Lecture 16: Properties of the Fourier Transform - PowerPoint PPT Presentation
Lecture 16: Properties of the Fourier Transform
in the frequency domain, it amounts to nothing more than. shifting in frequency. ... Application of Fourier to LTI systems. Remarks: ... – PowerPoint PPT presentation
Title: Lecture 16: Properties of the Fourier Transform
1
Lecture 16 Properties of the Fourier Transform
2
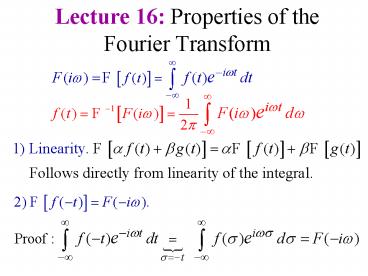
(No Transcript)
3
(No Transcript)
4
(No Transcript)
5
(No Transcript)
6
In the time domain, this is amplitude modulation
(AM)
Baseband signal (e.g. audio).
In the time domain, modulation is complicated.
However in the frequency domain, it amounts to
nothing more than shifting in frequency.
7
(No Transcript)
8
10) Parseval relation
Integral square is preserved between time and
frequency.
9
Application of Fourier to LTI systems
- Remarks
- The Fourier transform takes convolutions into
products. - Similar to Laplace, but here we do not require
causality, - and x(t) could be nonzero for all time.
10
(No Transcript)
11
Interpretation system response to a sinusoid
12
Application amplitude demodulation
y(t)
Demodulator
x(t)
v(t)
Q What operation can we do to make the received
signal v(t) equal to the message x(t)?
13
Solution another modulation lowpass filtering
14
Fourier and Convolution
PowerShow.com is a leading presentation sharing website. It has millions of presentations already uploaded and available with 1,000s more being uploaded by its users every day. Whatever your area of interest, here you’ll be able to find and view presentations you’ll love and possibly download. And, best of all, it is completely free and easy to use.
You might even have a presentation you’d like to share with others. If so, just upload it to PowerShow.com. We’ll convert it to an HTML5 slideshow that includes all the media types you’ve already added: audio, video, music, pictures, animations and transition effects. Then you can share it with your target audience as well as PowerShow.com’s millions of monthly visitors. And, again, it’s all free.
About the Developers
PowerShow.com is brought to you by CrystalGraphics, the award-winning developer and market-leading publisher of rich-media enhancement products for presentations. Our product offerings include millions of PowerPoint templates, diagrams, animated 3D characters and more.