Cognitive Dimensions - PowerPoint PPT Presentation
Title:
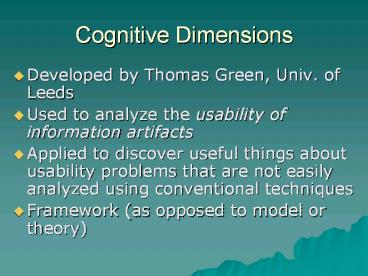
Cognitive Dimensions
Description:
Cognitive Dimensions ... such as Music Dance Programming languages And ... Comments in programming languages Pop-up boxes for icons Well-designed icons ... – PowerPoint PPT presentation
Number of Views:133
Avg rating:3.0/5.0
Title: Cognitive Dimensions
1
Cognitive Dimensions
- Developed by Thomas Green, Univ. of Leeds
- Used to analyze the usability of information
artifacts - Applied to discover useful things about usability
problems that are not easily analyzed using
conventional techniques - Framework (as opposed to model or theory)
2
Cognitive Dimensions (2)
- Focused on notations, such as
- Music
- Dance
- Programming languages
- And on information handling devices, such as
- Spreadsheets
- Database query systems
- Word-processors
- VCRs and DVD players
- Cell phones
3
Cognitive Dimensions (3)
- Gives descriptions of aspects, attributes, or
ways that a user thinks about a system, called
dimensions - The 14 dimensions follow
4
Viscosity
- Resistance to change
- Fixed mental model
- Hard-coded structure
- Examples
- Technical literature, with cross-references and
section headings (because introducing a new
section requires many changes to cross-references)
5
Visibility
- Ability to view components easily
- Non-encapsulation
- Examples
6
Premature Commitment
- Constraints on order of operations
- Noun/verb
- Verb/noun
- Syntax of operations
- Examples
- Declarations required before problem analysis
7
Hidden Dependencies
- Important links between entities are not visible
- Examples
- class hierarchies
- HTML links
- spreadsheet cells
8
Role-Expressiveness
- Purpose of an entity is readily inferred (or
obvious) - Uniform vs. distinguishing appearance of objects
- Examples
9
Error-Proneness
- Notations (or actions) invite mistakes and the
system gives little protection - Examples
10
Abstraction
- Types and availability of abstraction mechanisms
- Examples
11
Secondary Notation
- Extra information in means other than formal
syntax - Examples
- Comments in programming languages
- Pop-up boxes for icons
- Well-designed icons
12
Closeness of Mapping
- Closeness of representation to domain
- Examples
13
Consistency
- Similar semantics are expressed in similar
syntactic forms - Examples
14
Diffuseness
- Verbosity of language
- Examples
15
Hard Mental Operations
- High demand on cognitive resources
- Examples
16
Provisionality
- Degree of commitment to actions or marks
- Examples
17
Progressive Evaluation
- Work to date can be checked at any time
- Examples
18
Summary
- Viscosity
- Visibility
- Premature commitment
- Hidden dependencies
- Role expressiveness
- Error proneness
- Abstraction
- Secondary notation
- Closeness of mapping
- Consistency
- Diffuseness
- Hard mental operations
- Provisionality
- Progressive evaluation
19
Supplementary Material
- Cognitive Dimensions of Notations website
www.cl.cam.ac.uk/afb21/CognitiveDimensions - 10th Anniversary CD of Notations Workshop
www.cl.cam.ac.uk/afb21/CognitiveDimensions/worksh
op2005/index.html
20
Supplementary Material (2)
- Sally Fincher, Patterns in HCI
- Marian Petre, Expert Design Reasoning