Measuring Microhabitat - PowerPoint PPT Presentation
1 / 22
Title:
Measuring Microhabitat
Description:
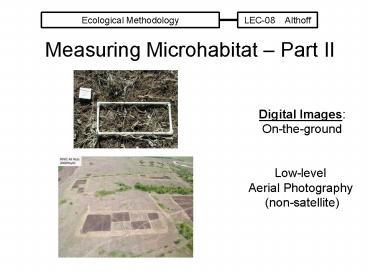
Ecological Methodology LEC-08 Althoff Measuring Microhabitat Part II Digital Images: On-the-ground Low-level Aerial Photography (non-satellite) – PowerPoint PPT presentation
Number of Views:54
Avg rating:3.0/5.0
Title: Measuring Microhabitat
1
Ecological Methodology
LEC-08 Althoff
- Measuring Microhabitat Part II
Digital Images On-the-ground Low-level Aerial
Photography (non-satellite)
2
Digital Photographs Advantages over film
- __________ per image
- ________ verification of image taken (if one so
chooses) - Time/Date Stamp
- Image Analysis Potential a) during a project
- b) across projects
- _____________________
3
VOR Measures - Improvements
- Daubenmire Frame, Robel Pole, and Nudds Board
___________________________ imagesthen
____________ in the office, not the field, to
improve accuracyand verify field estimate/record - Limb et al. 2007 -________________________
Limb, R.F., K.R. Hickman, D.M. Engle, J.E.
Norland, and S.D. Fuhlendorf. 2007.
Digital photography reduced investigator
variation in visual obstruction measurements for
southern tallgrass prairie. Rangeland
Ecology and Management 60548-552.
4
Limb et al. 2007
- Used ___ megapixels images (i.e., camera
resolutionit was 2006-2007)now can easily go to
______ megapixel so for same cost of
improved digital camera equipment - Compared digital image estimates of VOR to those
using both Nudds Board and Robel Pole - Shot digital photo on calm days, with 1 x 1 m
frame positioned as a backdrop
5
Limb et al. 2007
Digital Image
Imported to Adobe Photoshop
Converted to black and white
6
Limb et al. 2007
- Adobe PhotoShop used a) software threshold
function to convert color images to black and
white images - Used same threshold setting for all images (128),
which was often the default setting. - Used the histogram feature to provide of black
and white pixels per imageactual measure was
percent of black pixelsthen used ___________
___________________ to compare precision across
methods
7
CV 6.7 Digital 32.1 Nudds 52.2 Robel
1
________________________ with the digital
photoapproach (i.e., more idiot proof less
user variability)
8
estimation of biomass tighter with the Digital
Image estimate than the Robel Pole
2
_________________ __________ with the digital
photo approach
9
Low-Level Aerial Photography
- Some early efforts in the late 1960s early
1970s - Original efforts used SLR cameras. Very limited
because usually 24 or 36 images per launch
restriction - By _______________, transition occurring from SLR
cameras to digital cameras a) lighter b)
lower cost per camera c) lower cost per
image d) easily can exceed ___ images per
launch
10
(No Transcript)
11
Basic System
- 3 basics components a) lift
platform b) camera platform c)
on-the-ground platform/controls - Bigger the lift platform, the bigger the camera
platform it can support - Camera platform major weight is the _______
_______ to power camera, transmitter (video) and
receiver (signals from ground unit). More
battery power provides longer launch sessions
12
Lift Platforms
BLIMP Helium-filled More stable up to 20 mph
winds
KITE less stable
BALLOON Helium-filled More stable yet up to 30
mph winds
Early efforts
currently moving towards this type
13
Lift Platformsnext generation!
14
Camera Platform
BATTERIES
PAN TILT adjustments
CAMERA
15
Ground Controls
16
Challenges -- In the field
- ______________________
- Stay lt _________ (otherwise FAA regs)
- Transporton groundof the lift platform
- Topography (also see analysis)
- _______________ (tree challenges)
- Create _____________________
17
Creating Landmarks/GPS points
18
(No Transcript)
19
Challenges -- Analysis
- Software some off-the-shelf, some very
expensive (gt3,000 per user) vs. domain-free (0)
image processing - What to measure? ______ vs. ____________
- ______________________________rain distortion
of land surface increases from flat to steep - ______________.good to rectify photo (i.e.,
need _____________________in photo and use
ARCMap, ARCGIS type software for doing this and
more
20
Costs of Low-Level Aerial Photography Systems
- Went from over __________ per system in the late
1990s to - Today ___________ with much more capability
- Costs typically less than satellite images
(although smaller area) and the these systems
offer more flexibility in scheduling (vs. working
with government or private satellite operations)
21
(No Transcript)
22
1 hectare 2.45 acres (100 m x 100 m)