Integumentary System - PowerPoint PPT Presentation
1 / 9
Title:
Integumentary System
Description:
Integumentary System Includes: the skin hair nails a variety of glands Integumentary System Skin Covers the entire exterior of the human body Functions: protection ... – PowerPoint PPT presentation
Number of Views:381
Avg rating:3.0/5.0
Title: Integumentary System
1
Integumentary System
2
Integumentary System
- Includes
- the skin
- hair
- nails
- a variety of glands
3
Skin
- Covers the entire exterior of the human body
- Functions protection,
- water retention, sensory reception, body
temperature regulation, and vitamin D synthesis.
4
(No Transcript)
5
Skin
- Composition
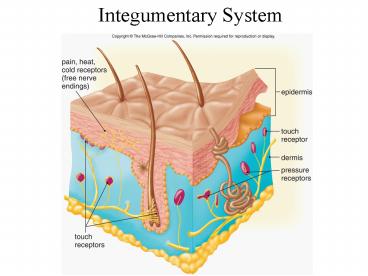
- Two distinct tissue layers
- Epidermis the outer layer
- Dermis the inner layer
- Hypodermis (subcutaneous tissue)
- A layer under the skin (not part of the skin)
- Anchors skin to underlying bone and muscle
tissue.
6
Epidermis
- The outer cells are nonliving and create a
waterproof covering that prevents excessive water
loss. - cells may be replaced because an inner epidermal
layer is composed of living cells that constantly
produce new cells. - Lower section contains melanocytes, cells that
produce melanin, a dark brown pigment.
7
Dermis
- Composed of connective tissue
- Contains blood vessels, nerves, sense organs,
and also the expanded portions of oil (sebaceous)
and sweat glands and hair follicles. - Sweat glands produce the watery secretions known
as sweat, which contains salt, water, and other
compounds.
8
Dermis Sebaceous glands, (oil glands) produce
oily secretions known as sebum that spreads out
along the surface of the skin and keeps the
epidermis flexible and waterproof. Small
muscle fibers, (arrector pili muscles) attach to
hair follicles contract and pull hair upright
when you are cold, producing what is commonly
called goose bumps.
9
Subcutaneous layer
This is a layer of adipose tissue (fat and
connective cells) that lies beneath the skin
proper and serves to insulate, protect inner body
parts, and acts as an energy reserve.