Eastern%20Europe - PowerPoint PPT Presentation
Title: Eastern%20Europe
1
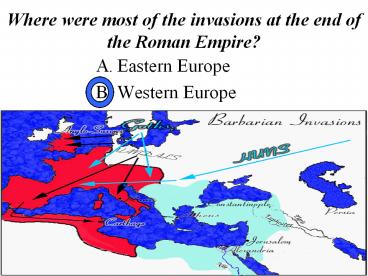
Where were most of the invasions at the end of
the Roman Empire?
- Eastern Europe
- Western Europe
2
Who moved the capital of the Roman Empire to
Byzantium (he also legalized Christianity)?
- Justinian
- Augustus
- Constantine
3
What protected Constantinople from invasions?
- It wasnt worth invading
- It was built on a peninsula fortified with land
and sea walls
4
What was another reason Constantinople was chosen
as the capital?
- It was a crossroads of trade
- It was closer to invasions
- It was home to the Pope
5
Under which emperor did the Byzantine Empire grow
to its largest size?
- Alexis
- Justinian
6
What was Justinians longest lasting legacy?
- His code of laws that were later adopted by
Western European Monarchs - His conquests in Western Europe and North Africa
7
Byzantine achievements in art and architecture
include
- A. Humanistic paintings, sculptures and
architecture - B. Pyramids and murals
- C. Icons, mosaics, and domed buildings
8
What was one of the buildings erected under the
rule of Justinian?
- Pantheon
- Parthenon
- Hagia Sophia
9
What are icons?
- Religious images meant to inspire spirituality
- Realistic images of daily life
10
What are Mosaics?
- A. images made up of bits of glass, ceramic, and
stone - B. tapestries made of woven cloth
11
What type of culture flourished in the Byzantine
Empire?
- Islamic culture
- Far Eastern culture
- Greco-Roman culture
12
What was the first schism in the Christian Church?
- Sunni and Shia
- Roman Catholic and Protestant
- Roman Catholic and Eastern Orthodox
13
All of the following are reasons the split
between the Eastern and Western Churches EXCEPT
- A. The West accepted the Pope as leader of the
church, the East did not. - B. The West used Latin in the liturgy the East
used Greek. - C. Priests could not marry in the West, but they
could in the East. - D. They believed in Baptism in the West, but not
in the East.
14
How did Byzantine monks preserve Greco-Roman
culture?
- A.They kept Greek and Roman manuscripts in
airtight chambers. - B. They copied and illustrated ancient Greek and
Roman works.
15
Who called for a crusade to regain control of the
Holy Land?
- Pope Urban
- Pope Gregory
- Pope Benedict
16
Who attacked, burned, and looted Constantinople
in 1204?
- Muslim Turks
- Christian Crusaders
- Mongol Warriors
17
What effect did the Crusades have on the
Byzantine Empire?
- It strengthened it
- It weakened it
- It completely destroyed it.
18
Who conquered the Byzantine Empire in 1453?
- Magyars
- Mongols
- OttomanTurks
19
- Constantinople became capital of the Ottoman
Empire. Today Constantinople is
- Moscow, Russia
- Istanbul, Turkey
- Rome, Italy
20
How did the Byzantine Empire influence Russia and
Eastern Europe?
- Trade and missionaries
- Conquest
- Mass Media
21
All of the following are ways that the Byzantine
Empire influenced Russia EXCEPT?
- A. Orthodox Christianity
- B. Art and architecture (icons and onion domes).
- C. Arabic Alphabet
- D. Trade routes between the Black and Baltic Seas
22
- Who adapted Greek alphabet to Slavic languages of
Eastern Europe and Russia?
- St. Cyril
- St. Patrick
- St. Nicholas
23
What type of writing is this?
- Cuneiform
- Arabic
- Cyrillic
24
Which invaders came from Central Asia, invaded
Eastern and Western Europe, and settled in
Hungary?
- Magyars
- Vikings
- Ottomans
25
Which invaders settled in Russia and helped
establish trade routes between the Black and
Baltic Seas?
- Germanics
- Vikings
- Ottomans
26
Where did the Vikings come from?
- Central Asia
- Germanic Areas
- Scandinavia
27
Which invaders created an empire and ruled Russia
for over 200 years?
- Magyars
- Mongols
- Ottomans
28
Who freed Moscow from the Mongolsand united and
expanded the Russian nation?
- Ivan the Terrible
- Ivan the Great
- C. Catherine the Great
29
What title did Ivan the Great take?
- emperor
- tsar
- king
30
How did Ivan and other Russian tsars rule?
- They allowed nobles complete control over their
lands - They only bowed to the Pope
- They ruled with absolute authority
31
Who was the protector of the Russian Orthodox
Church?
- the tsar
- the patriarch
- the caliph












![[READ] The Eastern Front: A History of the Great War, 1914-1918 PowerPoint PPT Presentation](https://s3.amazonaws.com/images.powershow.com/10134795.th0.jpg?_=20241108013)

















