Figure 28.0x A ciliated protozoan - PowerPoint PPT Presentation
1 / 55
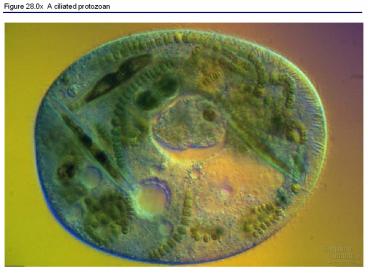
Title: Figure 28.0x A ciliated protozoan
1
Figure 28.0x A ciliated protozoan
2
Figure 28.1a Too diverse for one kingdom Amoeba
proteus, a unicellular "protozoan"
3
Figure 28.1b Too diverse for one kingdom a
diatom, a unicellular "alga"
4
Figure 28.1c Too diverse for one kingdom a
slime mold (Physarum polychalum)
5
Figure 28.1d Too diverse for one kingdom
Australian bull kelp (Durvillea potatorum)
6
Figure 28.2 The kingdom Protista problem
7
Figure 28.3 Euglena an example of a
singlecelled protist
8
Figure 28.03x Euglena
9
Figure 28.4 A model of the origin of eukaryotes
10
Figure 28.5 Secondary endosymbiosis and the
origin of algal diversity
11
Figure 28.6 Traditional hypothesis for how the
three domains of life are related
12
Figure 28.7 An alternative hypothesis for how
the three domains of life are related
13
Figure 28.8 A tentative phylogeny of eukaryotes
14
Figure 28.9 Giardia lamblia, a diplomonad
15
Figure 28.10 Trichomonas vaginalis, a parabasalid
16
Figure 28.x1 Trichonympha
17
Figure 28.11x Trypanosoma, the kinetoplastid
that causes sleeping sickness
18
Figure 28.12 A dinoflagellate
19
Figure 28.12x1 Dinoflagellate
20
Figure 28.12x2 Swimming with bioluminescent
dinoflagellates
21
Figure 28.13 The two-host life history of
Plasmodium, the apicomplexan that causes malaria
22
Figure 28.14c Ciliates Paramecium
23
Figure 28.14x Ciliates Stentor (left),
Paramecium (right)
24
Figure 28.15 Conjugation and genetic
recombination in Paramecium caudatum
25
Figure 28.15x Paramecium conjugating
26
Figure 28.16 The life cycle of a water mold
(Layer 1)
27
Figure 28.16 The life cycle of a water mold
(Layer 2)
28
Figure 28.16 The life cycle of a water mold
(Layer 3)
29
Figure 28.16x1 Zoospore release
30
Figure 28.16x2 Water mold Oogonium
31
Figure 28.x2 Powdery mildew
32
Figure 28.17 Diatoms Diatom diversity (left),
Pinnularia (left)
33
Figure 28.17x Diatom shell
34
Figure 28.18 A golden alga
35
Figure 28.20x1 Kelp forest
36
Figure 28.20x2 Kelp forest
37
Figure 28.21 The life cycle of Laminaria an
example of alternation of generations
38
Figure 28.22 Red algae Dulse (top),
Bonnemaisonia hamifera (bottom)
39
Figure 28.23 Colonial and multicellular
chlorophytes Volvox (left), Caulerpa (right)
40
Figure 28.x3 Spirogyra conjugating
41
Figure 28.24 The life cycle of Chlamydomonas
42
Figure 28.25 A hypothetical history of plastids
in the photosynthetic eukaryotes
43
Figure 28.26 Use of pseudopodia for feeding
44
Figure 28.26x1 Amoeba
45
Figure 28.26x2 Vampyrella
46
Figure 28.27 Actinopods Heliozoan (left),
radiolarian (right)
47
Figure 28.27x Radiolarian skeleton
48
Figure 28.28 Foraminiferan
49
Figure 28.29 The life cycle of a plasmodial
slime mold, such as Physarum
50
Figure 28.29x1 Plasmodial slime mold
51
Figure 28.29x2 Slime mold Sporangia
52
Figure 28.30 The life cycle of a cellular slime
mold (Dictyostelium)
53
Figure 28.30x1 Dictyostelium life cycle
54
Figure 28.30x2 Stages of Dictyostelium
55
Table 28.1 A Sample of Protistan Diversity