STL Functors: Functions vs. Function Objects - PowerPoint PPT Presentation
Title:
STL Functors: Functions vs. Function Objects
Description:
STL Functors: Functions vs. Function Objects STL Functors support function call syntax Algorithms invoke functions and operators E.g., calling operator – PowerPoint PPT presentation
Number of Views:64
Avg rating:3.0/5.0
Title: STL Functors: Functions vs. Function Objects
1
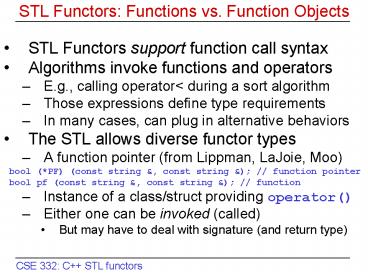
STL Functors Functions vs. Function Objects
- STL Functors support function call syntax
- Algorithms invoke functions and operators
- E.g., calling operatorlt during a sort algorithm
- Those expressions define type requirements
- In many cases, can plug in alternative behaviors
- The STL allows diverse functor types
- A function pointer (from Lippman, LaJoie, Moo)
- bool (PF) (const string , const string ) //
function pointer - bool pf (const string , const string ) //
function - Instance of a class/struct providing operator()
- Either one can be invoked (called)
- But may have to deal with signature (and return
type)
2
STL Functors Extend STL Algorithms
- Make the algorithms/containers even more general
- Can be used parameterize policy
- E.g., the order produced by a sorting algorithm
- E.g., the order maintained by an associative
container - Each functor does a single, specific operation
- Often implemented as small functions or
classes/structs - E.g., a struct with one public member function,
operator() - Function objects may also have member variables
- Arguments not stored may be supplied at point of
call - Member variables can parameterize the operation
- E.g., the value k for a functor that adds k to
another value - E.g., arguments for an invocation on a remote
object
3
Function Object Use in an Algorithm
- struct GT_magnitude
- public binary_functionltdouble,
- double,
- boolgt
- bool operator()
- (double x, double y)
- return
- fabs(y) lt fabs(x)
- struct LT_magnitude
- public binary_functionltdouble,
- double,
- boolgt
- bool operator()
- (double x, double y)
- return
- fabs(x) lt fabs(y)
int main (int, char ) vectorltdoublegt u,v
for (double d 0.0 d lt 10.1 d 1.0)
u.push_back (d) v.push_back (d)
sort (u.begin(), u.end(),
GT_magnitude()) sort (v.begin(), v.end(),
LT_magnitude()) ostream_iteratorltdoublegt
o (cout, ) copy (u.begin(), u.end(), o)
copy (v.begin(), v.end(), o) return 0
4
Function Use in an Algorithm
- include ltiostreamgt
- include ltvectorgt
- include ltstringgt
- include ltiteratorgt
- include ltalgorithmgt
- using namespace std
-
- struct Employee
- Employee (const char n, int i) name_(n),
id_(i)
- string name_
- int id_
-
-
- typedef Employee EmployeePtr
-
- ostream operatorltlt (ostream os,
- const EmployeePtr e)
- os ltlt e-gtname_ ltlt " " ltlt e-gtid_ ltlt " "
- return os
int main (int, char )
vectorltEmployeePtrgt v
v.push_back(new Employee("Claire", 23451))
v.push_back(new Employee("Bob", 12345))
v.push_back(new Employee("Alice", 54321))
cout ltlt "v "
copy (v.begin(), v.end(),
ostream_iteratorltEmployeePtrgt(cout))
cout ltlt endl // "v
Claire 23451 Bob 12345 Alice 54321 "
sort (v.begin(),
v.end(), id_compare)
cout ltlt "v "
copy (v.begin(),
v.end(), ostream_iteratorltEmployeePtrgt(co
ut)) cout ltlt
endl // "v Bob 12345 Claire 23451 Alice
54321 "
// clean up pointers "own" the heap objects
for (vectorltEmployeePtrgtite
rator i v.begin()
i ! v.end() i)
delete i
return 0
heap object
function name ok here
5
Function Object Use in a Container
- include ltsetgt
- include ltstringgt
- include ltiteratorgt
- include ltalgorithmgt
- using namespace std
-
- struct Employee
- Employee (const char n, int i) name_(n),
id_(i)
- string name_
- int id_
-
- ostream operatorltlt (ostream os,
- const Employee e)
- os ltlt e.name_ ltlt " " ltlt e.id_ ltlt "
- return os
-
-
- // set needs this (orders by name then id)
- bool operatorlt (const Employee e, const
Employee f)
int main (int, char ) vectorltEmployeegt v
v.push_back(Employee
("Claire", 23451))
v.push_back(Employee
("Bob", 12345))
v.push_back(Employee
("Alice", 54321))
cout ltlt "v "
copy (v.begin(),
v.end(), ostream_iteratorltEmployeegt(cout)
) // "v
Claire 23451 Bob 12345 Alice 54321 "
setltEmployeegt s
s.insert(v.begin(), v.end())
cout ltlt "s "
copy (s.begin(), s.end(),
ostream_iteratorltEmployeegt(cout))
// "s Alice 54321 Bob
12345 Claire 23451
setltEmployee, EmployeeIdCompgt t
t.insert(v.begin(), v.end())
cout ltlt "t "
copy (t.begin(), t.end(), ostream_iteratorltEmpl
oyeegt(cout))
// "t Bob 12345 Claire 23451 Alice 54321
return 0
temporary object
function object needed
6
STL ltfunctionalgt Before and After C11
- Parts were deprecated in C11, but are still
available in Visual C 2010 - E.g., inherit from unary_function and
binary_function to decorate a callable object
with associated types reflecting its function
call signature - E.g., make a functor for a member function call
through a pointer using mem_fun - E.g., make a functor for a member function call
through a reference using mem_fun_ref - E.g., bind first argument using
binder1stltBinaryFungt - E.g., bind second argument using
binder2ndltBinaryFungt - See http//www.sgi.com/tech/stl/table_of_contents.
html for more details - New versions introduced in C11, are also
available in Visual C 2010 - E.g., bind any argument using bind and _1 _2 _3
etc. - E.g., make a functor for a member function call
through pointer or reference using mem_fn - E.g., wrap a callable object with a function call
signature using function - New versions provide similar capabilities, but
are more consistent and general than before - Availability may depend on compiler version,
older code may involve previous versions - See http//en.cppreference.com/w/cpp/utility/funct
ional for more details
7
Pre-C11 Member Function Adaptor Example
- // Based on the SGI C STL page examples
- struct B virtual void print() 0
- struct D1 public B void print() coutltlt"I'm a
D1"ltlt endl - struct D2 public B void print() coutltlt"I'm a
D2"ltlt endl - int main(int, char )
- D1 d1
- D2 d2
- vectorltBgt v
- vectorltD2gt w
- v.push_back(d1) v.push_back(d2)
- v.push_back(d2) v.push_back(d1)
- w.push_back(d2)
- for_each(v.begin(), v.end(), mem_fun(
Bprint)) - cout ltlt endl ltlt endl
- for_each(w.begin(), w.end(), mem_fun_ref(
Bprint)) - return 0
different wrappers needed
8
C11 Member Function Adaptor Example
- // Previous example modified to use mem_fn in
both cases - struct B virtual void print() 0
- struct D1 public B void print() coutltlt"I'm a
D1"ltlt endl - struct D2 public B void print() coutltlt"I'm a
D2"ltlt endl - int main(int, char )
- D1 d1
- D2 d2
- vectorltBgt v
- vectorltD2gt w
- v.push_back(d1) v.push_back(d2)
- v.push_back(d2) v.push_back(d1)
- w.push_back(d2)
- for_each(v.begin(), v.end(), mem_fn(
Bprint)) - cout ltlt endl ltlt endl
- for_each(w.begin(), w.end(), mem_fn(
Bprint)) - return 0
same wrapper for both
9
STL Functor Concepts
- Basic Functor Concepts
- Generator
- Unary Function
- Binary Function
- Adaptable Function Objects (turn functions into
function objects) - Adaptable Generator
- Adaptable Unary Function
- Adaptable Binary Function
- Predicates (return a boolean result)
- Predicate
- Binary Predicate
- Adaptable Predicate
- Adaptable Binary Predicate
- Strict Weak Ordering
- Specialized Concepts
- Random Number Generator
- Hash Function
10
STL Functor Concept Hierarchy
Assignable
is-refined-by
Generator
Binary Function
Unary Function
Adaptable Generator
Binary Predicate
Adaptable Binary Function
Random Number Generator
Predicate
Adaptable Unary Function
Hash Function
Adaptable Predicate
Adaptable Binary Predicate
Strict Weak Ordering
Basic Function Object
Predicate
Specialized
Adaptable Function Object
11
Assignable Concept
- Does not refine any other STL concept
- Valid Expressions
- Copy Constructor
- X(x) X x(y) X x y
- Assignment
- x y
- Models of Assignable
- Almost every non-const C built-in type
- and function pointers
- but not functions (cannot construct or assign
them) - Here, all Basic Function Object concepts
- Generator, Unary Function, Binary Function
- And the concepts that specialize them
12
Generator Concept
- Refines Assignable
- Abstracts pointers to 0-ary functions (no
arguments) - Valid Expressions
- Function call signature with no arguments
- f()
- Semantics
- Returns some value of type Result
- Different invocations may return different values
- Or, can represent a constant as a 0-ary functor
- Invocation may change the function objects
internal state - So, operator() need not be a const member
function
13
Generator Example
- Goal fill a vector with random numbers
- Generic generate algorithm
- Fills in a range given in its 1st and 2nd
arguments - applies Generator Concept to its 3rd argument
- Here, the functor is simply a function pointer
- To the ltcmathgt (0-ary) rand() function
- vectorltintgt v(100)
- generate(v.begin(), v.end(), rand)
14
Unary Function Concept
- Also a refinement of Assignable
- Valid Expression
- Function call signature with one argument f(x)
- May ignore or use single argument
- Similar return, const semantics to generator
- Pre-C11 Example using unary_function
- struct sine
- public unary_functionltdouble,doublegt
- double operator()(double x) const
- return sin(x)
- sine func
- C11 Example using function
- functionltdouble (double)gt func(sin)
15
Binary Function Concept
- Also a refinement of Assignable
- Valid Expression
- Function call signature with two arguments
f(x,y) - May use or ignore either or both of its arguments
- Similar const and return semantics to Unary
Function - Pre-C11 Example using binary_function
- struct exponentiate
- public binary_functionltdouble,double,doublegt
- double operator()(double x, double y) const
- return pow(x,y)
- C11 Example using function
- functionltdouble (double,double)gt func(pow)
16
Adaptable Function Objects
- Allow functors to be used with Function Object
Adaptors - Associated types of argument(s), and especially
return value - How to access these associated types ?
- Define Adaptable Function Object Concepts
- Adaptable Generator
- F1result_type
- Adaptable Unary Function
- F2argument_type F2result_type
- Adaptable Binary Function
- F3first_argument_type F3second_argument_typ
e F3result_type - Models
- Function pointers like Result(f)(Arg) do not
model these concepts - Helper adapters make Adaptable Function Objects
from these functions - Pre-C11 ptr_fun(f) or C11 functionltResult
(Arg)gt(f)
17
Adaptable Function Object Example
- Each value printed out will be 3.0 larger than
the corresponding element in v1 - int main(int, char )
- const int vector_size 10
- vectorltdoublegt v1(vector_size)
- generate(v1.begin(), v1.end(), rand) //
random values - transform(v1.begin(), v1.end(),
- ostream_iteratorltdoublegt(cout, " "),
- bind1st(plusltdoublegt(), 3.0))
- transform(v1.begin(), v1.end(),
- ostream_iteratorltdoublegt(cout, " "),
- stdbind(plusltdoublegt(),
- stdplaceholders_1,
3.0)) - return 0
Pre-C11 function adapter
Adaptable function objects
C11 function adapter
18
Predicate Concepts
- Predicate
- Refinement of Unary Function
- Return type must be convertible to bool
- Adaptable Predicate
- Refinement of Predicate, Adaptable Unary Function
- Adds typedefs for argument, return types
- Binary Predicate
- Refinement of Binary Function
- Return type again must be convertible to bool
- Adaptable Binary Predicate
- Refinement of Binary Predicate, Adaptable Binary
Function - Adds typedefs for the 2 arguments, return types
- Strict Weak Ordering
- Refinement of Binary Predicate (for comparison
operations) - Similar semantics to operatorlt but with type
constraints