Ancient and Classical India - PowerPoint PPT Presentation
Title: Ancient and Classical India
1
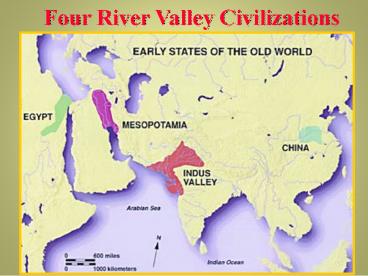
Four River Valley Civilizations
2
Early Society in South Asia
- Indus Valley Civilization centered around twin
fortified cities Harappa Mohenjo-daro,
declined gt 2000 BCE - Aryans Indo-European Migrants from the Caspian
Sea area arrived - 2000 BCE - pastoral nomads, light-skinned, warrior
culture - clashed with dark-skinned Dravidians
(sedentary, agricultural) - established a society that was male dominated,
dev. Sanskrit language, est. local kingdoms, dev.
a social class system, Hinduism
3
Indus River Valley Civilization
4
3200 BC
Neolithic Culture
ANCIENT INDIA
Indus Valley Settlements Harappan Civilization
2500 BC
Harappan Civilization Ends
1750 BC
Aryan Invasions of Indus Valley
1500 BC
Aryan Kingdoms Develop
1000 BC
Hinduism Develops and Spreads
750 BC
Buddhism Begins and Spreads
530 BC
Alexander the Great Invades
326 BC
Chandragupta begins Mauryan Empire
321BC
Chandragupta dies. Son assumes throne
301 BC
Asoka becomes king of Mauryan Empire
269 BC
232 BC
Asoka dies. Empire begins to decline
Chandra Gupta forms Gupta Dynasty
320 AD
335 AD
Samudra Gupta becomes king
375 AD
Chandra Gupta II becomes king
5
Hinduism
- Evolved from native and Aryan polytheistic
beliefs - No one single Holy Book many books called the
Vedas - Brahman - supreme being creator of the universe
(not worshipped directly by the masses - Vishnu the sustainer protects humanity
- Shiva the destroyer destroys the universe so
that the cycle may begin again - Hindus believe the universe has been created and
destroyed many times - Dharma the duties of a person according to their
Varna - Follow your dharma achieve good karma
6
Social Classes (Varnas)
Brahmans priests
Kshatriyaswarriors, rulers
Viasyas common people, merchants, artisans,
farmers
Sudras unskilled laborers, servants
Pariahs untouchables, slaves
- Castes determined by the previous life
- caste system is a rigid social system that
allows for NO social change - Occupation, marriage, education, even diet is
determined by hereditary caste - Promoted social harmony everyone followed
rules of behavior - Pariahs are not part of the system and are
called untouchables b/c they are considered dirty
7
- Your Karma in this life determines your form in
the next life (higher or lower Varna) - Reincarnation cycle of life and rebirth
- Goal to escape this cycle and be reunited with
Brahman - Effects of Hinduism on Society
- reinforced social hierarchy
- promoted high ethical standards
- respect for all living things
- promotes a vegetarian diet and honors the
sacred cow
8
- founded by Siddhartha Gautama.
- In his late twenties he became aware of the pain
of illness, the sorrow of death, and the effects
of old age on ordinary people. - He then decided to spend the rest of his life
searching for an end to human suffering. - While in meditation under a Bo Tree he achieved
enlightenment as to the meaning of life. - His teachings became the foundation for Buddhism.
- challenged people to be responsible for their own
lives. - taught that the pain, poverty, and sorrow that
afflict human beings are caused by their
attachment to things of this world. - also rejected the caste system.
9
- Following his death in 480 B.C.E., the Buddhas
followers traveled throughout India spreading his
message. - Buddhist monasteries were also established to
promote his teachings and provide housing and
training for monks dedicated to the simple life
and pursuit of wisdom.
10
(No Transcript)
11
4 Philosophies of Ancient China
- Buddhism introduced from India along the Silk
Road - Confucianism favored by rulers and adopted by
the Han Emperor as the official state belief
system - Daoism stressed harmony with nature
- Legalism opposed Confucian belief that proper
behavior would solve societies problems.
Encouraged strict laws, severe punishments, a
strong central govt.
12
Dynastic ChinaZhou Dynasty (1027-256 BCE)
- Claimed they had a right to rule because they
possessed the Mandate of Heaven permission to
rule was granted by the divine power - Mandate of Heaven was later used to explain the
Dynastic Cycle a dynasty would remain in power
as long as it was providing good govt. - Dev. of silk and the beginnings of the
exportation of this resource - Dev. of bookmaking
13
(No Transcript)
14
River Dynasties in China
15
5000 BC
Neolithic Culture
ANCIENT CHINA
First Chinese Cities Xia Dynasty Formed
2000 BC
Shang Dynasty Formed
1700 BC
Zhou Dynasty overthrows Shang Dynasty
1027 BC
Birth of Confucius
551 BC
Zhou Dynasty Ends. Replaced by Qin Dynasty
256BC
Shi Huangdi becomes Qin Emperor
221 BC
Han Dynasty replaces Qin. Liu Bang becomes emperor
202 BC
195 BC
Death of Liu Bang. Empress Lu rules
Wudi begins 54 year reign
141 BC
Former Han Dynasty Ends
9 AD
25 AD
Later Han Dynasty Begins
Paper Invented
105 AD
220 AD
Later Han Dynasty Ends
16
Ancient Chinese Civilization
Vocabulary
- Yin and Yang
- Qin Dynasty
- Shi Huangdi
- Autocracy
- Han Dynasty
- Liu Bang
- Centralized Government
- Empress Li
- Wudi
- Civil Service
- Assimilation
- Wang Mang
- Loess
- Anyang
- Shang Dynasty
- Oracle Bones
- Mandate of Heave
- Dynastic Cycle
- Feudalism
- Zhou Dynasty
- Confucius
- Filial Piety
- Daoism
- Legalism