Plate Tectonics - PowerPoint PPT Presentation
1 / 36
Title:
Plate Tectonics
Description:
Plate Tectonics Possible Causes of Tectonic Plate Motion What causes the motion of tectonic plates? This movement occurs because of changes in the density within the ... – PowerPoint PPT presentation
Number of Views:135
Avg rating:3.0/5.0
Title: Plate Tectonics
1
Plate Tectonics
2
The Theory Of Plate Tectonics States
- The Lithosphere is divided into ten major plates
and a number of smaller plates.
3
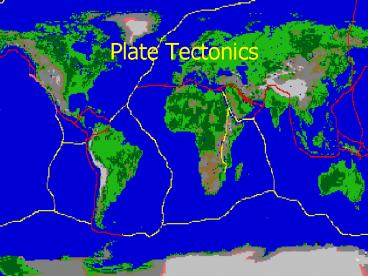
Global Picture Of the Earths Tectonic Plates
4
- Plates are in constant motion and are continually
changing shape and size.
5
- Most of the Earths Volcanoes, Earthquakes and
Mountain Ranges occur along Plate Boundaries!
6
- There are three types of plate boundaries
- Divergent Boundaries
- Convergent Boundaries
- Transform Boundaries
7
Divergent boundaries
- Plates moves apart
- New crust is created as hot magma rises up from
the mantle. - Mountains associated with divergent boundaries
are called ridges.
8
Divergent Boundary
9
Examples of Divergent Boundaries Mid-Atlantic
Ocean Ridge, East African Rift, and Red Sea
10
Spreading Centers
11
East Africa Rift and Red Sea
12
(No Transcript)
13
Convergent Boundaries
- Plates move toward each other and collide.
- There are three types of convergent boundaries.
- Collisions between two oceanic plates
- Collisions between two continental plates
- Collisions between a continental and oceanic
plate.
14
Convergent Boundary
15
Collisions Between Two Oceanic Plates
- Sinking crust melts in the mantle. The less
dense magma created from the melted crust rises
up through the crust forming a chain of volcanic
islands called island arcs. - Where one plate sinks underneath another plate is
called a subduction zone. - Examples
- Japanese and Philippines Islands
16
(No Transcript)
17
Mt. Pinatubo
Mt Unzen
18
Collision Between Two Continental Plates
- Neither plate sinks because continental plates
are light and buoyant. - As the plates collide they buckle and form huge
mountain ranges and plateaus. - Examples
- Alps, Himalayas, Tibetan Plateau
19
(No Transcript)
20
India Is still moving into Asia Today
21
Himalayas
India Today
22
Himalayas
23
Collision between A Continental Plate and an
Oceanic Plate
- The heavier oceanic plate will sink under the
lighter continental plate. - The convergence causes the continental plate to
buckle up forming mountains. - As the heavier oceanic plate subducts it melts in
the mantle and hot magma rises up forming
volcanoes called a Volcanic Arc on the
continental plate. - Examples
- Mt. St. Helens and Lassen Peak in the Cascade
Mountain Range and the Andes Mountains
24
Continental and Oceanic Crust Collision
25
(No Transcript)
26
Mt. St. Helens
Lassen peak
27
Transform Boundaries
- At transform boundaries plates slide past each
other. - Crust is neither being destroyed nor created.
- Transform boundaries join segments of ridge
systems on the ocean floor. - Transform boundaries join segments of converging
and diverging boundaries. - Examples
- San Andreas Fault
28
Transform Boundary
29
San Andreas Fault System And Attached Ridges
30
San Andreas Fault System
31
Identify the Plate Boundaries below A. B.
C. D. E.
32
(No Transcript)
33
Section 3 The Theory of Plate Tectonics
Causes of Tectonic Plate Motion
Click below to watch the Visual Concept.
Visual Concept
34
Section 3 The Theory of Plate Tectonics
Possible Causes of Tectonic Plate Motion
- What causes the motion of tectonic plates? This
movement occurs because of changes in the density
within the asthenosphere. - The following Visual Concept presentation
examines three possible driving forces of
tectonic plate motion.
35
Section 3 The Theory of Plate Tectonics
Tracking Tectonic Plate Motion
- Tectonic plate movements are so slow and gradual
that you cant see or feel them. The movement is
measured in centimeters per year. - Scientists use a system of satellites called the
global positioning system (GPS) to measure the
rate of tectonic plate movement.
36
Section 3 The Theory of Plate Tectonics
Newtons Second Law of Motion, continued
Click below to watch the Visual Concept
Visual Concept