Voet%20 - PowerPoint PPT Presentation
Title:
Voet%20
Description:
Voet & Voet, Biochemistry. Intracellular Pathogens ... Voet & Voet, Biochemistry. Acquired immunity depends on non-specific protein-peptide interactions ... – PowerPoint PPT presentation
Number of Views:906
Avg rating:3.0/5.0
Title: Voet%20
1
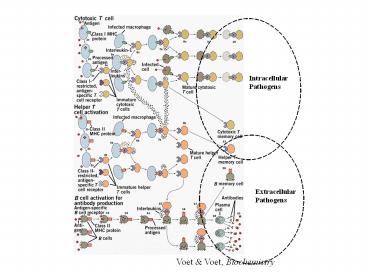
Intracellular Pathogens
Extracellular Pathogens
Voet Voet, Biochemistry
2
Acquired immunity depends on many specific
protein-protein interactions
Part 1 Antigen Specific
- Antibody - Antigen
- Cytotoxic T-cell receptor - MHC class I
protein/peptide complex - Helper T-cell receptor - MHC class II
protein/peptide complex
3
Voet Voet, Biochemistry
4
Acquired immunity depends on non-specific
protein-peptide interactions
- MHC class II - peptides generated in the
endosome/lysosome (antigens of extracellular
origin) recognized by helper T cells - MHC class I - peptides generated in the cytoplasm
(antigens of intracellular origin) recognized by
cytotoxic T cells
5
Antigen Processing and Presentation to Helper
T-cell
Antigen Internalization e.g., via IgG receptor
Endosome/Lysosome
6
Peptides bind to MHC Class II molecules in a
common polyproline II conformation
Jardetzky et al., PNAS 93 734-738 (1996)
7
Antigen Recognition by Antibodies (Ab) and T-cell
Receptors (TCR)
Ab - Ag
TCR MHC/peptide
- Surface area 2x750 Å2
- gt 50 hydrophobic
- 1-2 H-bonds
- Epitope discontinuous in antigen (Ag) sequence
- Surface area 2x1000 Å2
- Ag peptide contributes only 40 of surface area
- Epitope continuous in Ag sequence
- Otherwise similar to Ab - Ag recognition
8
Peptide Binding by Major Histocompatibility
Complex (MHC) Antigen-presenting Proteins
MHC I
MHC II
- Peptides of intracellular origin
- Peptides 9-10 residues long
- Deep pockets bind peptide sidechains
- Deep pockets bind peptide N- and C-termini
- Peptides of extracellular origin
- Peptides 15 residues or longer
- Shallow pockets bind peptide sidechains
- Peptide termini free
- H-bonds to peptide backbone
9
Acquired immunity depends on many specific
protein-peptide interactions
Part 2 Transport/Immunoregulatory (a few
examples)
- IgG receptor - IgG
- MHC class II protein - CD4
- MHC class I protein - CD8
- IL-2 - CD25
- TNF - TNF receptor
10
The efficiency of antigen processing may control
the T-cell cytokine profile for a given epitope
by the size of its immunological synapse
Grakoui et al., Science 285 221-227 (1999)