Structure of a Neuron - PowerPoint PPT Presentation
1 / 10
Title:
Structure of a Neuron
Description:
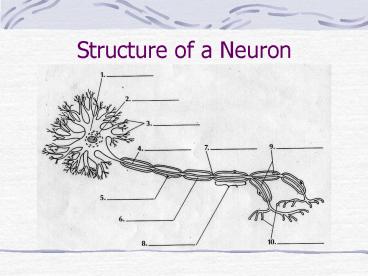
Structure of a Neuron Structure of a Neuron cell body nucleus dendrites axon Schwann cell nucleus myelin sheath node of Ranvier Schwann cell terminal branches ... – PowerPoint PPT presentation
Number of Views:144
Avg rating:3.0/5.0
Title: Structure of a Neuron
1
Structure of a Neuron
2
Structure of a Neuron
- cell body
- nucleus
- dendrites
- axon
- Schwann cell nucleus
- myelin sheath
- node of Ranvier
- Schwann cell
- terminal branches
- synaptic knobs
3
Impulses Along a Neuron
- Dendrites receive the nerve impulse and carry it
toward the cell body, which contains the nucleus. - The axon carries the impulse from the cell body
toward the synaptic knobs where it will be
transferred to other neurons.
4
(No Transcript)
5
Myelinated vs. Unmyelinated
- Myelinated neurons (those that have a myelin
sheath) carry nerve impulses faster than
unmyelinated ones because the impulse jumps from
one node of Ranvier to the next, instead of
traveling the whole length of the axon.
6
Normal Neural Pathway
- Specialized receptors (light, sound, taste,
touch, odors) react to a stimulus and generate
nerve impulses in the sensory neurons around
them. - The sensory neurons carry the impulse to the
spinal cord and then to the brain where
interneurons interpret the sensory information.
7
- The interneurons send out impulses to motor
neurons which cause a response by an effector
(muscle or gland).
8
Reflex Arc Pathway
- The simplest neural pathway is called a reflex
arc and it does not involve the brain. - The pathway is receptor, sensory neuron,
interneuron in spinal cord, motor neuron,
effector.
9
Reflex Arc
10
- The fact that the decision is made in the
spinal cord saves the time that it would take the
nerve impulse to travel through the many circuits
of the brain. - A faster response time can save the body from
further damage. - Reflexes are protective mechanisms that are
important in maintaining homeostasis.