ALKYNES - Chapter 7 - PowerPoint PPT Presentation
1 / 40
Title:
ALKYNES - Chapter 7
Description:
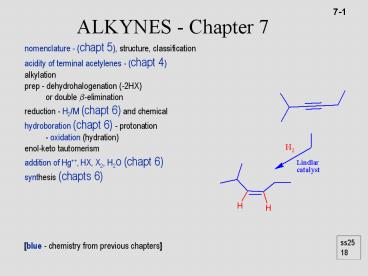
nomenclature - (chapt 5), structure, classification acidity of terminal acetylenes - (chapt 4) alkylation prep - dehydrohalogenation (-2HX) or double -elimination – PowerPoint PPT presentation
Number of Views:212
Avg rating:3.0/5.0
Title: ALKYNES - Chapter 7
1
ALKYNES - Chapter 7
nomenclature - (chapt 5), structure,
classification acidity of terminal acetylenes -
(chapt 4) alkylation prep - dehydrohalogenation
(-2HX) or double ?-elimination
reduction - H2/M (chapt 6) and
chemical hydroboration (chapt 6) - protonation
- oxidation (hydration) enol-keto
tautomerism addition of Hg, HX, X2, H2O (chapt
6) synthesis (chapts 6)
ss25 18
blue - chemistry from previous chapters
2
nomenclature - structure, classification acidity
of terminal acetylenes ) alkylation
?-elimination
reduction - H2/M chemical hydroboration -
protonation - oxidation
enol-keto tautomerism
addition Hg/H2O, HX, X2 synthesis
but first
3
nomenclature - structure, classification acidity
of terminal acetylenes ) alkylation
?-elimination
reduction - H2/M chemical hydroboration -
protonation - oxidation
enol-keto tautomerism
addition Hg/H2O, HX, X2 synthesis
4
acetylene, ethyne
Structure - two general types
(1) internal - R and R alkyl, Aryl, etc.
(2) terminal - R alkyl, Aryl, etc.
lt-- creates additional chemistry
8,28
5
Alkyne Nomenclature
Common alkyl alkyl' acetylene
6
Nomenclature
IUPAC - longest chain containing the most
important functional group(s) root -alkyne
4-chloro-6-cyclohexyl-5-methyl-2-hexyne
add substituents with s
7
Acetylene - linear geometry - sp hybridization
180o bond angles
R-C-C-R
? -bond 180o bond angle
8
Name ______________ seat ____
Write the product(s) of the following reactions.
9
Acidity of organic compounds
pKa 25
H-Csp
Why ? recall chapter 4
10
Relative basicity (acidity)
11
Acid-Base reactions
organometallic reagent (15)
12
Acid-Base reactions
last Thursday
R' alkyl D
13
Alkylation of Acetylides
Recall RX type substitution
acetylide anions undergo substitution rx
with 1o alkyl halides
form new C-C bonds
termed alkylation
14
Alkylation of Acetylides
15
Alkylation of Acetylides
16
Alkylation of Acetylides
- Acetylide anions - 2 and 3 halides
- ?-eliminates (strong base, reverse of addition)
no alkylation 2R-X
17
Preparation Dehydrohalogenation (-2 HX)
two ?-eliminations
2 arrangements of diBrs gt same acetylene
18
Preparation Dehydrohalogenation (-2 HX)
two ?-eliminations
2 arrangements of diBrs gt same acetylene
19
Preparation Dehydrohalogenation (-2 HX)
two ?-eliminations
2 arrangements of diBrs gt same acetylene
20
Preparation Dehydrohalogenation (-2 HX)
21
Reactions - several like CC - additions
A. Reduction - addition of hydrogen
syn addition (2x)
22
Reactions - several like CC - additions
A. Reduction - addition of hydrogen
With choice of catalyst - stop at olefin (add 1
eq H2).
Lindlar cat.
syn addition (2x)
23
Chemical reduction of a triple bond.
trans olefin for internal acetylenes
24
Acetylene chemistry - recall olefin chemistry
R H, alkyl
25
Hydroboration of an internal alkyne
terminal
26
Terminal acetylene
hindered borane adds once
di-sec-isoamylborane or HB(sia)2
27
Terminal acetylene
hindered borane adds once
di-sec-isoamylborane or HB(sia)2
tautomerism H transfer (O to C)
28
internal with oxidation - ketone
29
(No Transcript)
30
regiochemistry
31
enol-keto tautomerism H transfer C ? O
from HB/O Hg2/H2O other rxs
mechanism e(-) arrows
or
32
Hydration of acetylenes
terminal yne - HBR2/O ? aldehyde
- Hg/H2O ? ketone
internal yne
- either ? ketone(s)
33
electrophilic additions Br2 / Cl2
Assume bromonium (chloronium) ion ( like alkene
X2 addition )
Mechanism for 1st addition of X2
34
addition of HX
vinyl bromide
35
addition of HX - second addition
2o carbocation with resonance
36
How could the vinyl bromide be converted into the
Z-olefin? Use any number of reactions but show
all necessary reagents and expected products of
each step.
how?
a. H2/Lindlar(cat.)
how?
Na-NH2
or b. (1)BH3, (2)AcOH/?
37
convert 2-bromopropene to 2-hexanone
38
compare carbon skeleton functional groups
convert 2-bromopropene to 2-hexanone
39
compare carbon skeleton functional groups
40
(No Transcript)