Primate origin - PowerPoint PPT Presentation
1 / 21
Title:
Primate origin
Description:
Primate. origin. K-T boundary marked by an asteroid impact. Evidence, ... Primate Origins. Challenge is to minimize speculation on things that do not fossilize. ... – PowerPoint PPT presentation
Number of Views:68
Avg rating:3.0/5.0
Title: Primate origin
1
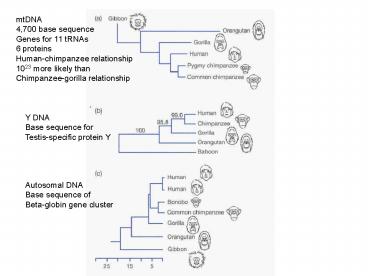
mtDNA 4,700 base sequence Genes for 11 tRNAs 6
proteins Human-chimpanzee relationship 1023 more
likely than Chimpanzee-gorilla relationship
Y DNA Base sequence for Testis-specific protein Y
Autosomal DNA Base sequence of Beta-globin gene
cluster
2
(No Transcript)
3
(No Transcript)
4
(No Transcript)
5
Primate origin
K-T boundary
6
- K-T boundary marked by an asteroid impact
- Evidence, early 1980s
Cretaceous / Tertiary boundary
95 localities
Iridium rare on earth common in asteroids
meteorites
7
Impact crater locatednd asteroid 10-15 km
dia 65 mya
8
Primate Origins
- Challenge is to minimize speculation on things
that do not fossilize. - We live in the Cenozoic Era (past 65 m.y.)
- Earliest primate fossils date from c. 55 mya
Eocene Epoch - Originated from primate-like mammals
9
Continental drift
Origin
10
An Eocene mammal
An Eocene primate
Post-orbital bar
11
A common problem
- How many species are represented?
- E.g., lack of information on ranges of variation
12
Anthropoid Origins
Aegyptopithecus Basal to the ape- Old World
monkey separation ca. 33 mya
13
A transitional? group
- Genus Proconsul
- Many species
- Mixture of monkey-like and ape-like
characteristics - 23 mya
- Africa
the only extant tailless monkey is
the Barbary Ape.
14
Sivapithecus 14 mya Asia
15
Adjusting branch-points an ongoing process e.g.,
fossil dated at 7 mya
East Africa, Rift Valley system major hominid
sites
16
Rocky Mountain News - July 11, 2002
17
Rocky Mountain News - July 11, 2002
Sahelanthropus tchadensis
18
Hominin or ape?Skull characteristics
Foramen magnum position
19
Early Hominids
- Sahelanthropus tchadensis (6-7 mya)
- Bipedalism suggested by foramen magnum position
- Orrorin tugenensis (6 mya)
- Definitive evidence from femur of bipedalism
- Ardipithecus ramidus (5.8 mya)
- Australopithecus anamensis (4.2 mya)
- basal to other australopithecines)
- Derivative australopithecines divided into
gracile and robust species groups - Paranthropus
20
(No Transcript)
21
(No Transcript)