Cell Structure and Function - PowerPoint PPT Presentation
1 / 22
Title:
Cell Structure and Function
Description:
Cell Structure and Function It wasn t until the 1600s that scientists were able to use microscopes to observe living things. Cells In 1665, Robert Hooke observed ... – PowerPoint PPT presentation
Number of Views:249
Avg rating:3.0/5.0
Title: Cell Structure and Function
1
Cell Structure and Function
2
Discovery of Cells
- It wasnt until the 1600s that scientists were
able to use microscopes to observe living things.
3
Cells
- In 1665, Robert Hooke observed cork cells under
the microscope. He called them cells. - This is a drawing he made of the cork cells.
4
More Cork Cells
- Here is what cork cells look like in a modern
microscope with special lighting.
5
Leeuwenhoeks Microscope
- Anton Van Leeuwenhoek used a single-lens
microscope to view pond water and other things. - Here is his microscope.
6
Cell Theory
- The Cell Theory States
- All living things are made of cells.
- Cells are the basic units of structure and
function in living things. - New cells are produced from existing cells.
- It wasnt long before scientists realized that
all living things were made up of cells. This
discovery brought about the formulation of the
cell theory.
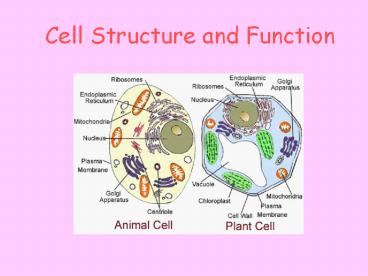
7
Types of Cells
- Cells are classified as prokaryotic or
eukaryotic. - Prokaryotic cells have genetic material that is
not inside a nucleus. No nucleus. - Eukaryotic cells have genetic materials in a
nucleus. (true nucleus)
8
Cell Structures
- Cells contain small structures called organelles.
Each organelle has a specific job it performs in
the cell.
9
1.The Nucleus
- This is a membrane-bound structure that contains
the DNA. DNA is the genetic material that is the
code for making proteins. - EX Chief Executive Officer (CEO)
10
2. Chromatin
- The DNA and surrounding protein.
- EX blueprints to factory product
11
3. Ribosomes
- Ribosomes are protein assembly organelles.
- Ribosomes can be free in the cytoplasm or on
the endoplasmic reticulum. - EX Workers in the assembly line
12
4. Endoplasmic Reticulum
- The endoplasmic reticulum is the site where
lipids of the cell membrane are assembled, along
with proteins and other materials. - It can contain ribosomes and be Rough ER or have
no ribosomes and be Smooth ER - EX Assembly line (where workers do their work)
13
5. Golgi Apparatus
- The golgi apparatus modifies, sorts, and packages
proteins and other materials from the ER. - EX Finishing / packaging department
14
6. Lysosomes
- Lysosomes are small organelles that contain
enzymes. - These enzymes breakdown lipids, carbohydrates,
and proteins into small molecules that can be
used by the cell. - Lysosomes also remove junk and clutter in the
cell. - EX Maintenance crew
15
7. Vacuoles
- Vacuoles are storage organelles.They store water,
salts, proteins, etc. - Plants have a large vacuole that helps plants
support leaves and stems. - EX storage/supply room
16
8. Mitochondria
- The mitochondria is the organelle that converts
chemical energy from food into ATP to power cell
processes. - EX Power plant
17
9. Chloroplasts
- Chloroplasts are organelles that capture sunlight
energy and convert it into chemical energy in a
process known as photosynthesis. - EX Power plant
18
10. Cell Membrane
- The cell or plasma membrane surrounds the cell
and regulates what enters and exits the cell. - Ex shipping and receiving department of a
factory.
19
11. Cytoplasm
- The cytoplasm (cytosol) is the fluid outside the
nucleus. It contains the organelles. - EX factory floor where most of the products are
assembled, finished, and shipped.
20
12. Centrioles
- Centrioles are cylindrical bundles of
microtubules that function in cell reproduction.
21
Division of Labor
- In multicellular organisms, each cell has a
specialized task to keep the organism alive. - Specialized cells include blood, muscle, heart
cells, etc. - Living things are organized into the following
hierarchy. - 1. Cells
- 2. Tissues
- 3. Organs
- 4. Organ Systems
- 5. Organisms
22
Levels of Organization
- This chart shows the increasing complexity of
organization from tiny molecules to the whole
biosphere.
1. Macromolecules
2. Organelles
3. Cells
4. Tissues
5. Organs
6. Organisms
7. Populations
8. Communities
9. Ecosystems
10. Biosphere