Nucleotides - PowerPoint PPT Presentation
Title:
Nucleotides
Description:
Nucleotides Specification: State that deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) is a polynucleotide, usually double stranded, made up of nucleotides containing the bases adenine (A ... – PowerPoint PPT presentation
Number of Views:27
Avg rating:3.0/5.0
Title: Nucleotides
1
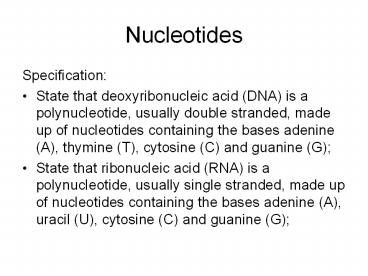
Nucleotides
- Specification
- State that deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) is a
polynucleotide, usually double stranded, made up
of nucleotides containing the bases adenine (A),
thymine (T), cytosine (C) and guanine (G) - State that ribonucleic acid (RNA) is a
polynucleotide, usually single stranded, made up
of nucleotides containing the bases adenine (A),
uracil (U), cytosine (C) and guanine (G)
2
Polynucleotides
- Nucelic acids come in two forms DNA and RNA
- They hold all the information to make proteins
which is what all living things are made up of - Almost all of the DNA in a eukaryotic cell is
found in the nucleus - RNA is found in 3 different forms
3
Monomers
- The monomer of all nucleic acids (DNA and RNA) is
called a nucleotide - Each single nucleotide is made up of one
phosphate group, one sugar molecule, one organic
nitrogenous base - All three sub-units are joined by covalent bonds
P
Base
S
4
Nucleotides
- There are five different nucleotides called A, T,
C, G and U - The phosphate group in all nucleotides is the
same - The sugar molecule is a 5 carbon sugar either
deoxyribose in DNA or Ribose in RNA - The 5 possible bases are adenine A, Thymine T,
Guanine G, Cytosine C, and Uracil U
5
Joining nucleotides together
- A condensation reaction occurs between the
phosphate group of one nucleotide and the sugar
of another nucleotide - Repeating the bonding gives a long chain of
nucleotides - This forms the backbone of the molecule
6
(No Transcript)
7
Nucleotides to Nucleic Acids
- Chains of nucleic acids bond together to make
nucleic acids - Only nucleic acids carrying the same sugar
(ribose or deoxyribose) can be binded together - This makes nucleic acids either RNA or DNA
8
Too Much Nucleic Acid
- Uric acid is produced when excess purines
(Adenine and Guanine) are broken down in the
liver - It is excreted in urine
- Some people have too much uric acid in the blood
which is turned into crystals that are deposited
at the joints making them swollen (this is called
gout)
9
Task
- Using Cambridge Biology p124- 126, outline the
structure of DNA- you must include the key words
in bold in the paragraphs - When finished, complete the DNA modelling task
titled Have Your DNA and Eat It - Then complete the questions on the printed slide-
they will be peer assessed next lesson!
10
Questions
- Outline how DNA replicates
- Define the term anti-parallel
- Write down the complimentary strand sequence for
DNA and RNA- ATTAGGCTAT - If a DNA is 20 Thymine, what percentage of each
of the other types would it contain? - What type of disease can result from DNA copying
going wrong?
11
Questions
- Outline how DNA replicates semiconservatively-
the double helix is untwisted, the hydrogen bonds
between the bases are broken apart and unzip to
expose the bases, free DNA nucleotides are
hydrogen bonded onto the exposed bases according
to the base pairing rule A-T G-C, covalent bonds
are formed between the phosphate of one
nucleotide and the sugar of the next to seal the
backbone - Define the term anti-parallel prallel, but with
chains running in opposite directions - Write down the complimentary strand sequence for
DNA and RNA- ATTAGGCTAT DNA TAATCCGATA RNA
UAAUCCGAUA - If a DNA is 20 Thymine, what percentage of each
of the other types would it contain? 20 Adenine,
30 Cytosine, 30 Guanine - What type of disease can result from DNA copying
going wrong? Cancer may occur if DNA is not
copied properly
12
(No Transcript)
13
DNA- Information Storage
- DNA is a long chain polymer of nucleotide
monomers - The polymer is called a polynucleotide
- A DNA molecule forms when two polynucleotide
molecules come together forming a ladder like
structure
14
Hydrogen Bonding and Base Pairing
- The two DNA strands run parallel to each other
- The term anti-parallel is used because the
strands run in opposite directions to one another - The chains are always the same distance apart
because bases pair up in a specific way. - When a purine appears on one side, a pyrimidine
appears on the other - Adenine always pairs with thymine, and guanine
always pairs with cytosine - As the strands come together, hydrogen bonds form
between the bases - The base pairing is described as complimentary
15
Double Helix
- In a complete DNA molecule, the anti-parallel
chains twist, like twisting a rope ladder, to
form the final structure known as a double helix
16
Making Copies
- DNA replication takes place during interphase of
the cell cycle - It is the process that creates identical sister
chromatids
17
Making Copies
- In order to make a new copy of a DNA molecule
- The double helix is untwisted
- Hydrogen bonds between the bases are broken apart
to unzip the DNA and expose the bases - Free DNA nucleotides are hydrogen bonded onto the
exposed bases according to the base pairing rules
(A-T and C-G) - Covalent bonds are formed between the phosphate
of one nucleotide and the sugar of the next to
seal the backbone.
18
Making Copies
- This continues all the way along the molecule
until two new DNA molecules (double helices) are
formed, each is an exact replica of the original
DNA molecule because of the base pairing rules. - This process is known as semi-conservative
replication. - Each new DNA molecule consists of one conserved
strand plus one newly built strand
19
How is the Structure of DNA related to its
function?
- The sequence of bases acts as information storage
in the form of codes to build proteins - The molecules are long to store more information
- The base pairing means that complementary strands
of information can be replicated - The double helix gives the molecule stability
- Hydrogen bonds allow for easy unzipping for
copying and reading information
20
Reading the Instructions
- RNA
- Contains the sugar ribose
- Has uracil instead of thymine
- Usually single stranded
- Exists in 3 forms
21
Base Pairing of RNA
- Contains the purines adenine and guanin and the
pyrimidines cytosine and uracil - Base pairing of A-U and G-C occur
22
Three forms of RNA
- mRNA messenger RNA is made as a strand that is
complimentary to one strand of the DNA molecule
(the template strand) it is therefore a copy of
the other DNA strand as it contains the opposite
bases plus Uracil - rRNA is ribosomal RNA and is found in ribosomes-
it decodes mRNA into amino acids - tRNA transfer RNA carries amino acids to the
ribosomes where they are bonded together to form
polypeptides
Task Now complete the Protein Synthesis sentence
sort
23
(No Transcript)
24
Sentence Sort What are the instructions for?
- The sequence of bases on DNA make up codes for
particular proteins- they code for the sequence
of amino acids - The sequence coding for a particular protein (a
gene) can be exposed by splitting the hydrogen
bonds in the particular area of the DNA molecule - RNA nucleotides from a complementary strand
(mRNA) which is a copy of the DNA coding strand
(or gene) - The mRNA peels away from the DNA and leaves the
nucleus through a nuclear pore - The mRNA attaches to a ribosome
- The tRNA molecules bring amino acids to the
ribosome in the correct order, according to the
base sequence of the mRNA - The amino acids are joined by peptide bonds to
give a protein with a specific primary structure
which can then give rise to the secondary and
tertiary shape of the protein
25
Task
- Complete a windows movie explaining the steps
involved in protein synthesis - Success Criteria
- No more than one minute
- Include scientific information and diagrams
- Explain simply the terms transcription and
translation
26
Questions
- Explain why the MRNA strand produced in the
nucleus is complementary to the template strand,
and a copy of the coding strand - If a DNA template strand code reads ATTCGCGTTAAT,
what would the complementary MRNA strand read? - Suggest why MRNA is less stable than DNA, and
explain why this is a necessary feature of MRNA - Make a table to compare and contrast the
structure of DNA with that of RNA
27
Questions
- Explain why the MRNA strand produced in the
nucleus is complementary to the template strand,
and a copy of the coding strand complementary RNA
nucleotides are lined up against each base on the
template strand, producing a complementary
strand. As base pairing rules apply, this lining
up will be the same as it appears on the coding
strand- apart from U in RNA replacing T in DNA - If a DNA template strand code reads ATTCGCGTTAAT,
what would the complementary MRNA strand read?
UAAGCGCAAUUA - Suggest why MRNA is less stable than DNA, and
explain why this is a necessary feature of MRNA
RNA is single stranded and so less stable, as
nucleotide bases are exposed and not paired. It
also contains uracil instead of thymine, which
may contribute to the lower stability of the
molecule. mRNA results in the production of
proteins. If the cell is to control protein
production, the disintegration of mRNA stops too
much of a certain protein being made, and so
allows for regulation of the protein levels in a
cell - Make a table to compare and contrast the
structure of DNA with that of RNA