AFM Diagram - PowerPoint PPT Presentation
1 / 36
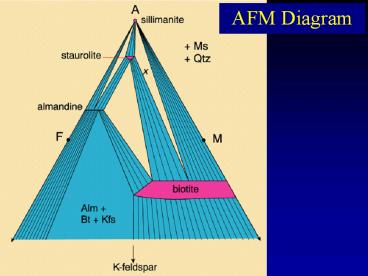
Title: AFM Diagram
1
- AFM Diagram
2
- At different P-T conditions, the diagrams change
- Other minerals become stable
- Different arrangements of the same minerals
(different tie-lines connect different coexisting
phases) - Use to graphically show important isograd
reactions
low P-T
high P-T
3
Below the isograd
Bulk rock composition
low P-T
A B ? C D
At the isograd
Above the isograd
high P-T
This is called a tie-line flip, and results in
new mineral assemblages in the next metamorphic
zone
4
Review and P-T Application
AFM basics
5
2. Getting P-T constraints
chl
gar
bio
Example Over what P-T range is the assemblage
GarChlBio stable?
6
Step 1 find AFM range for assemblage
Where in P-T space does this assemblage occur?
7
Step 2 use AFM labels to find P-T field
This is the only part of P-T space where
garchlbio can coexist
8
Metapelites
- Metapelites metamorphosed mudstones and shales
- Distinguishing chemical characteristics high
Al2O3 and K2O, and low CaO - Reflect the high clay and mica content of the
original sediment and lead to the dominance of
muscovite and quartz throughout most of the range
of metamorphism - High proportion of micas common development of
foliated rocks, such as slates, phyllites, and
mica schists - the petrogenesis of pelites is represented well
in AKF and AFM diagrams
9
Barrovian Zones in Metapelites
- Chlorite zone
- Biotite zone
- Garnet zone
- Staurolite zone
- Kyanite zone
- Sillimanite zone
- K-feldspar zone
10
Variable P-T Conditions in a Convergent Plate
Setting
Barrovian
Barrovian Series rocks typical of regional
metamorphism at mid- to lower crust in mountain
belts
11
Barrovian Series metapelites have kyanite
12
Barrovian
Buchan
Dutchess Co. Trip
13
(No Transcript)
14
Barrovian Zones in Metapelites
- Chlorite zone
- Biotite zone
- Garnet zone
- Staurolite zone
- Kyanite zone
- Sillimanite zone
- K-feldspar zone
15
P-T grid
Barrovian Series
16
Metamorphic zones based on metapelites can give
relatively high resolution P-T estimates
Granulite
Amphibolite
Greenschist
Kfs Zone
Sil Zone
Ky Zone
Barrovian Series
St Zone
Grt Zone
Bt Zone
Chl Zone
P-T grid
17
Chlorite Zone
- lower greenschist facies
- 300 400C
18
Biotite Isograd
- tie-line flip (discontinuous) reaction type
- Chl Kfs ? Bt phengitic Ms
- 400 425C
19
P-T grid
? Biotite Isograd
20
Chapter 28 Metapelites
Biotite Zone
- Continuous reactions (over a range of P-T)
involving solid solution - gradual expansion of Ms-Bt-Chl triangle to
include more pelite compositions
- middle to upper greenschist
- 400 500C
P,T increasing
21
Garnet Isograd
Part 1
- tie-line flip (discontinuous) reaction type
- Cld Bt ? Grt Chl
- 500C
22
Chapter 28 Metapelites
Garnet Isograd
Part 2
- Continuous reaction type (over a range of P-T)
involving solid solution
- Chl Bt ? Grt Mg-rich Chl Mg-rich Bt
- This is the garnet isograd for almost all common
metapelites
- 525 555C
23
P-T grid
? Garnet Isograd
24
Chapter 28 Metapelites
Staurolite Isograd
Part 1
- terminal point reaction type
(chloritoid-out disappearance of chloritoid)
- Cld ? Grt Chl St
- 550C
25
Chapter 28 Metapelites
Staurolite Isograd
Part 2
- tie-line flip (discontinuous) rxn
- Chl Grt ? St Bt
- This is the staurolite isograd for almost all
common metapelites
- 550 600C
26
P-T grid
??? Staurolite Isograd
27
Part 1
Kyanite Isograd
- tie-line flip (discontinous) rxn
- St Chl ? Ky Bt
- 625C
28
Chapter 28 Metapelites
Part 2
Kyanite Isograd
- terminal point reaction type
(staurolite-out disappearance of staurolite)
Ky
- St ? Grt Bt Ky
- This is the kyanite isograd for almost all
common metapelites
- 625-675C
29
P-T grid
? Kyanite Isograd
30
Chapter 28 Metapelites
Sillimanite Isograd
- polymorphic transition
Sil
- Ky ? Sil
- 650 - 700C
31
P-T grid
? Sillmanite Isograd
32
Chapter 28 Metapelites
K-feldspar Isograd (2nd sillimanite isograd)
- breakdown of muscovite dehydration reaction
- Ms Qtz ? Sil Kfs H2O
- 750C
Kfs
- liberated H2O may cause partial melting
33
P-T grid
11 K-feldspar Isograd
34
Granulite Facies
- Breakdown of biotite dehydration reactions
- presence of cordierite and/or Opx (depending on
P)
- Bt Sil ? Grt Crd H2O Bt
Qtz ? Opx Kfs H2O
- gt750 - 800 C
- liberated H2O may cause partial melting
35
Migmatites
- migmatite mixed rock part igneous, part
metamorphic
- Breakdown of muscovite and biotite at high
grades may cause partial melting
36
Metamorphic zones based on metapelites can give
relatively high resolution P-T estimates
Granulite
Amphibolite
Greenschist
Kfs Zone
Sil Zone
Ky Zone
St Zone
Grt Zone
Bt Zone
Chl Zone