - PowerPoint PPT Presentation
Title:
Reaction Orientation (ortho/meta/para)
Description:
Reaction Orientation (ortho/meta/para) Examine mechanism of the substitution reaction. For benzene + Br2 : Intermediate: in the delocalized carbocation intermediate, – PowerPoint PPT presentation
Number of Views:100
Avg rating:3.0/5.0
Title: Reaction Orientation (ortho/meta/para)
1
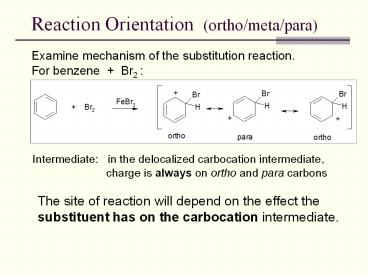
Reaction Orientation (ortho/meta/para)
Examine mechanism of the substitution reaction.
For benzene Br2
Intermediate in the delocalized carbocation
intermediate, charge is always on ortho and
para carbons
The site of reaction will depend on the effect
the substituent has on the carbocation
intermediate.
2
Alkyl Groups Ortho/Para Directors
- Alkyl groups direct substitution to positions
ortho and para to themselves. (They also are
activators.)
meta notstabilized
3
-OH and -NH2 Groups ortho/para
- Alkoxyl, and amino groups have a strong,
electron-donating resonance effect. They are
strong activators. - Direct substitution to the ortho/para positions.
meta notstabilized
4
Activating Substituents o/p directors
- For activating sustituents, cation intermediates
formed from ortho or para attack are stabilized,
so reaction there is favored. - Meta attack gives a delocalized carbocation
without any special stabilization.
x
5
Meta Directing Deactivators - Carbonyl
meta - noproblem
6
Deactivating Substituents meta directors
- For deactivating sustituents, cation
intermediates formed from ortho or para attack
are destabilized. - Meta attack gives a delocalized carbocation
without any special destabilization, so meta is
favored.
x
7
Deactivating Substituents meta directors
- Ortho/para attack is bad, meta attack is no
problem. - Deactivating substituents such as carbonyl or
-CF3 are therefore generally meta directors.
x
8
Halogens Contradictory Effects
- A halogen substituent -X (-F, -Cl, -Br, -I) will
withdraw electron density via an inductive effect
due to high electronegativity.
deactivates ringby induction,slows reaction rate
resonance suggestshalogens may be ortho-para
directors
9
Substituent Effects in Aromatic Rings
- Electron donating goups increase rate of
reaction. - Electron withdrawing groups decrease rate of
reaction.
Due to inductive effects (based on
electronegativity), halogens make aromatic rings
slightly less reactive.
But resonance effects cause halogens to be
ortho/para directors.
10
Halogens o/p directing deactivators
- Electron-withdrawing inductive effect controls
reactivity, and makes halogens deactivators. - Induction controls rate of reaction
- Resonance effect controls the orientation of
reaction, makes halogens ortho/para directors. - Resonance controls position of reaction
11
Halogens o/p Directing Deactivators
12
Summary Effect of Substituents
All activating groups (make reactions faster)
are ortho/para directors. Deactivating groups
(slow the reaction rate) are meta
directors. Exception Halogens are
deactivating groups and ortho/para directors.