Ionic Bonding - PowerPoint PPT Presentation
1 / 11
Title:
Ionic Bonding
Description:
Ionic Bonding What makes an atom most stable? When the highest occupied energy level is filled with electrons the atom is stable, and probably will not react chemically. – PowerPoint PPT presentation
Number of Views:137
Avg rating:3.0/5.0
Title: Ionic Bonding
1
Ionic Bonding
2
- Ionic bonds form between a metal and a non-metal
and dissolve easily in water. - In solution, ionic compounds easily dissolve to
form ions. - Ionic bonds produce salts which tend to form
crystals with high melting temperatures.
3
What makes an atom most stable?
- When the highest occupied energy level is filled
with electrons the atom is stable, and probably
will not react chemically. - Elements in the noble gas family have the highest
energy level filled and have the most stable
electron configuration.
4
Electron Dot Diagrams(Lewis Structures)
- The easiest way to see if an element is stable,
is to draw its Lewis Dot structure showing only
the valence electrons. - The Lewis Dot will allow you to see how many
electrons an element needs to fill its outer
shell and how it may react with other elements. - For instance oxygen has 6 valence electrons and
thus can gain two electrons to fill its outer
shell. - This means that oxygen could take 2 electrons
from one other element or one each from two
different elements.
5
OCTET RULE
- Elements become happy when they have a complete
outer shell. They are usually happy when the
closest outer shell has 8 or 2 in the case of
Helium. - Completing the outer shell is known as the Octet
Rule (8 valence electrons) - In order to do this they will either lose or gain
electrons.
6
Ion formation
- If an atom has greater than 4 valence electrons
- It will gain enough to make 8 (octet rule)
- Becomes negatively charged ion (anion) because
there are more electrons(-) than protons () - This applies to elements in groups 5, 6, and 7
because they are much closer to the noble gases
thus it is much easier to gain than lose
electrons.
7
Ion formation
- If an atom has less than 4 valence electrons
- It will lose those outer electrons so that its
outermost shell of electrons is now full. - Becomes positively charged (cation) because there
are more protons left than electrons. - This applies to elements in Groups 1, 2, and 3
because it is easier to lose electrons than gain
to fill the outermost shell.
8
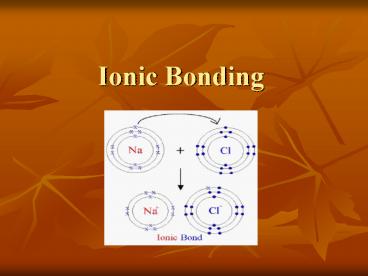
Ionic bonds
- Once positive and negative ions are formed, they
are attracted to each other. - They form a chemical bond known as an ionic bond
the force that holds cations and anions
together results from the transfer of electrons
from one element to another. - http//www.youtube.com/watch?v5IJqPU11ngYfeature
player_detailpage
9
Practice with Ionic Bonding
- Using the Lewis Dot models for each element, show
the ions, with their oxidation number, that would
form for each group - Potassium (K) and Bromine (Br)
- Magnesium (Mg) and Chlorine (Cl)
- Lithium (Li) and Oxygen (O)
- Next, using the ions you formed, show the
transfer of electrons for each group (remember to
use Lewis Dot!!) - Finally determine the formula for each new
compound that is formed. (subscript number of
each element used.)
10
Oxidation Number vs. Subscripts
- Ionic bonding is when two ions bond to each other
forming an ionic compound. - Ex. One Na (sodium ion)(METAL) and one Cl-
(chloride ion)(Non-metal) bond to make NaCl
(sodium chloride) - One Mg 2 (magnesium ion) and two F - (fluoride
ions) bond to make MgF2 (magnesium fluoride) - The number at the top of the ion is the oxidation
number. (This is the number of electrons needed
to reach a full outer shell plus the overall
charge of the element after the loss or gain of
electrons) - Once the ions combine you have a subscript that
tells how many of each type of atom were needed
to form a neutral compound. (Mg3N2)
11
Naming Ionic Compounds
- The rules for naming ionic compounds are
- Ex. Na Cl NaCl
- Step 1 Name the metal/cation first
- Sodium
- Step 2 Name the non-metal/anion second
- Chlorine
- Step 3 Drop the ending (last syllable) of the
anion listed and replace it with ide. - Result would be Sodium Chloride
- Try naming these ionic compounds
- KBr, MgCl2, Li2O, Na3N