Method 2a: KVL - PowerPoint PPT Presentation
1 / 10
Title:
Method 2a: KVL
Description:
2. Define either clockwise or counterclockwise direction as voltage drop ... resistor: if current direction is the same as the loop direction, - other wise) ... – PowerPoint PPT presentation
Number of Views:95
Avg rating:3.0/5.0
Title: Method 2a: KVL
1
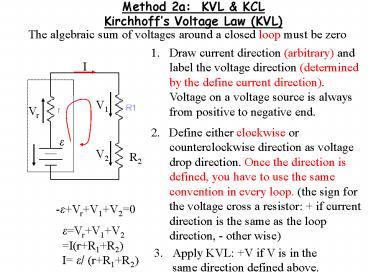
Method 2a KVL KCL Kirchhoffs Voltage Law
(KVL)
The algebraic sum of voltages around a closed
loop must be zero
- Draw current direction (arbitrary) and label the
voltage direction (determined by the define
current direction). Voltage on a voltage source
is always from positive to negative end.
2. Define either clockwise or counterclockwise
direction as voltage drop direction. Once the
direction is defined, you have to use the same
convention in every loop. (the sign for the
voltage cross a resistor if current direction
is the same as the loop direction, - other wise)
-eVrV1V20
eVrV1V2 I(rR1R2) I e/ (rR1R2)
- Apply KVL V if V is in the same direction
defined above.
2
Kirchhoffs Voltage Law multiloop
- Draw current direction (arbitrary) and label the
voltage direction (determined by the define
current direction.
- Define either clockwise or counterclockwise
direction as positive voltage direction. Once the
direction is defined, you have to use the same
convention in every loop.
- Apply KVL V if V is in the same direction
defined above.
-eVrV1V20 -V2V30
eIrIR1I2R2 -V2V30
3
Kirchhoffs Current Law (KCL)
The algebraic sum of current at a node must be
zero IinIout
eIrIR1I2R2 (2) V3-V20
(3)
II2I3 (1)
e3 V, r1 W, R13 W, R25 W, R310 W I - I2
- I3 0 (4) 4I 5I2 0I3 3 (5) 0I
5I210I3 0 (6)
Cramers Rule Append. A
4
Last note on KVL KCL
If solutions to currents or voltages are
negative, they mean the real directions are
opposite to what you have defined!
5
Sample Problem
Find magnitude and direction of currents
6
Method 2b Mesh Analysis
- Example 2 meshes
- Step 1 Assignment of mesh currents (clockwise)
(mesh is a loop that does not contain other
loop). - Step 2 Apply KVL to each mesh
- The so-called self-resistance is the effective
resistance of the resistors in series within a
mesh. The mutual resistance is the resistance
that the mesh has in common with the neighboring
mesh. - To write the mesh equation in standard form,
evaluate the self-resistance, then multiply by
the mesh current. This will have units of
voltage. - From that, subtract the product of the mutual
resistance and the current from the neighboring
mesh for each such neighbor. - Equate the result above to the driving voltage,
taken to be positive if its polarity tends to
push current in the same direction as the
assigned mesh current.
e1 - e2
(R1R2)I1
Mesh 1
- R2I2
Mesh 2
(R2R3)I2
- R2I1
e2 e3
Step 3 Solve currents
7
Sample circuit 3 meshes
Mesh 1
Mesh
2
Mesh 3
8
Detailed Mesh Analysis Example
Find currents in each branches Step 1 Replace
any combination of resistors in series or
parallel with their equivalent resistance. Step
2 Choose clockwise mesh currents for each mesh
and label accordingly. Step 3 Write the mesh
equation for each mesh. Left mesh
11 I1 - 6 I2 9 Right mesh
- 6 I1 18 I2 9 Here I suppress the "k" for
each resistor the final currents will be in
milliamps. Step 4 Solve the equations
Solution I1 4/3 mA 1.33 mA I2 17/18
mA 0.94 mA
9
Mesh Analysis with Current Source
10
Example with mixed sources mesh analysis
- Identify mesh currents and label accordingly.
- Write the mesh equations
- Mesh 1 I1 -2
- mesh 2 -4I1 8I2 -4I4 12
- Mesh 3 8I3 -12
- Mesh 4 -4I1 4I2 6I4 10
I1 - 2.0 AI2 1.5 AI3 - 1.5 AI4 2.0 A
Ix I2 - I3 Ix 3.0 A