Input - PowerPoint PPT Presentation
1 / 23
Title:
Input
Description:
Input Hardware. Devices that translate data into a form the computer can process ... Output Hardware ... Input Hardware. Keyboards: convert letters, numbers, ... – PowerPoint PPT presentation
Number of Views:192
Avg rating:3.0/5.0
Title: Input
1
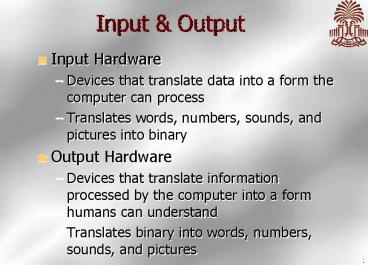
Input Output
- Input Hardware
- Devices that translate data into a form the
computer can process - Translates words, numbers, sounds, and pictures
into binary - Output Hardware
- Devices that translate information processed by
the computer into a form humans can understand - Translates binary into words, numbers, sounds,
and pictures
2
Input Hardware
- Keyboards convert letters, numbers, and
characters into electrical signals - How keyboards work
- You press a key
- This interrupts the current flowing through the
circuits - It compares the input with the (x,y) character
map for the language on the keyboards ROM chip - A character is stored in 16-byte keyboard memory
buffer - Sent to PC as a data stream via wire or wireless
connection - OS interprets its own operating-system-specific
commands and sends the others to the application
for interpretation
3
Input Hardware
- Keyboard types
- 104 108 keys desktop standard
- 85 keys for laptops
- Wired
- Connect to CPU via a serial or USB port
- Wireless use either
- IR (infrared) technology
- Radio Frequency (RF) technology
- Require line of sight to connect
- Virtual keyboard used with PDAs and smartphones
4
Input Hardware Pointing Devices
- Control the position of the cursor or pointer in
the screen and allow the user to select options
displayed on the screen - Mouse is the principal pointing tool
- Rolls around on a mouse pad or desktop and
directs a pointer on the computers display
screen - Ball inside the mouse touches the desktop and
rolls around - Two internal rollers touch the ball
- One roller picks up motion in x (up), the other
in y (down) - The rollers turn a shaft that spins a disk that
breaks an LED signal into light pulses that are
seen by an infrared sensor - Processor chip in mouse reads the pulses and
turns it into binary
5
Input Hardware Pointing Devices
- Other types of Mice
- Optical Mouse
- Trackball
- Touchpad
- Pointing Stick
6
Input Hardware Pointing Devices
- Touch Screens
- A video display screen sensitized to receive
input from a finger - Problems touch screens that show a display that
is not precisely aligned with the input - Pen input
- Use a pen-like stylus for input rather than
typing on a keyboard - Use handwriting recognition to translate
handwriting into data
7
Input Hardware
- Light Pen
- A light-sensitive pen-like device that uses a
wired connection to a computer terminal - Bring the pen to the desired point on the display
screen and press a button to identify the screen
location - Less crude than a touch screen
8
Input HardwareScanning Reading Devices
- Source Data Entry devices create machine-readable
data and feed it directly into the computer - Scanners
- Use light-sensing equipment to translate images
of text, drawings, and photos into digital form - Image scanners are used in electronic imaging
- Resolution refers to the image sharpness,
measured in dots per inch (dpi) higher the
better quality
9
Input HardwareBar-Code Readers
- Photoelectric (optical) scanners that translate
bar code symbols into digital code - The digital code is then sent to a computer
- The computer looks up the item and displays its
name and pricing info
10
Input HardwareMark Recognition Readers
- Mark Recognition readers
- MICR Magnetic-ink character recognition
- Uses special magnetized inks
- Must be read by a special scanner that reads this
ink - Used by Banks to read checks
- OMR Optical mark recognition
- Uses a special scanner that reads bubble marks
- Used in standardized tests like the ACT and SAT
- OCR Optical character recognition
- Converts scanned text from images (pictures of
the text) to an editable text format - You use this to read in non-computer documents
where you dont have the source files
11
Input HardwareFax Machines
- Facsimile Transmission Machines scan an image
and send it as electronic signals over telephone
lines to a receiving fax, which prints out the
image on paper - Dedicated fax machine
- Is a stand-alone unit that only sends and
receives faxed documents - Fax modem
- Is a circuit board installed in the PC
- Is a modem that can send and receive faxes
- Can send documents directly from your word
processor to a fax machine - Saves you printing out the document, then faxing
it
12
Input HardwareWebcams and Video-input Cards
- Webcams
- Video cameras attached to a computer to record
live moving images into a computer - Require special software, usually included with
the camera - Full-motion video card
- Can convert analog to digital signals at rates up
to 30 frames per second - Typically used to capture TV signals and convert
to digital video
13
Input HardwareSpeech-Recognition Systems
- Uses a microphone or telephone as an input
device. Converts a persons speech into digital
signals by comparing against 200,000 or so stored
patterns. - Used in places where people need their hands free
warehouses, car radios, stock exchange trades - Helpful for people with visual or physical
disabilities that prevent them from using other
input devices - Still not easy enough to use to substitute for
the mouse/keyboard for fast document processing
14
Input HardwareRFID Tags
- Radio-frequency ID tags are based on an
identifying tag with a microchip containing
specific code numbers - Scanners use radio waves to read them and match
the codes to a database - Enables items to be tracked without physical
contact - Drivers put RFID tags in cars to automatically
pay tolls - FDA is tagging certain drugs with RFID to avoid
counterfeits - Carmakers are using it for car electronic keyless
entry - RFID tags are implanted under skin of pets to aid
in recovery and identification when they get lost
15
Input HardwareBiometrics
- The science of measuring individual body
characteristics, then using them to identify a
person through a fingerprint, hand, eye, or
facial characteristic - Becoming a big business as more companies become
concerned about security - Makes identity theft much more difficult when
records are identified by biometrics as well as
passwords
16
Output Hardware
- Softcopy
- Data that is shown on a display screen or is in
audio or voice form exists electronically - Non-Physical (Virtual) representation
- Hardcopy
- Printed and film output
- Physical (Real) representation
17
Output HardwareDisplay Screens
- Making a good choice when choosing a display
- Dot pitch (dp) is the amount of space between
adjacent pixels (picture elements) on screen - The closer the pixels, the crisper the image
- Get .25 dp or better
- Resolution refers to the image sharpness
- The more pixels the better the resolution
- Expressed in dots per inch (dpi)
- Color depth or bit depth is the number of bits
stored in a dot - The higher the number the more true the colors
- 24-bit color depth is better than 8-bit color
depth - Refresh rate is the number of times per second
the pixels are recharged a higher rate gives
less flicker
18
Output HardwareMonitors
- Cathode Ray Tube (CRT) is a vacuum tube used in a
computer or terminal display screen - Flat panel displays are made of 2 plates of glass
separated by a layer of liquid crystals that line
up to transmit or block light - Preferable to CRTs because they take up less room
on the desktop - Latency problems make them less desirable for
watching video (but the technology is advancing
quickly)
19
Output HardwarePrinters
- Impact Printers
- Laser Printers
- Inkjet Printers
- Thermal Printers
- Form characters or images by striking a print
hammer or wheel against an ink ribbon - Dot matrix printers
- Use drums and toner like in photocopiers
- Expensive
- Produce crisp, professional pages
- Spray ink from 4 nozzles at high speed
- Quiet, inexpensive color printers
- Often less precise than laser printers
- Low to medium resolution printers that use
thermal paper that darkens in time
20
I/O Quality of Life Health Ergonomics
- PCs impact health
- Overuse injuries and repetitive stress injuries
- Result when muscle groups are forced through
fast, repetitive motions - May effect data-entry operators who average
15,000 keystrokes an hour - May effect PC users whose monitor, keyboard, and
workstation are not arranged for comfort - Carpal tunnel syndrome is caused by pressure on
the median nerve in the wrist, caused by short
repetitive movement - Computer vision syndrome is eyestrain, headaches,
and double vision caused by improper use of
computer display screens
21
I/O Quality of Life Health Ergonomics
- Ergonomics is the methodology of designing a
workplace to make working conditions and
equipment safer and more efficient - Keyboards must be placed at the correct height
depending on each workers size - Monitor refresh rates must be fast enough to
avoid eyestrain - Monitor heights must be correct for comfortable
viewing - Sound-muffling should be used for loud printers
to reduce workplace noise - Wrist rests may help avoid carpal tunnel syndrome
22
Future of Input and Output
- This is a fruitful area for research, including
- Intelligent sensors
- More data input from remote locations
- More source data automation
- Input help for the disabled
- More sophisticated touch devices
- Better speech recognition
- Improved digital cameras
- Gesture recognition
23
Future of Input and Output
- This is a fruitful area for research, including
- Pattern-recognition and biometric devices
- Brainwave devices
- Better and cheaper display screens
- Improved video on PCs
- 3-Dimensional output
- Miniaturization for improved data transfer speeds
to I/O devices