Diapositive 1 - PowerPoint PPT Presentation
Title:
Diapositive 1
Description:
Diapositive 1 – PowerPoint PPT presentation
Number of Views:73
Avg rating:3.0/5.0
Title: Diapositive 1
1
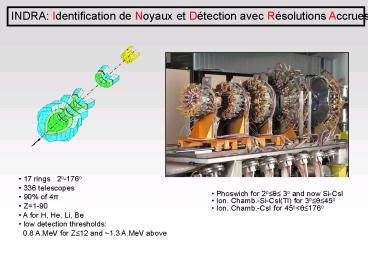
INDRA Identification de Noyaux et Détection avec
Résolutions Accrues
- 17 rings 2o-176o
- 336 telescopes
- 90 of 4p
- Z1-90
- A for H, He, Li, Be
- low detection thresholds
- 0.8 A.MeV for Z12 and 1.3 A.MeV above
- Phoswich for 2o? 3o and now Si-CsI
- Ion. Chamb.-Si-CsI(Tl) for 3o?45o
- Ion. Chamb.-CsI for 45olt?176o
2
The INDRA data base on multifragmentation
3
INDRA Identification de Noyaux et Détection avec
Résolutions Accrues
- Experimental case
- 5 campaigns of measurements (4 in Ganil-France
1 at GSI-Germany) - versatile detector coupling with first Chimera
ring, with other telescopes for time of flight
measurements, - position sensitive detectors for crystal
blocking experiments (fission of SHE),
spectrometer (Vamos) - Symmetric-asymmetric systems, reverse direct
kinematic, Ebeam5A.MeV to 1A.GeV - Well suited for central collisions of symmetric
systems but some drawbacks for asymmetric one
when - C.M. velocity is small (especially at backward
angles) - Physical results
- physical analysis on vaporization of QP,
fission, central collisions of fusion-like
sources, deexcitation - studies for a large range of hot nuclei, mid
rapidity emission, neck formation - intra-event correlations b estimation, reaction
plane determination, calorimetry, reconstruction
of hot - primary fragments
- Phase transition temperature, heat capacity,
?scaling, scaling laws, bimodality, spinodal
decomposition - Reaction mechanism mid-rapidity, neck, fusion
like event, fission, momentum transfer, fragment
formation, - isospin equilibration, chronometer of the
process - Deexcitation of hot nuclei from evaporation to
vaporization, fission and multifragmentation of
any kind - Comparison with model statistical as well as
dynamical
4
GARFIELD General ARray for Fragment
Identification and for
Emitted Light particles in Dissipative collisions
- General characteristics
- High granularity (400 ?E-E telescopes ? ?4o-150o
) - Low energy thresholds (ionization chambers as
?E) - A and Z identification (1Z8) up to ? ?90o
- Digital electronics for pulse-shape
discrimination
- The Garfield drift chamber
- 180 Double Stage E (CsI(Tl)) - DE (MSGC)
telescopes - Angular coverage (30o 85o 95o 150o)
- Charge resolution from p to heavy-ions, with
DZ/Z1/28 - Angular resolution (??1 ?f 7.5 )
Side detectors from Multics
5
GARFIELD General ARray for Fragment
Identification and for
Emitted Light particles in Dissipative collisions
32S 58Ni at 11 AMeV
Multi fragment production Fizika B12 (2003) 39
32S 58,64Ni at 14.5 AMeV
Evaporation residue Mass
identification Correlation
functions Phase transition in strongly
interacting matter, Prague 2004 Nucl. Phys. (to
be published) 5th Italy-Japan Symposium Naples
2004 (to be published)
6
Multics Miniball
Multics telescopes
Beam hole
87 of 4p
- Multics
- 3 layers telescopes
- Si-500 µm position sensitive
- CsI(Tl) photodiode
- 3o?lab25o
- Energy threshold 1.5 A.MeV
- Z identification up to the beam charge
- Miniball
- 171 phoswich detectors
- 25o?lab160o
- Energy threshold 2-3-4 A.MeV for Z3-10-18
- Z20 identification
- isotopic identification for Z1-2
7
Results of the MulticsMiniball experiment
Nucl. Phys. A 724 (2003) 455
Nucl. Phys. A 650 (1999) 329
Phys. Lett. B 473 (2000) 219 Nucl. Phys. A 699
(2002) 795) Nucl. Phys. A 734 (2004) 512
- Au Liquid-Gas
- ??????????????????? ????????????
- ??????????????? ????????????
- e?c ????????????eV
Phase transition in strongly interacting matter,
Prague 2004 Nucl. Phys. (to be published)
5th Italy-Japan Symposium Naples 2004 (to be
published)
8
FAZIA Four p A-Z Indentification Array
half forward part
- 6000 telescopes Si-ntd/Si-ntd/CsI
- possibility of coupling with other detectors
like spectrometer, gas chamber, neutron detectors - 1000 hits/s
- maximum multiplicity 150/event
- complete Z identification and A up to 30
- digital electronics for pulse-shape
discrimination