Multi-Platform Data Access - PowerPoint PPT Presentation
1 / 66
Title:
Multi-Platform Data Access
Description:
Developed by JavaSoft, a subsidiary of Sun Microsoft ... Components are delimited by semi colons. CursorLocation: Client side or server side ... – PowerPoint PPT presentation
Number of Views:203
Avg rating:3.0/5.0
Title: Multi-Platform Data Access
1
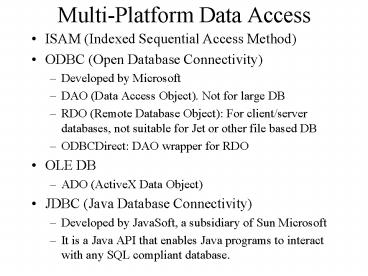
Multi-Platform Data Access
- ISAM (Indexed Sequential Access Method)
- ODBC (Open Database Connectivity)
- Developed by Microsoft
- DAO (Data Access Object). Not for large DB
- RDO (Remote Database Object) For client/server
databases, not suitable for Jet or other file
based DB - ODBCDirect DAO wrapper for RDO
- OLE DB
- ADO (ActiveX Data Object)
- JDBC (Java Database Connectivity)
- Developed by JavaSoft, a subsidiary of Sun
Microsoft - It is a Java API that enables Java programs to
interact with any SQL compliant database.
2
Reasons Move from DAO to ADO
- Universal data access requirement ODBC - OLE DB
- Software Size
- DAO350.DLL 569KB
- MSJET35.DLL 1,022KB
- RDO 368KB
- ODBCDirect
- ADO2.0 342KB
- Difficult to maintain three packages (DAO,RDO,
ODBCDirect)
3
Using ODBC
- DSN (Data Source Name)
- User DSN Only be recognized locally
- System DSN Recognized by the network
- ODBC Driver
- Server/Database
- ODBC Administrator
- Examples DSN to Access and SQL Server
4
OLE DB Providers
- See Page. 94
5
ADO Object Hierarchy
- Connection Specify the OLE DB data provider,
establish a connection to the data source. - Command A set of functions to handle queries,
usually SQL statements or stored procedures, or a
direct link to a table. - Recordset Host the result of a command object,
or the link (pointer) to a table.
6
Visual Basic Database Tools I
- Data Environment Designer Create database
objects based on ADO. Available for Data Project - Data View Window Access the linked database.
Available in Menu ViewData View Window - Report Designer Build up reports
7
Visual Basic Database Tools II
- Query Designer A graphic tool that uses Drag and
Drop to create a view or query. Available in Data
View WindowViewDesign Database Designer A
graphic designer for Database Diagrams. Available
in Data View Window Database Diagrams - SQL Editor A editor to create Views or Stored
Procedures. Available in Data View WindowStored
ProceduresDesign - T-SQL Debugger Debug the stored procedures.
Available in Data View WindowStored
ProceduresDebug
8
Data Binding
- Data Source Produces the data
- Data Consumer Consume (read, edit) data
- Data binding is a technique to link a data source
with a data consumer - Data Controls The object link to a table
- Data Control Using DAO
- RemoteData Control Using RDO
- ADODC Using ADO
- Bound Controls The object bounded to a field
9
Form Controls in VB
- Intrinsic Controls Deal with simple data
bounding. Exist intrinsically in all VB
environments - Check Box, Combo Box, List, Text Box, etc.
- ActiveX Bound Controls True COM objects. Deal
with complex data bounding. Needed to be call in
as necessary (Menu ViewComponents) - DataList, DataCombo,MaskEdit, etc.
10
Example of Data Binding Using ADODC
- Create an AODDC
- Configure the properties
- note the data link related properties can be
available in popup menu rather than in the
property window - Provider
- Data Source
- Row Source
- Create text boxes bounded to one of the fields
11
Useful VB Examples I
- Convert the inputted letters into upper case
- Key issue ASCII code order and KeyAscii variable
- Use DateTimePicker Control
- Drop down calendar format (.UpDownTrue)
- Spin box format (.UpDownFalse)
- See example \VB6DB\Chapter08\Controls\Project1
12
Useful VB Examples II
- Use StatusBar to show message
- See example \VB6DB\Chapter08\Validate\Project1
- Some other useful external controls
- ProgressBar Provides dynamic progress status for
long time processing.
13
Data Environment Designer
- The methods to enable DED
- Add DED in Standard Exe Project MenuMore
ActiveX DesignerData Environment Designer - Create a Data Project
- Three object blocks in DED
- Connection
- Command
- Chile Command (for Child tables)
14
Using DED at Run Time I
- Each Command object in DED will have a Recordset
object with rs plus the commands name - Three ways to reference in DED
- DEDName.Recordsets(n).Fields(nstring).value
- DEDName. RecordsetName.Fields(nstring).value
- DEDName. RecordsetName(nstring).value
- See example in \VB6DB\Chapter09\DataEnv\proj
15
Using DED at Run Time II
- Open a command
- Open the recordset applying to the command
- Set a recordset pointing to the result of command
- Open the command with parameters
- NO OPEN method for command object
- Add a ADODC to navigate
- Set ADODC1.RecordsetDE1.rsCommand1
- Navigate DE object DE.rsCommand1.MoveNext
- Reuse DED File (.dsr)
16
ADO Programming
- ADO Object Vs DED object
- DED object is easier to configure at design time
- ADO object is more flexible in run time
17
Connect Object I
- Object Hierarchy
- Command, Recordset, Errors
- Important Properties
- ConnectionString data provider, data location,
user name, password. Components are delimited by
semi colons. - CursorLocation Client side or server side
- Mode Permission for the data
- State State of the object
18
Connect Object II
- Important Methods
- Close Close the connection
- Open Open the connection
- Execute Execute a command object
- BeginTrans, CommitTrans, RollbackTrans For
transaction operations - Examples of Opening a connection
- \VB6DB\Chapter12\ConnectionDemo\Project1
19
Connect Object III
- Analyzing Errors
- Property
- Count The number of errors in current object
- Method
- Clear Clear errors for current object
- Each error in Errors collection is an object
- Description
- Source
- Number
- Example ..\Chapter12\ConnectionDemo\Project1
WriteError()
20
Command Object I
- Primary Purpose
- Run a non record returning execution
- Run a stored procedure with parameters
- Important Properties
- ActiveConnection An opened connection object
- CommandType Type of command
- CommandText Command content
- State Command state
- ActiveConnection and CommandText are basic info
- Important Collections
- Parameters Contains all parameters of the
command object
21
Command Object II
- Important Methods
- CreateParameter Create a new parameter
- Set parameter command.CreateParameter (Name,
Type, Direction, Size, Value) - Execute Execute the command
- Set recordset command.Execute( RecordsAffected,
Parameters, Options ) - command.Execute RecordsAffected, Parameters,
Options
22
Command Object III
- Execute a command with parameters
- Method 1 Creation and Assign are in three steps
- CreateParameter, Append, Assign
- Method 2 Creation and Assign are in one steps
- CreateParameter (Name, Type, Direction, Size,
Value) - Method 3 Parameters info are entered with
Execute method The parameter values must be put
in an Array() function to convert into a variant - Command linked to a stored procedure has the
ability to retrieve the parameter definition - obj.Parameters.Refresh
- obj.Parameters(_at_ParaName).Valuevalue
23
Command Object Examples
- Execute Command SQL Statement with Parameter,
and Put Into a Recordset - ..\Chapter13\..\Command3_click()
- Execute Command DDL SQL with no record returning
- ..\Chapter13\..\Command5_click()
- Execute Command Stored procedure with parameter
- ..\Chapter13\..\Command6_click()
- Notice the parameter setting
24
Recordset Object I
- Recordset is the real object that contains the
data retrieved from database - Important properties
- ActiveConnection
- CursorLocation Client/Server
- CursorType Read only/Visibility to the change
- LockType
- RecordCount The number of records retrieved
- BOF/EOF/NoMatch
- Bookmark/AbsolutionPosition
25
Recordset Object II
- Important Methods
- Open Open a recordset
- recordset.Open Source, ActiveConnection,
CursorType, LockType, Options - AddNew Add a new record
- recordset.AddNew FieldList, Values
- Delete Delete the specified records
- recordset.Delete AffectRecords
- Update Save changes made to current record
- recordset.Update Fields, Values
26
Recordset Object III
- Ways to create a recordset
- Use a command as the Source Normally for calling
stored procedures with parameters - Use an Active Connection and assign the other
properties Cursor Location, Type and Lock - Use Connection Execute method For read-only,
forward-only, highest performance. - ..\Chapter14\RecordsetDemo\Project1
27
Recordset Object IV
- Methods to search a record
- Find Searches for the record that satisfies the
specified criteria. - Find (criteria, SkipRows, searchDirection, start)
- FindFirst LastNextPrevious
- FindFirst criteria
- For best performance, the criteria should be in
either the form "field value"or "field LIKE
prefix" (e.g., LIKE DATA) where field is an
indexed field - Use NoMatch or EOF property to determine whether
the search is successful.
28
Recordset Object V
- Methods to move around
- Move Move specific number of records
- recordset.Move NumRecords, Start
- MoveFirstLastNextPrevious
- Moves to the first, last, next, or previous
record - Bookmark Vs AbsolutePosition
- AbsolutePosition is a sequential number, may
change when records are added or deleted - Bookmark is a unique value, not affected
29
Analyze Example (p. 5860)
- DataGrid properties
- DataSource, AllowAddNew, AllowDelete
- Connection
- Provider (property) Open (method)
- Recordset properties
- ActiveConnection, CursorType, LockType
- Method Open
30
Analyze Example (p. 5860)
- Dim (Private) As New
- DoEvents Yields execution so that the operating
system can process other events. - With End With Executes a series of statements
on a single object or a user-defined type.
31
Add Navigation Buttons
- Make the data control to be public to all
procedures in the form - rstNwind navigation methods
32
The Factors Related to Permission of Changing
Table
- Properties
- AllowNew, AllowDelete, AllowUpdate
- LockType ReadOnly, Optimistic, BatchOptimistic
- Integrity rules in relationship
33
LockType Options
- ReadOnly Default. Read-onlyyou cannot alter the
data. - Pessimistic locking records at the data source
immediately upon editing. - Optimistic locking records only when you call the
Update method. - BatchOptimistic required for batch update mode as
opposed to immediate update mode.
34
Important Properties, Methods and Events
Connection Object
- Properties
- ConnectionString Info about opening a connection
- CursorLocation Sets or returns the location of
the cursor engine (Client or Server side) - DefaultDatabase Indicates the default database
for a Connection object. - Provider Indicates the name of the provider for
a Connection object
35
Connection Property Example 1
- ' Open a connection using the Microsoft ODBC
provider. Set cnn1 New ADODB.Connection
cnn1.ConnectionString "driverSQL Server"
_ "serverbigsmileuidsapwdpwd" cnn1.Open
strCnn cnn1.DefaultDatabase "pubs"
36
Important Properties, Methods and Events
Connection Object
- Methods
- Close Close the connection
- Execute Executes the specified query, SQL
statement, stored procedure, or provider-specific
text. The result is forward only. - Open Open a connection.
37
Methods Syntax
- For a nonrow-returning command string
- connection.Execute CommandText, RecordsAffected,
Options - For a row-returning command string
- Set recordset connection.Execute (CommandText,
RecordsAffected, Options) - Open
- connection.Open ConnectionString, UserID,
Password, OpenOptions
38
Examples of Openning a Connection
- Use example on P. 59
- Use full strConnection argument after Open method
(P. 77) - Use all connection information as properties (P.
78) - Advantage
39
Important Properties, Methods and Events
Connection Object
- Events. To use the events, the connection must be
declared by - Private (Dim) WithEvents cnnName As
ADODB.Connection - The usage of events (P. 83)
40
Error Collection and Objects
- Example of using error collection and objects
41
Important Properties, Methods and Events Command
Object
42
Important Recordset Object Properties
- ActiveConnection
- BOF, EOF
- Bookmark
- CursorLocation
- CursorType, LockType
- DataMember, DataSource
- EditMode
- Filter
43
Important Recordset Object Properties
- RecordCount
- Sort
- Source
- adCmdTable generating an internal SELECT query
- adCmdTableDirect retrieve rows directly from
table - State About the whole object open or close
- Status About current record (Add/Update/Delete)
44
Important Recordset Object Methods
- AddNew two methods, with or without parameters
(see example) - Close, Open, Requery (CloseOpen)
- Delete
- Find (further study about CRITERIA)
- Move, MoveFirst,
- Methods to mover the pointer
- Supports
- Update
45
Batch Update
- Ste LockType to adLockBatchOptimistic
- Set CursorType adOpenKeySet or adOpenStatic
- Set CursorLocation to adUseClient
- Do the editint (Change, AddNew, Delete)
- Call UpdateBatch method to apply the batch update
46
Manipulating Data Object with VBA
- Using DED Easy to use, code less
- Using VBA
- Reduce number of active connections
- Easy to customize and user oriented
- Better readability
47
Independence of ADO Objects
- Three objects Connection, Command and Recordset
can be independently exist. Whereas DAO has to
follow hierarchy (See exp. on p138) - Default CursorLocation using DED it is
adUseClient, using VBA it is adUseServer - Example on p. 147-152 (..\Chapter03\adoOpen.vbp)
provides five methods to create a recordset
48
File for Recordset
- Why need a file to store temp recordset data
without utilize a local database engine. - File is in ADTG (Advanced Data TableGram) format
with extension .rst - Use recordset method Save to save a the data to a
file - rstName.Save FileName
49
Using Array() to Add/Edit Rows
- Returns a Variant containing an array
- Syntax Array(arglist)
- The required arglist is a comma-delimited list of
values that are assigned to the elements of the
array contained within the Variant. - Exp.1 Example in Help system
- Exp.2 rstOrders.AddNew Array(CustomerID,
OrderDate), Array(VINET,6/6/1998) - Exp3 rstOrders.Update Array(CustomerID,
OrderDate), Array(VINET,6/6/1998)
50
Fields Collection and Methods of Referencing a
Field
- A Fields collection contains all the Field
objects of a Recordset object. - rstName.Fields(FieldName)
- rstName.Fields(CustomerID)
- rstName.Fields(strName) strNameCustomerID
- rstName.Fields(index) index0,1,2,...
- rstName!FieldName
- rstName!CustomerID
- rstName(FieldName)
- rstName(CustomerID)
- rstName(strName) strNameCustomerID
51
Close Recordset When not is Use
- Minimize active connection
- Most properties are read only when in use
- Note if try to close a recordset not previously
opened, an error occurs.
52
Methods to Create a Recordset
- Example - Five methods to create a recordset (P.
147-152, ..\Chapter03\adoOpen.vbp) - Create a recordset directly
- Open a recordset on a Connection object
- Open a Recordset on a Command object
- Open a Recordset from File
- Open a Recordset from Array
53
Usage of Data Objects
- Connection to build up a connection to a
database which can be used to host the different
Command and Recordset objects - Command normally only used to execute non-record
return commands such as INSERT, DELETE, UPDATE,
and so on) - Recordset real connection to a table or a data
object
54
Execute and Open Methods
- Execute method is used to create a forward only
recordset, which is faster and more efficient. - Open method open a recordset point to a data
object for read/write purposes.
55
ADO Find Method
- Syntax of Find method (ADO)
- rstName.Find criteria, SkipRows, searchDirection,
start - Syntax of Find???? Methods (DAO)
- rstName.Find???? Criteria
- Changes from Find???? To Find
- Criteria is limited, not a SQL Where clause
- Single field
- Common comparison orpertors
- More parameters
- Example code (p. 154-156)
56
Argument Values for Find????
- Find???? Skip SearchDirection Start
- FindFirst 0 adSearchForward
adBookmarkFirst - FindLast 0 adSearchBackward
adBookmarkLast - FindNext 1 adSearchForward
adBookmarkCurrent - FindPrev 1 adSearchBackward
adBookmarkLast
57
Move Methods
- Move and Move???? Both available in ADO
- Syntax for Move method
- recordset.Move NumRecords, Start
- Syntax for Move???? Methods
- recordset.Move????
58
Find, Seek and SELECT
- ADO doesnt have Seek method
- Find method cant automatically use the built
indexes - Use SELECT, which can apply the built-in query
optimizer to find appropriate index, to extract
the data - Use Find method to do refine work on a small,
local data set
59
Hierarchical Data View
- Two kinds of View
- Tree view (Maximum number of levels 4-5)
- Form/Subform view
- MSHFlexGrid configuration
- Bands (levels)
- Visible Fields
- Difference of Left click and Right click drag
60
Grouping and Aggregate
- Add Grouping command
- Add Aggregate function
- Example on p. 162 (Tree like hierarchy)
- Example of subform hierarchy
- Example of grouping and aggregate
61
Data Bound Controls
- Single-bound controls
- TextBox, CheckBox
- Example on p. 192 (VBAEntry.vbp)
- Complex-bound controls
- DataGrid, DataList, DataRepeater, MSFlexGrid
62
Complex-bound controls
- DataGrid Properties
- General Enabling AllowAddNew, AllowDelete
- Keyboard Enabling Tab navigation
- Columns Link each column to a field
- Retrieve and Clear fields
- Layout behavior of each column
- Format value display format
63
Complex-bound controls
- Data bounded DataCombo and DataList
- Compare with ComboBox and ListBox
- Two methods to bound to a data source
- Use DED
- Use VBA (Run-time assign RowSource, RowMember,
cant use AddItem) - Analyze example on p. 198
- Style property DropDownList vs DropDownCombo
64
Complex-bound controls
- MSFFlexGrid
- Doesnt have Columns, Format property sections
- Use Format() to format the cells (code on p. 200)
65
Complex-bound controls
- DataList
- Code on p. 203
- Filter property (faster than create a new
recordset) - DoEvent force an operation execute after another
one
66
Useful Topics
- Ways to link to a table
- Command object recordset (rsCommandName)
- ADODB.Recordset
- Enabling Addition
- Change property EOFAction
- Reuse DED designer files
- Add .dsr file into current project