Cell Theory and Microscope Technology - PowerPoint PPT Presentation
1 / 17
Title:
Cell Theory and Microscope Technology
Description:
All cells contain cytoplasm, an organized internal region where energy conversions, protein synthesis, movements of cell parts, and other required activities proceed. – PowerPoint PPT presentation
Number of Views:114
Avg rating:3.0/5.0
Title: Cell Theory and Microscope Technology
1
Cell Theory and Microscope Technology
2
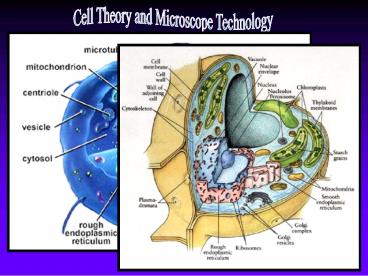
All cells contain cytoplasm, an organized
internal region where energy conversions, protein
synthesis, movements of cell parts, and other
required activities proceed.
Prokaryotic cells contain DNA, but no nucleus.
Eukaryotic cells contain DNA within a
membrane-bound nucleus.
Instead, prokaryotes contain a region within
called a nucleoid where the genetic material can
be found.
3
Early Scientists
Before microscopes were invented, people thought
diseases were caused by curses and supernatural
spirits.
With the invention and use of the microscope,
scientists discovered a new world filled with
previously unknown organisms.
4
The First Microscopes
The first microscope that Anton van Leeuwenhoek
used in the 1600s was considered a simple light
microscope, and amazingly enough was able to
magnify things as much as 300x!
Anton van Leeuwenhoek (1632-1723).
5
What we used to think...
Abiogenesis, or the origins of life, is now more
precisely known as spontaneous generation.
- Before the microscope, it was believed that
living organisms were generated by decaying
organic substances. According to Aristotle it
was a readily observable that - aphids arise from the dew which falls on plants
- fleas from putrid matter
- mice from dirty hay
- crocodiles from rotting
- logs at the bottom
- of bodies of water
6
The first step was taken by the Italian Francesco
Redi, who, in 1668, proved that no maggots
appeared in meat when flies were prevented from
laying eggs.
7
What is the most basic difference between
prokaryotes, and eukaryotes? In what region of
a prokaryote does DNA reside? Who is given
credit with the invention of the
microscope? What are two names that the origins
of life also go by?
8
Early Scientists...Continued
- Robert Hooke used a compound light microscope to
study corkthe dead cells of oak bark.
- German scientist Matthias Schleiden observed
plant tissues under a microscope, and came to the
conclusion that all plants were composed of cells.
- Theodor Schwann observed animal tissues under
the microscope and came up with a similar
conclusion.
Because of the work of each of these scientists,
the fundamental ideas of the cell theory were
formulated. They are as follows
9
The Cell Theory
1. All organisms are composed of one or more
cells.
10
2. The cell is the basic unit of structure and
organization of organisms.
11
3. All cells come from preexisting cells.
12
What is Robert Hooke credited with? What are
Schwann and Schleiden credited with? What are
the three parts of the cell theory that Hooke,
Schwann and Schleiden contributed?
13
Today's Light Microscopes
14
The Electron Microscope
The microscopes weve discussed and used in class
have combinations of lenses, and light to
magnify objects.
At most, these compound light microscopes can
magnify things about 1500x.
In the 1930s and 1940s, a new kind of microscope
was invented that could actually get a look
inside the cell, at organelles. Instead of using
beams of light, it used beams of electrons.
We could now see things magnified up to 500,000x
using these electron scopes!
15
Glomerulus of Kidney
The transmission electron microscope (TEM) is
used to study structures contained within a cell
The scanning electron (SEM) microscope is
generally used to study the surfaces of cells to
learn their three-dimensional shape.
Another electron microscope, the scanning
tunneling microscope or (STM) uses the flow of
electrons to create computer images of atoms on
the conductive surface of metals, as seen here.
16
UTSA Kleburg Advanced Microscopy Laboratory
ARM200
The new Atomic Resolution Scanning Transmission
Electron Microscope
The machine allows scientists see samples at a
magnification of 20 million times! To put it in
perspective, a strand of human hair magnified 20
million times would be the size of San Antonio.
- Practical applications include using
nanoparticles for cancer treatment. - They will place nanoparticles inside a tumor and
use an infrared laser to pinpoint and burn away
damaged cells without harming the surrounding
healthy cells. - As you can imagine, pinpoint accuracy is
important!
17
Briefly describe how light microscopes magnify
tiny objects. How are light microscopes
different from electron microscopes? What is
the highest magnification possible on Earth today
with current microscope technology? How can
microscope technology be employed in a useful and
practical way (other than simply looking at
stuff)?