DNA,%20RNA,%20and%20PROTEIN%20SYNTHESIS - PowerPoint PPT Presentation
Title:
DNA,%20RNA,%20and%20PROTEIN%20SYNTHESIS
Description:
DNA is a molecule that carries the instructions for how to make an organism DNA, genome, instructions, blueprint, chromosomes, genes All MEAN DNA!!!! – PowerPoint PPT presentation
Number of Views:192
Avg rating:3.0/5.0
Title: DNA,%20RNA,%20and%20PROTEIN%20SYNTHESIS
1
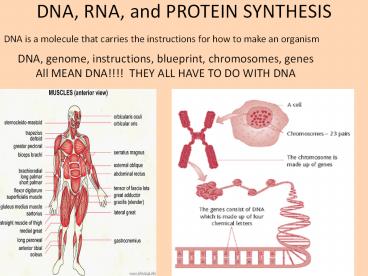
DNA, RNA, and PROTEIN SYNTHESIS
DNA is a molecule that carries the instructions
for how to make an organism
DNA, genome, instructions, blueprint,
chromosomes, genes All MEAN DNA!!!! THEY ALL
HAVE TO DO WITH DNA
2
- DNA is organized into bundles called CHROMOSOMES.
Humans have 46 chromosomes - CHROMOSOMES have segments on them that code for
certain qualities (eye color, hair color) - The segments or areas are called GENES and they
code for all of an organisms TRAITS or
characteristics
3
- Gametes sperm/egg
- DNA is found in, and cannot leave the nucleus
(too big).
- The types of cells that carry information from
parents to offspring are called gametes. - Gametes are sex cells, sperm and egg.
- Humans and their cells have 46 chromosomes.
- 23 come from mom (egg), 23 come from dad (sperm).
- Since it has such important information it is
guarded in the nucleus of cells. - DNA carries information from parents to offspring
(kids)
4
- DNA (DeoxyRiboNucleic Acid) is made up of
nucleotides that repeat. - Each nucleotide is made of 3 parts
1.Nitrogen base
2.Deoxyribose sugar group Dewithout Oxy
Oxygen Ribosesugar
3.Phosphate group
5
There are 4 nitrogen basesAdenine (A), Cytosine
(C), Thymine (T), and Guanine (G)The sequence
of nitrogenous bases determines the traits that
will appear. The sequence of codons (3 letter
codes)
6
DeoxyribonucleicAcid (DNA) the Double Helix
The sugar and phosphate groups make up the
outside part of the ladder. The base pairs make
up the inside steps of the ladder.
7
Watson Crick were the first to successfully
show the structure of DNA. (Double Helix)
According to Chargaffs rule A pairs to TC
pairs to G The bases are found in a 11 ratio
adenine bonds with thymine
guanine bonds with cytosine
The two halves of the DNA strand are called
complementary because they pair together
8
Reasons why cells divide
Mitosis/Cell Division
- The cell becomes too big.
- The larger a cell becomes, the more demands the
cell places on its DNA - Also, a larger cell has more trouble keeping up
with the needs of the cell - Cells will continually divide during the growth
of an organism.
9
The process by which cells divide
- Before a cell divides it must make an exact
copy or replica of its DNA. - The copy or replica of DNA is made during the
S-Phase of Interphse. - After Interphase is complete the cell can divide
by Mitosis. - Cell Division or Mitosis allows organisms to grow
larger while cells remain small
10
Replication First the DNA unzips
11
Next new nucleotides are added to each side until
2 identical strands are made (remember A to T and
C to G)
12
Replication / Mitosis
Mitosis results in 2 identical daughter
cells Each has all 46 chromosomes An exact copy
of the original
13
Protein Synthesis
- 1. DNA is the code the instructions for how
to make PROTEINS, the main structures of the
body. - 2. DNA is in the nucleus of the cell, but
PROTEINS are made in the cytoplasm by RIBOSOMES. - Remember, DNA cannot leave the nucleus.
- We need a way to get the DNA out of the nucleus
to the ribosomes. Protein synthesis happens in 2
steps.
14
Protein Synthesis Step 1 Transcription
- The DNA strand in the nucleus separates.
- In order to get BIG DNA out of the nucleus we
must re-write it as a messenger (RNA). - This RNA acts as a messenger (mRNA) that carries
the instructions out of the nucleus to the
ribosome - When the genetic code (DNA) is copied/re-written
to messenger RNA, mRNA this is called
transcription.
15
Rna (ribo-nucleic-acid)
- RNA has Ribose as its sugar instead of
Deoxyribose - It is Single Stranded, meaning that it is only
half of the ladder (double helix) - RNA has Uracil as a base instead of Thymine
- Guanine Cytosine
- Adenine Uracil (no T, Thymine in RNA)
16
Step 2 Translation
We translate 3 letter codons into an amino acid
chain.
- mRNA attaches to a RIBOSOME
- Every 3 letter group on a strand of mRNA is a
CODON which codes for an AMINO ACID - - amino acids are the building blocks of
proteins (20 of them 9 are essential)
AMINO ACIDS
3. The RIBOSOME reads the mRNA, then transfer
RNA (tRNA) brings the correct AMINO ACID to form
the protein chain
3 letter CODONS on mRNA tell what the AMINO ACID
will be
17
What 2 amino acids do these CODONS code for?
18
The Central Dogma
19
Mitosis vs. Meiosis
Meiosis results in 4 genetically Different
haploid cells. Haploid means half The Gametes
(sex cells) have ½ the info
Mitosis results in 2 identical daughter
cells Each has all 46 chromosomes
20
(No Transcript)
21
(No Transcript)
22
NameDate Biologyclass pd.Write about DNA.
What is DNA?What is the structure and parts of
DNA?How is DNA used to make proteins in protein
synthesis