Figure 8.1 Artificial membranes (cross sections) - PowerPoint PPT Presentation
1 / 20
Title:
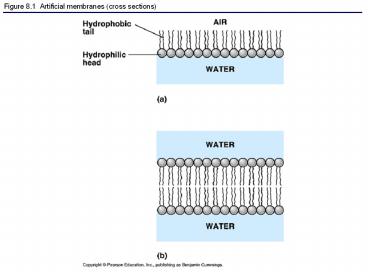
Figure 8.1 Artificial membranes (cross sections)
Description:
Figure 8.1 Artificial membranes (cross sections) Figure 8.2 Two generations of membrane models Figure 8.3 Freeze-fracture and freeze-etch Figure 8.4 The fluidity of ... – PowerPoint PPT presentation
Number of Views:94
Avg rating:3.0/5.0
Title: Figure 8.1 Artificial membranes (cross sections)
1
Figure 8.1 Artificial membranes (cross sections)
2
Figure 8.2 Two generations of membrane models
3
Figure 8.3 Freeze-fracture and freeze-etch
4
Figure 8.4 The fluidity of membranes
5
Figure 8.5 Evidence for the drifting of membrane
proteins
6
Figure 8.6 The detailed structure of an animal
cells plasma membrane, in cross section
7
Figure 8.7 The structure of a transmembrane
protein
8
Figure 8.8 Sidedness of the plasma membrane
9
Figure 8.9 Some functions of membrane proteins
10
Figure 8.10 The diffusion of solutes across
membranes
11
Figure 8.11 Osmosis
12
Figure 8.12 The water balance of living cells
13
Figure 8.13 The contractile vacuole of
Paramecium an evolutionary adaptation for
osmoregulation
14
Figure 8.13x Paramecium
15
Figure 8.14 Two models for facilitated diffusion
16
Figure 8.15 The sodium-potassium pump a
specific case of active transport
17
Figure 8.16 Review passive and active transport
compared
18
Figure 8.17 An electrogenic pump
19
Figure 8.18 Cotransport
20
Figure 8.19 The three types of endocytosis in
animal cells