PN Junction / DIODE - PowerPoint PPT Presentation
1 / 21
Title:
PN Junction / DIODE
Description:
PN Junction / DIODE * Bollen * * * * * * * * * * * AGENDA Bollen SEMICONDUCTOR Pure silicium P material boron doped N material stibium doped P material and N material ... – PowerPoint PPT presentation
Number of Views:360
Avg rating:3.0/5.0
Title: PN Junction / DIODE
1
PN Junction / DIODE
Bollen
2
AGENDA
SEMICONDUCTOR Pure silicium P material boron
doped N material stibium doped P material and N
material PN junction PN junction layer 0V7 PN
junction characteristic
DIODE characteristic DIODE DC and ac
resistance DIODE load line DIODE flipped
resistorline DIODE DC resistance DIODE ac
resistance
Bollen
3
Semiconductor, pure silicium
Pure silicium 4 electrons Ideal is to have 8 So
share with your neighbour Co-valence
bounding Electrical neutral
Bollen
4
Semiconductor, pure silicium
Pure silicium 4 electrons Ideal is to have 8 So
share with your neighbour Co-valence
bounding Electrical neutral
Bollen
5
Semiconductor, P material boron doped
P material silicium (4) boron (3) doped Boron
misses 1 positvie charge (positon) 1 negative
charge (electron) Co-valence bounding Electrical
neutral P material misses one electron, or has a
place for one electron, this is called a free
hole
Bollen
6
Semiconductor, N material stibium doped
N material silicium (4) stibium (5)
doped Stibium has got extra 1 positive charge
(positon) 1 negative charge (electron) Co-valen
ce bounding Electrical neutral N material has
got one extra electron out of the bounding,
this is called a free electron
Bollen
7
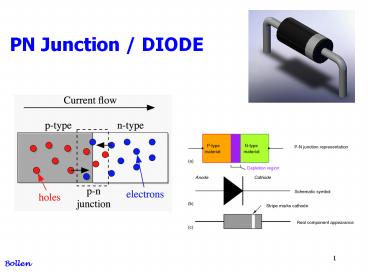
P material and N material
N material Free electrons
P material Free holes
Bollen
8
PN junction
Anode Pmaterial Kathode N material KNAP
handsome K Negative A Positive
Bollen
9
PN junction, depletion layer 0V7
Depletion layer can be made Wider by external
reverse voltage Smaller by External froward
voltage Depletion layer Uth 0V7
Bollen
10
PN junction, characteristic
Forward Depletion layer is gone Ud gt 0V7 Current
can flow
Reverse Depletion layer is wider Ud lt 0V0 Current
can NOT flow
Bollen
11
Diode, characteristic
a Diode Is a one way street for current
Bollen
12
Diode, characteristic
Assumption Treshold Voltage for silicium Ud
0V7 for germanium Ud 0V2
Bollen
13
Diode, characteristic
Where id diode current Vd diode voltage KT/q
26 mV Iss leakage current (1uA)
Bollen
14
Diode, DC and ac resistance
Bollen
15
Diode, Load line
How to calculate the exact value of vd and
id Graphical use load line, indicates the load
of the diode
Bollen
16
Diode, Load line
For shure id ir i For shure vs vd vr
Bollen
17
Diode, Load line
For shure For shure id ir i vs vd vr
Bollen
18
Diode, Flipped resistor line
Flip the resistor line and push the two curves
horizontally to fit vs vd vr
Bollen
19
Diode, Load line
The flipped resistor line is called LOAD-LINE
Bollen
20
Diode, DC resistance
For DC resistance use the load line method For
large voltages normally Vd 0V7 is used
Bollen
21
Diode, ac resistance
Differentiating gives Rd ?vd/?id 26 mV /
Id Where kT/q 26 mV
Bollen