1' dia - PowerPoint PPT Presentation
1' dia
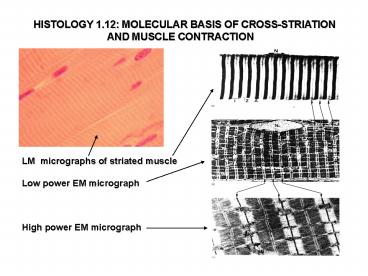
LM micrographs of striated muscle. Low power EM micrograph. High power EM micrograph ... Arrangement of the myosin molecules within the filament (250-350 ... – PowerPoint PPT presentation
Title: 1' dia
1
HISTOLOGY 1.12 MOLECULAR BASIS OF
CROSS-STRIATION AND MUSCLE CONTRACTION
LM micrographs of striated muscle Low power EM
micrograph High power EM micrograph
2
Structure of the myofibrils
Sarcomer 2,2-2,5 mm
Myofilaments Thick (myosin) Thin (actin)
3
Myofilaments 1. The thin filament
6-9 nm
F-actin (made up by several G-actins)
Further proteins involved
4
Myofilaments 2. The thick filament
Building block the myosin molecule
L-chains
H-chains
Heads
Arrangement of the myosin molecules within the
filament (250-350 molecule/filament)
Bipolar structure
Myosin heads
12- 15 nm
5
The sliding filament mechanism of the
contraction
6
Cytoskeletal proteins within the sarcomer
7
The sarcoplasmic reticulum and the transverse
tubular system (T-system)
Sarcoplasmic reticulum Longitudinal
tubules Terminal cisterns
triads
Triad T-tubule two adjacent terminal cisterns
of the sarcoplasmic reticulum
PowerShow.com is a leading presentation sharing website. It has millions of presentations already uploaded and available with 1,000s more being uploaded by its users every day. Whatever your area of interest, here you’ll be able to find and view presentations you’ll love and possibly download. And, best of all, it is completely free and easy to use.
You might even have a presentation you’d like to share with others. If so, just upload it to PowerShow.com. We’ll convert it to an HTML5 slideshow that includes all the media types you’ve already added: audio, video, music, pictures, animations and transition effects. Then you can share it with your target audience as well as PowerShow.com’s millions of monthly visitors. And, again, it’s all free.
About the Developers
PowerShow.com is brought to you by CrystalGraphics, the award-winning developer and market-leading publisher of rich-media enhancement products for presentations. Our product offerings include millions of PowerPoint templates, diagrams, animated 3D characters and more.