KIDNEY RLO 1 - PowerPoint PPT Presentation
1 / 6
Title: KIDNEY RLO 1
1
KIDNEY RLO 1 anatomy
Page 1
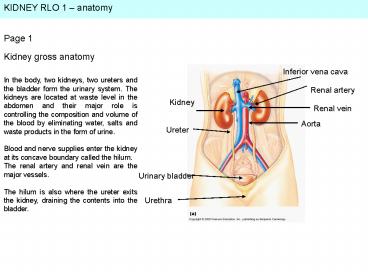
Kidney gross anatomy
Inferior vena cava
In the body, two kidneys, two ureters and the
bladder form the urinary system. The kidneys are
located at waste level in the abdomen and their
major role is controlling the composition and
volume of the blood by eliminating water, salts
and waste products in the form of urine. Blood
and nerve supplies enter the kidney at its
concave boundary called the hilum. The renal
artery and renal vein are the major vessels. The
hilum is also where the ureter exits the kidney,
draining the contents into the bladder.
Renal artery
Kidney
Renal vein
Aorta
Ureter
Urinary bladder
Urethra
2
KIDNEY RLO 1 anatomy
Page 2
Renal capsule
Kidney internal structure
Cortex
The kidney is surrounded by a fibrous capsule
called the renal capsule. Internally there is an
outer cortex layer, and inner medulla which
comprises of the medullary pyramids which are
striped in appearance. This striped feature is
due to the position of the tubes and collecting
ducts associated with the nephron, the functional
unit of the kidney (see page 3). Urine formed in
the tubules and collecting ducts of the kidney
drain into the renal pelvis, and exits the kidney
via the ureter.
Renal pelvis
Medullary pyramid
Ureter
Fig 2. Vertical section of the kidney
3
KIDNEY RLO 1 anatomy
Page 3
The nephron
Distal convoluted tubule
Bowmans capsule
The nephron is the basic functional unit of the
kidney, and there are around 1 million per
kidney. The nephron is a tube with different
regions specialised in different functions. The
nephron begins with a cup-like structure called
Bowmans capsule which opens into a coiled region
of tube called proximal convoluted tubule. This
tubule thins and straightens into the loop of
Henle, which then forms another coiled region
called the distal convoluted tubule. The distal
tubule empties into the collecting duct. The
long Loop of Henle extends down into the renal
medulla of the kidney.
Proximal convoluted tubule
Renal cortex
Renal medulla
Loop of Henle
Collecting duct
Fig 3. The nephron
4
KIDNEY RLO 1 anatomy
Page 4
Cortical Nephron
Types of nephron
Juxtamedullary Nephron
There are two types of nephron. The
juxtamedullary nephron has a long loop of Henle
which penetrates into the medulla. The cortical
nephron which is shorter and remains within the
renal cortex.
Renal cortex
Renal medulla
Fig 4. Types of nephron
5
KIDNEY RLO 1 anatomy
Page 5
Glomerulus
Efferent arteriole
Afferent arteriole
Blood supply to the nephron
In order to perform its function of removing
waste products from the blood, and regulating
water and electrolyte balance, the nephrons have
a rich blood supply. The renal artery branches
into high-pressure afferent arterioles which form
a knot of capillaries called the glomerulus,
which sit within the Bowmans capsule. The
glomeruls drains into the efferent arteriole
(Efferent Exit) which entwines the kidney
tubules and forms large loops parallel to the
loop of Henle, called the vasa recta. The blood
vessels re-join and exit the kidney in the renal
vein.
Vasa recta
Fig 5. Blood supply to the nephron
6
KIDNEY RLO 1 anatomy
Page 6
B
Passage of Urine
A
Urine formed in each nephron drains down the
collecting ducts (A). The collecting ducts empty
into the renal pelvis (B). Urine exits via the
ureter, which joins each kidney to the bladder
(C). From the bladder, urine is voluntarily
eliminated through a small tube called the
urethra, in the process of micturation (C).
Ureter
Bladder
C
Urethra