Ecological Pyramids - PowerPoint PPT Presentation
1 / 5
Title:
Ecological Pyramids
Description:
-Define the following population interactions and relate them to real world examples: neutralism, ammensalism, mutualism, commensalism, and parasitism. – PowerPoint PPT presentation
Number of Views:91
Avg rating:3.0/5.0
Title: Ecological Pyramids
1
(No Transcript)
2
(No Transcript)
3
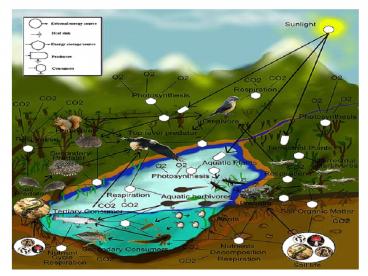
Ecological Pyramids Graphical models of the
quantitative differences that exist between
trophic levels of a single ecosystem.
They can be pyramids of numbers, biomass, or
productivity.
4
Ecology Students will be able to -Define the term trophic level and identify and explain trophic levels in food chains and food webs. -Explain the principles of pyramids or numbers, pyramids of biomass and pyramids of productivity, and construct such pyramids from given data. -Discuss how the pyramid structure affects the functioning of an ecosystem. -Define the following population interactions and relate them to real world examples neutralism, ammensalism, mutualism, commensalism, and parasitism.
Bioaccumulation the accumulation of
substances, such as pesticides, or other
organic chemicals in an organism.
5
Population interactions occur in 5 main ways.
Interspecific competition When members of two or
more species interact to
gain access to the same limited resources.
Ex. Food, light, or space.
Predation - occurs when a member of one species
feeds directly on all or part of a member of
another species.
Parasitism occurs when one organism feeds on the
body of, or the energy is used by, another
organism, usually by living on or in the host.
Mutualism is an interaction that benefits both
species by providing each with food, shelter, or
some other resource.
Commensalism an interaction that benefits one
species but has little, or no, effect on the
other.