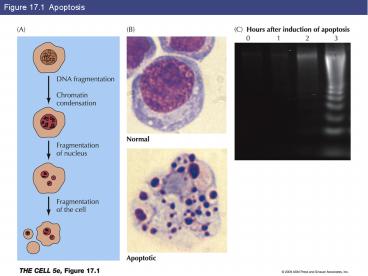
Figure 17.1 Apoptosis - PowerPoint PPT Presentation
Title:
Figure 17.1 Apoptosis
Description:
Figure 17.1 Apoptosis Figure 17.2 Phagocytosis of apoptotic cells Key Experiment 17.1: Photomicrographs of a normal worm (A) and a ced-3 mutant (B) Figure 17.3 ... – PowerPoint PPT presentation
Number of Views:272
Avg rating:3.0/5.0
Title: Figure 17.1 Apoptosis
1
Figure 17.1 Apoptosis
2
Figure 17.2 Phagocytosis of apoptotic cells
3
Key Experiment 17.1 Photomicrographs of a normal
worm (A) and a ced-3 mutant (B)
4
Figure 17.3 Programmed cell death in C. elegans
5
Figure 17.4 Caspase targets
6
Figure 17.5 Caspase activation
7
Figure 17.6 The Bcl-2 family
8
Figure 17.7 Regulatory interactions between
Bcl-2 family members
9
Figure 17.8 The mitochondrial pathway of
apoptosis
10
Figure 17.9 Regulation of caspases by IAPs in
Drosophila
11
Figure 17.10 Role of p53 in DNA damage-induced
apoptosis
12
Figure 17.11 The PI 3-kinase pathway and cell
survival
13
Figure 17.12 Cell death receptors
14
Figure 17.12 Cell death receptors (Part 1)
15
Figure 17.12 Cell death receptors (Part 2)
16
Figure 17.13 Skin fibroblasts
17
Figure 17.14 Endothelial cells
18
Figure 17.15 Proliferation of endothelial cells
19
Figure 17.16 Liver regeneration
20
Figure 17.17 Stem cell proliferation
21
Figure 17.18 Formation of blood cells
22
Figure 17.19 Renewal of the intestinal epithelium
23
Figure 17.19 Renewal of the intestinal
epithelium (Part 1)
24
Figure 17.19 Renewal of the intestinal
epithelium (Part 2)
25
Figure 17.19 Renewal of the intestinal
epithelium (Part 3)
26
Figure 17.20 Stem cells of the skin
27
Figure 17.21 Muscle satellite cells
28
Figure 17.22 Hematopoietic stem cell
transplantation
29
Key Experiment 17.2 Embryonic stem cells
differentiate in culture to a variety of cell
types
30
Figure 17.23 Culture of mammalian embryonic stem
cells
31
Figure 17.24 Differentiation of embryonic stem
cells
32
Figure 17.25 Cloning by somatic cell nuclear
transfer
33
Figure 17.26 Therapeutic cloning
34
Figure 17.27 Induced pluripotent stem cells