CHAPTER 22- ENERGY FLOW - PowerPoint PPT Presentation
Title:
CHAPTER 22- ENERGY FLOW
Description:
CHAPTER 22- ENERGY FLOW ALL LIFE DEPENDS ON THE SUN PHOTOSYNTHESIS the process of using the suns energy, water, and carbon dioxide to produce Oxygen and the sugar ... – PowerPoint PPT presentation
Number of Views:71
Avg rating:3.0/5.0
Title: CHAPTER 22- ENERGY FLOW
1
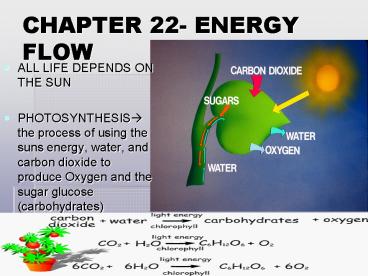
CHAPTER 22- ENERGY FLOW
- ALL LIFE DEPENDS ON THE SUN
- PHOTOSYNTHESIS? the process of using the suns
energy, water, and carbon dioxide to produce
Oxygen and the sugar glucose (carbohydrates)
2
Producer-
- Defined as an organism that can make its own food
- Scientific term is AUTOTROPH will literally
stands for self- feeding - Examples are plants, some protists, and some
bacteria-
3
PRODUCERS
- almost all of them use the green pigment
(chlorophyll) to capture the energy from the sun - EXCEPTION- deep water ecosystems which use energy
from deep ocean vents. Bacteria can break down
the hydrogen sulfide to make its own energy
4
CONSUMER
- Defined as organisms that get their energy by
eating other organisms - Scientific term is HETEROTROPH which literally
means other feeders - Examples- animals, fungi
5
CLASSIFICATION based on what consumers eat
- HERBIVORES- consumer that only eats producers
- CARNIVORES-consumer that only eats other
consumers - OMNIVORES- consumer that eats both producers and
consumers - DECOMPOSERS-consumer that break down dead
organisms
6
How do consumers get their energy?
- Use oxygen we breathe to breakdown the sugar
glucose - This is called CELLULAR RESPIRATION
- Each cell in our body takes in oxygen and use it
to release energy from food
7
(No Transcript)
8
CELLULAR RESPIRATION
- ALL ORGANISMS USE CELLULAR RESPIRATION TO GET
ENERGY FROM FOOD - EVEN PRODUCERS USE CELLULAR RESPIRATION
- ENERGY IS USED FOR GROWTH, CELL REPAIR, MOVEMENT,
ETC - EXCESS ENERGY IS STORED AS FAT OR SUGAR
9
ENERGY TRANSFER
- Each time one organism eats another organism
there is an energy transfer - Scientists study energy transfer by examining
- FOOD CHAINS
- FOOD WEBS
- TROPHIC LEVELS
10
FOOD CHAIN (pg 122)
- Sequence in which energy is transferred from one
organism to the next as each organism is eaten
11
FOOD WEB
- Many food chains linked together
- More realistic because most animals eat more than
one type of food - Shows good interaction in the ecosystem
12
TROPHIC LEVEL
- Defined as each step in the energy transfer of a
food chain - Will rarely have more than 4 consumer levels
- This is due to energy loss from one level to the
next
13
TROPHIC LEVELS
- EACH TIME ENERGY IS TRANSFERRED FROM ONE LEVEL TO
THE NEXT ENERGY IS LOST AS HEAT AND LESS ENERGY
IS AVAILABLE - About 90 of energy is used up
- Only 10 of energy is passed on
14
ENERGY PYRAMID
- Shows the relationship of consumers in an
ecosystem and how energy is transferred - - Each step in the pyramid is a power of ten
15
BIO MASS
- Amount of living mass in a trophic level
16
(No Transcript)
17
CYCLING OF ELEMENTS
- Law of Conservation of Mass- the amount of mass
in the universe remains constant- therefore the
amount of mass of each element in the universe
remains constant (exception is radioactive
materials)
18
WATER CYCLE
19
CARBON CYCLE
- All living things are made of carbon
- Carbon is the key ingredient in fats, proteins,
sugars, and nucleic acids - Carbon is found in the air and water (Carbon
Dioxide) - Carbon is also found in the soil naturally as
limestone or as the remains of once living
organisms- oil, coal, and natural gas
20
How do humans affect the Carbon cycle?
- When we burn fuel (oil, coal, gas, wood) we
release carbon dioxide into the atmosphere - CELLULAR RESPIRATION- gives off CO2
- Increased carbon dioxide in atmosphere can lead
to global warming
21
CARBON CYCLE
22
NITROGEN
- Organisms need nitrogen to form proteins
- Nitrogen makes up 78 of the atmosphere
- Most organisms cannot use nitrogen as a gas to
make proteins - Nitrogen fixing bacteria turns atmospheric
nitrogen into usable nitrogen in the soil - Decomposers turn waste products and decaying
organisms into usable nitrogen
23
(No Transcript)
24
PHOSPHORUS CYCLE
- Needed to form bones and teeth in animals
- Phosphate rocks dissolve and release into the soil
25
HOW ECOSYSTEMS CHANGE
- If a Forest burns down for 80 acres then
- 1. What plants would you expect to see first?
- 2. What animals would you expect to see?
- 3. What would that area look like in 20 years?
What plants and animals?
26
ECOLOGICAL SUCCESSION
- Defined as- the gradual change and replacement of
types of species in a community - Example- first grass would grow- then bushes
may grow and kill off small areas of grass then
large trees grow and kill off all of the forest
floor plant life
27
Primary Succession
- Succession that occurs on a surface where no
ecosystem existed before - Examples- new island formed by a volcano, sand
dunes - What would you expect to see there?
28
Secondary Succession
- Succession on a surface where an ecosystem
previously existed - Example- forest burning down, chopping down rain
forest, flood, volcano, tsunami
29
PIONEER SPECIES
- First organisms to colonize a new area-
- Characteristics of pioneer species
- 1. fast reproducers- short lifespan
- 2. produce many offspring
- 3. have good method of dispersal
- 4. can remain dormant in rough environment if
needed - 5. small- and not good competitors
30
MATURE SPECIES
- Defined as a species that will eventually
dominate an ecosystem if given enough time - Characteristics-
- 1. slow reproducers but long life span
- 2. produce few offspring but care for young
- 3. slower dispersal
- 4. larger and very good competitors
31
CLIMAX COMMUNITY (page 132)
- Is the final and stable community when it fully
matures