I' The DNA Double Helix - PowerPoint PPT Presentation
1 / 29
Title: I' The DNA Double Helix
1
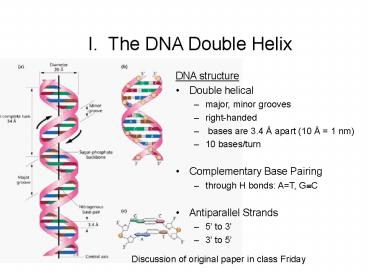
I. The DNA Double Helix
- DNA structure
- Double helical
- major, minor grooves
- right-handed
- bases are 3.4 Å apart (10 Å 1 nm)
- 10 bases/turn
- Complementary Base Pairing
- through H bonds AT, G?C
- Antiparallel Strands
- 5 to 3
- 3 to 5
Discussion of original paper in class Friday
2
Right- and Left-handed DNA
3
Base-Pairing in DNA
AT
G?C
4
Structure of RNA
Sugar ribose, not 2-deoxyribose Bases
uracil, not thymine Organization
single-stranded, not double-stranded
How is genetic information in DNA expressed?
First step is transcribing RNA from DNA -
single-stranded RNA is generated using DNA as a
template
5
Reading DNA Strands
Single strand of DNA 5-AGCATTCG-3 3-TCGTAAGC-
5 Complementary strand of above, usually written
5 to 3 5-CGAATGCT-3 Double-stranded
fragment is written 5-AGCATTCG-3 3-TCGTAAGC-5
6
Learning Check
The sequence of the dwarf gene in garden peas is
as follows
5 - A G C T A C G T -3 3 - T C G A T G C A -5
Write the RNA sequence transcribed from the top
strand of DNA, 5- 3.
7
II. Analytical analyses of nucleic acids
Denaturation/Renaturation
Determining the Tm allows for an estimate of the
base composition of a DNA sample
1
2
Which DNA has higher GC content and why?
8
Nucleic Acid Hybridization
Transcription of 1 strand of DNA 3
G G T T G G G C C A A C C C
A C G C T T G C G A
2
1
U U U G C G C
T T T G C G C A AA C G C G
3
Add RNA to denatured DNA allow to hybridize
Heat - denature
A C G C T T G C G A
G G T T G G G
G G T T G G G C C A A C C C
A C G C T
2
1
C C A A C C C
T G C G A
U U U G C G C
Hybrid
T T T G C G C
A A A C G C G
3
A AA C G C G
9
Nucleic Acid Gel Electrophoresis
10
What makes nucleic acids acidic?
Base Pairing Rules
11
Points to know about DNA structure
- Note how many hydrogen bonds are in the base
pairing - If 2, then the pair is AT
- If 3, then the pair is GC
- Recall that A and G are purines with 2 rings,
while T and C are pyrimidines with 1 ring also T
has a CH3 group on its ring.
12
III. DNA Replication
How is genetic information replicated accurately
at each cell division? Could each strand of the
DNA double helix act as a template for the
complementary strand?
At each cell division, 109 base pairs are
replicated. If error rate is 10-6 , then 3000
errors/cell division - TOO many.
13
DNA Replication is Semiconservative
14
Other Theoretical Possibilities
15
Separation of Nucleic Acids by CeCl Gradient
Centrifugation
16
Meselson-Stahl Experiment
DNA Labeling with 15N
Subsequent Generations Labeled with 14N
Cesium Chloride Gradient Banding
17
Expected Results From Conservative or Dispersive
Reproduction
If Conservative Two bands, heavy and light, in
1st and 2nd generations
If Dispersive, one smeary band in 1st and
2nd generations
18
Expected Results if Semiconservative
These results were obtained. A related
experiment was performed in plants (Fig. 12.5)
19
Bacterial DNA Replication begins at a Single
Origin and Proceeds Bidirectionally
Origin of Replication
20
DNA Polymerase I can Synthesize DNA
- Arthur Kornberg et al. (1957) discovered the
enzyme in E. coli - Requires template DNA strand, primer, MgCl2, and
4 dNTPs - Monomers added 5 to 3
21
5 to 3 Addition of Monomers
22
DNA polymerases I, II and III
- pol I
- most abundant (400/cell)
- RNA primer removal
- pol II
- unknown abundance
- DNA repair?
- pol III
- low abundance (15/cell)
- DNA replication
23
Problems of DNA Synthesis
- Unwinding
- Tension must be relieved
- Priming
- Antiparallel strands
- RNA primer removal
- Backbone joining
- Proofreading
24
Steps of DNA Synthesis
- Denaturation and Unwinding
- Priming and Initiation
- Continuous and Discontinuous Synthesis
- Including Proofreading and Error Correction
- Removal of Primer
- Ligation of nicks in backbone
25
Steps of DNA SynthesisDenaturation and
Unwinding of DNA
- DnaA, DnaB, DnaC proteins are helicases which
bind origin and separate strands - Single-strand binding protein (SSBP) keeps
strands apart - DNA gyrase, a type of DNA topoisomerase, cuts to
relax supercoiling
26
Initiation of Synthesis
- RNA Primase makes RNA primer on DNA template
- DNA Polymerase III extends primer with DNA
- DNA Polymerase I removes RNA primer, replaces
with DNA
27
Directionality of DNA synthesis
28
Proofreading occurs as polymerase moves along
if incorrect base pairing, base is removed and
replaced.
29
Continuous and Discontinuous Synthesis
- Continuous
- on Leading Strand.
- Discontinuous
- on Lagging Strand
- creates Okazaki
- fragments.
- DNA ligase joins
- nicks in backbone.