Figure 9.4 - PowerPoint PPT Presentation
1 / 16
Title:
Figure 9.4
Description:
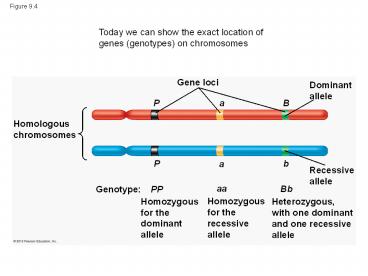
Figure 9.4 Today we can show the exact location of genes (genotypes) on chromosomes Gene loci Dominant allele a P B Homologous chromosomes b P a Recessive – PowerPoint PPT presentation
Number of Views:46
Avg rating:3.0/5.0
Title: Figure 9.4
1
Figure 9.4
Today we can show the exact location of genes
(genotypes) on chromosomes
Gene loci
Dominantallele
P
a
B
Homologouschromosomes
P
b
a
Recessiveallele
aa
PP
Bb
Genotype
Homozygousfor the recessiveallele
Homozygousfor the dominantallele
Heterozygous,with one dominantand one
recessiveallele
2
Figure 9.UN01
We can follow the inheritance patterns of these
gene location during reproduction
Homologouschromosomes
Alleles, residingat the same locus
Fertilization
Meiosis
Gametefrom theother parent
Diploid zygote(containingpaired alleles)
Paired alleles,different formsof a gene
Haploid gametes(allele pairs separated)
3
Figure 9.19B
The story of linked genes (two or more genes
found on the same chromosome) using fruit flies
as a model of genetics
4
Figure 9.18C-1
5
Figure 9.18C_2
The Explanation
g l
G L
GgLlFemale
ggllMale
g l
g l
Crossing over
g l
g l
G L
G l
g L
Eggs
Sperm
Offspring
g l
g L
G L
G l
g l
g l
g l
g l
Parental
Recombinant
6
Figure 8.16
Whats true for flies is (often) true for mammals
Coat-color genes
Eye-color genes
E
C
Brown
Black
Brown coat (C) black eyes (E)
E
C
E
C
Meiosis
e
c
c
e
e
c
White
Pink
Tetrad in parent cell (homologous pair
of duplicated chromosomes)
Chromosomes of the four gametes
White coat (c) pink eyes (e)
7
Figure 8.17B_1
C
E
Tetrad
(pair of homologous chromosomes in synapsis)
c
e
Breakage of homologous chromatids
1
C
E
c
e
Joining of homologous chromatids
2
C
E
Chiasma
c
e
8
Figure 8.17B_2
C
E
Chiasma
c
e
Separation of homologous chromosomes at anaphase I
3
C
E
C
e
E
c
c
e
9
Figure 8.17B_3
C
E
C
e
E
c
c
e
Separation of chromatids at anaphase II
and completion of meiosis
4
E
C
Parental type of chromosome
e
C
Recombinant chromosome
c
E
Recombinant chromosome
c
e
Parental type of chromosome
Gametes of four genetic types
10
Figure 9.19A
Mapping chromosomes
Section of chromosome carrying linked genes
g
c
l
17
9
9.5
Recombinationfrequencies
11
Figure 9.20B
Sex-determining chromosomes
Female
Male
44?XY
44?XX
Parents(diploid)
22?X
22?Y
22?X
Gametes(haploid)
Sperm
Egg
Offspring(diploid)
44?XX
44?XY
Female
Male
12
Fig. 9-20c
Alternate rules to determine males
One instead of two Homozygous Haploid
(no sex chromosomes)
13
Figure 9.22
Sex-linked diseases are more common in males than
females
QueenVictoria
Albert
Alice
Louis
Female
Male
CzarNicholas IIof Russia
Alexandra
Hemophilia
Carrier
Normal
Alexis
14
Figure 9.21C
Female
Male
XRY
XRXr
Sperm
Y
xR
XRY
XRXR
XR
Eggs
XrXR
Xr
XrY
R ? red-eye allele
r ? white-eye allele
15
Figure 9.21B
Female
Male
XrY
XRXR
Sperm
Xr
Y
Eggs
XR
XRXr
XRY
R ? red-eye allele
r ? white-eye allele
16
Figure 9.21D
Female
Male
XRXr
XrY
Sperm
Xr
Y
XRXr
XR
XRY
Eggs
XrY
Xr
XrXr
R ? red-eye allele
r ? white-eye allele