The Cell - PowerPoint PPT Presentation
Title:
The Cell
Description:
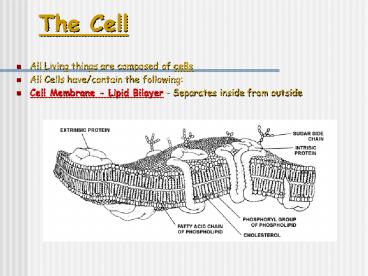
The Cell All Living things are composed of cells All Cells have/contain the following: Cell Membrane - Lipid Bilayer - Separates inside from outside – PowerPoint PPT presentation
Number of Views:46
Avg rating:3.0/5.0
Title: The Cell
1
The Cell
- All Living things are composed of cells
- All Cells have/contain the following
- Cell Membrane - Lipid Bilayer - Separates inside
from outside
2
Cytoplasm
- Cytoplasm - everything but DNA/Nucleus
3
Two Cell types
- Prokaryotic Cells
- 1. Primitive cells include bacteria
- 2. No nucleus
- 3. No Membrane-bound organelles
- 4. Very Small 1-10 micrometers
- 5. Single Strand of Circular naked DNA
- 6. Contain Ribosomes
4
Typical Prokaryotic Cell
5
Eukaryotic Cells
- Eukaryotic Cells
- 1. Contain a Nucleus which protects DNA /
Chromosomes - 2. Much larger than prokaryotic cells
- 3. Have many different types of Membrane
bound organelles - compartmentalization
efficiency
6
Eukaryotic Cells
Animal Eukaryotic Cell
Plant Eukaryotic Cell
7
Organelles
- Membrane-Bound organelles only found in
Eukaryotes - Localize Chemical Reactions making the cell far
more efficient
8
Major Organelles of the Eukaryotic Cell
- The Nucleus
- eukaryotic means true nucleus
- Contains protects the cells DNA
- Helps coordinate the division of cells
- Surrounded by a Nuclear Envelope
- Envelope is double layered with an Inner Outer
membrane - Has perforations called Nuclear Pores which allow
large molecules to pass in/out of the nucleus - Contains a Nucleolus
- Ribosomes are made in this region
- Contains DNA packaged in structures called
chromosomes
Chromosomes
9
Mitochondria
- Serves as the powerhouse of the cell by
generating chemical energy - Has its own DNA
- Can divide on its own
10
Chloroplasts (Plant Cell Only)
- Is the cells farm - meaning food is generated
here. - Does this by photosynthesis - the conversion of
CO2, H2O and sunlight into sugar - Contain Chlorophyll - a green pigment - which
does this - Has its own DNA
- Can divide on its own
11
Ribosomes
- Are NOT membrane-bound also exist in
prokaryotes - Are used to manufacture proteins
- Granular in appearance
- Often found on rough endoplasmic reticulum
12
Endoplasmic Reticulum
- Are folds of membranes used to package modify
proteins made by ribosomes. They also make
lipids - 2 types
- Rough - which is usually near nucleus and
covered with ribosomes giving it its rough
appearance. (Finishes proteins) - Smooth - which is usually away from the nucleus
(produce lipids)
13
Examples of Endoplasmic Reticulum
Smooth ER
Rough ER
14
Golgi Bodies
- Are the post offices of the cell
- Modify (address) proteins lipids and send them
in packages (vessicles) throughout (or out of)
the cell.
15
Lysosomes
- Small Vessicles which serve to digest particles
and clean-up cells - Contain Lysozyme a powerful digestive enzyme
- Digests food particles
- Destroys worn-out organelles
- Self-Destructs worn-out cells
16
Centrioles(Animal Cell Only)
- Serve as construction/organization points for
cellular microtubules - Organize and transfer chromosomes and other
organelles during Meiosis Mitosis - Occur in some prokaryotes, protists animals.
Do not occur with fungi and plants - Tube like structures usually at right angles to
each other. - Some animals have centriole-like structures at
the base of flagella called basal bodies.
17
Tonoplast(water vacuole)(plant cells only)
- Large H2O / Lipid / waste storage tank
- Provides pressure (Turgor pressure) to maintain
cell structure
18
Cell Wall
- Provides support / protection for plant cell
- Two layers of cell wall
- Primary Cell Wall Outer Cellulose only
- Secondary Cell Wall Inner Cellulose Lignin
- Cell membrane is innermost layer
19
Cytoskeleton
- Network of fibers which help organize the
internal arrangement within cells. - Three basic types of fibers compose cytoskeleton
- Actin Filaments
- Thinnest fibers 7nM
- Formed from protein Actin
- Microtubules
- Largest component of cytoskeleton 25 nM
- Formed from protein Tubulin
- Intermediate filaments
- Intermediate in size and can vary
- Form from several proteins inluding vimentin
keratin