Respiratory System - PowerPoint PPT Presentation
1 / 34
Title:
Respiratory System
Description:
Respiratory System Internal Respiration Internal respiration is the process by which the gases in the air that has already been drawn into the lungs by external ... – PowerPoint PPT presentation
Number of Views:149
Avg rating:3.0/5.0
Title: Respiratory System
1
Respiratory System
2
Internal Respiration
- Internal respiration is the process by which the
gases in the air that has already been drawn into
the lungs by external respiration are exchanged
with gases in the blood/tissues so that carbon
dioxide (CO2) is removed from the blood and
replaced with oxygen (O2).
3
External Respiration
- External respiration concerns the process by
which external air is drawn into the body in
order to supply the body with oxygen gas, and the
(used) air is expelled from the lungs in order to
remove carbon dioxide from to body
4
Cellular Respiration
- Internal respiration is important to cells
because without oxygen, all body functions would
cease due to a lack of ATP
5
Main Function
- Gas Exchange
- To work closely with the cardiovascular system to
supply the body with oxygen and to dispose of
carbon dioxide
6
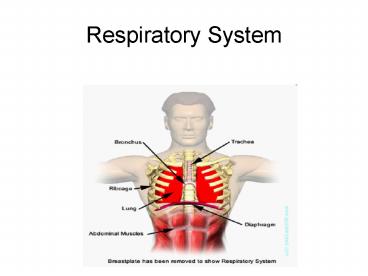
Organs Include
- 1. Nose
- 2. Pharynx
- 3. Larynx
- 4. Trachea
- 5. Bronchi
- And their smaller branches
- 6. Lungs
- Containing alveoli (terminal sacs)
7
The Nose
- Externally visible
- Nostrils External Nares
- Internally Nasal Cavity
- Divided by nasal septum
- Olfactory receptors in the superior cavity in the
mucosa
8
Function of Nose
- Mucosa lining rests on thin walled veins that
warm the air - Mucous produced by the mucosa, moistens the air
and traps bacteria and other particulates
9
Pharynx
- 13cm muscular passageway (Throat)
- Food and air passage
- Nasopharynx- Superior
- Oropharynx- central
- Laryngopharynx- Inferior
10
Pharynx
- Tonsils are located in the pharynx
- Pharangeal or Adenoids (superior)
- Palatine (oropharynx)
- Lingual (base of tongue)
11
Epiglottis
- epiglottis guards the entrance of the glottis
- normally pointed upward during breathing with its
underside functioning as part of the pharynx - during swallowing elevation of the hyoid bone
draws the larynx upward and prevents food from
going into the trachea instead directs it to the
esophagus
12
Larynx
- AKA Voice box, routes air, role in speech
- Inferior to pharynx
- Eight rigid hyaline cartilage
- Largest is Thyroid cartilage (Adams Apple)
- Protrusion angel 90 in males and 120 in females
- Cartilage flap Epiglottis protects opening
13
Larynx
- Mucous Membrane forms Vocal folds (vocal cords)
- allow us to speak
- Glottis - Slit-like passageway between the vocal
folds
14
Trachea
- Windpipe
- Goes to the 5th Thoracic Vertebrae
- Reinforced with C-shaped cartilage rings to keep
it open anteriorly and allow flexibility for food
to pass through the esophagus posteriorly
15
Main Bronchi
- Division of the trachea
- Runs obliquely
- Ends at the hilus (medial depression of the lung)
- The right is wider and shorter and more often the
site of inhaled objects
16
Bronchioles
- Primary bronchi subdivide into smaller branches
- Bronchial Tree
- Secondary Bronchi
- Tertiary Bronchi
- Then Bronchioles
17
Alveoli
- Small cavity or air sac
- Millions of clustered alveoli look like bunches
of grapes - Site of gas exchange
- Make up a bulk of the lungs
- Also stroma which is elastic
18
Diaphragm
- sheet of internal muscle that extends across the
bottom of the rib cage - The diaphragm separates the thoracic cavity
(heart, lungs ribs) from the abdominal cavity
and performs an important function in
respiration.
19
Diaphragm
- Inspiration During inhalation, the diaphragm
contracts, thus enlarging the thoracic cavity
(the external intercostal muscles also
participate in this enlargement). This reduces
intra-thoracic pressure In other words,
enlarging the cavity creates suction that draws
air into the lungs
20
Diaphragm
- Expiration When the diaphragm relaxes, air is
exhaled by elastic recoil of the lung and the
tissues lining the thoracic cavity in conjunction
with the abdominal muscles
21
Gas Exchange
- Diffusion, the spontaneous movement of gases,
without the use of any energy or effort by the
body, happens between the gas in the alveoli and
the blood in the capillaries in the lungs.
22
CO2 and O2
- The hemoglobin molecule is the primary
transporter of oxygen - Oxygen from the air enters the blood, and carbon
dioxide from the body trades places with the
oxygen by leaving the blood and entering the
alveoli. - Carbon dioxide is then exhaled out of the lungs.
- Oxygen must enter the blood and carbon dioxide
must leave the blood at a regular rate for our
body to function correctly.
23
Pulmonary Circulation
- The Pulmonary circulation is the portion of the
cardiovascular system which transports
oxygen-depleted blood away from the heart, to the
lungs, and returns oxygenated blood back to the
heart.
24
Systemic Circulation
- Systemic circulation is the portion of the
cardiovascular system which transports oxygenated
blood away from the heart, to the rest of the
body, and returns oxygen-depleted blood back to
the heart. - Carbon Dioxide is picked up along the way and is
also carried back to the heart to be exhaled
through the lungs.
25
Bone Structures
- Conchae- Increase surface area of mucosa and
create turbulance - Palate- Separates from oral cavity
- Hard palate (bone ) is anterior
- Soft palate(tissue) is posterior
26
Cleft Palate
- Genetic Defect
- Bones do not fuse medially
- Causes Problems
- Breathing
- Chewing
- Speaking
27
Paranasal Sinuses
- Surround the nasal cavity
- Located in Bones
- Frontal
- Sphenoid
- Ethmoid
- Maxillary
28
Function of Sinuses
- Lighten the skull
- Resonance for speech
- Produce mucous
- Nasolacrimal ducts
- Drain tears from eyes
29
Rhinitis, Sinusitis, Sinus Headache
- Inflammation of the nasal mucosa
- Virus
- Allergens
- Mucosa is continuous so that these infections
often spread
30
Lungs
- Occupy entire thoracic cavity (except mediastinum
where the heart is) - Narrow superior portion (apex) is deep to
clavicle - Broad base rests on the diaphragm
- Left lung 2 lobes
- Right lung 3 lobes
31
Lungs
- Surface covering is visceral serosa called
Pulmonary Pleura - Walls of the cavity are covered with parietal
pleura - Pleural fluid reduces friction during breathing
movements
32
Pleurisy
- Inflammation of the pleura due to decreased
secretion of pleural fluid - Pain with each breath
- Excess fluid may hinder breathing
33
Respiratory Membrane
- Thin squamous epithelial cells
- Alveolar pores connect sacs
- External surfaces have a cobweb of capillaries
- Respiratory Membrane is the Air / Blood barrier
34
Airway Obstruction
- Heimlich Maneuver
- Physical Procedure where someone assists in
dislodging a blockage - Tracheostomy
- Surgical Procedure cuts a new opening