Abstract - PowerPoint PPT Presentation
1 / 1
Title: Abstract
1
Genotypes and phenotypesin Anorexia Nervosa
Marek Brandys1, Judith Hendriks1, Unna Danner2,3,
Annemarie van Elburg2,4, Roger Adan1
1-Rudolf Magnus Institute of Neuroscience, Dept.
of Neuroscience and Pharmacology, University
Medical Center Utrecht, The Netherlands 2-Rintveld
Centre for Eating Disorders, Altrecht Mental
Health Institute, Zeist, The Netherlands 3-Dept.
of Clinical Health Psychology, Utrecht
University, The Netherlands 4-Rudolf Magnus
Institute of Neuroscience, Department of Child
and Adolescent Psychiatry, University Medical
Centre, Utrecht, The Netherlands
Abstract
Conclusions with regards to DRD2
Twin studies demonstrate that Anorexia Nervosa
(AN) is a highly heritable psychiatric disease.
The mechanisms of genetic susceptibility to AN
remain unclear. In this study we aim to determine
how genotypes affect phenotypes relevant to this
disease. Treatment outcome will also be
investigated in relation to genotypes and
phenotypes. Preliminary results concerning
Dopamine Receptor D2 (DRD2) gene are presented.
- DRD2 gene polymorphism is associated with AN
- Allele G is more often observed in AN than in
controls - It indicates the importance of dopamine signaling
in the etiology of the disease - In the literature, DRD2 has been associated with
Novelty Seeking, Reward Sensitivity and
Impulsivity - The susceptibility to AN conferred by DRD2
polymorphism may be mediated by personality
traits.
Next Steps
- How individuals with G allele are different from
those without it? To check - Treatment Outcome
- Novelty Seeking
- Reward Sensitivity
- Self-Reported Activity
- Set-Shifting
- BMI (highest ever, lowest ever)
Objectives
To determine how genes associated with AN affect
its subphenotypes and treatment outcome.
Methods and Procedure
- DNA and phenotypic data collected from patients
- Candidate genes genotyped
- Genetic info combined with phenotypic data
- diagnoses, BMI
- treatment course and outcome
- questionnaires (novelty seeking, harm avoidance,
reward sensitivity, anxiety, obsessive-compulsive
traits and others) - cognitive measures (set-shifting)
- Statistical analysis - to see if
- Distribution of genotypes / alleles is different
between patients and controls - Distribution is different between groups of AN
patients (based on phenotypic measures)
Phenotype e.g. reward sensitivity
Genotype
C/C
C/G
G/G
- Interpretaion which mechanisms may underlie it?
Dopamine signaling plays role in... - Reward processing
- Hedonic eating
- Homeostatic eating
- Cognitive flexibility
- Locomotor activity
- In the future, other genes and phenotypes will be
investigated in a similar fashion.
G e n o t y p e s
- anhedonia
- food liking/wanting
- emaciation
- set-shifting deficit
- hyperactivity
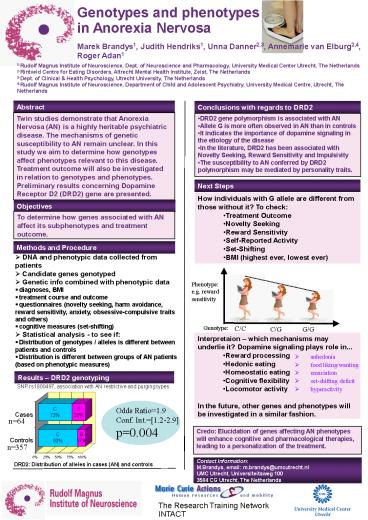
Results DRD2 genotyping
SNP rs1800497, association with AN restrictive
and purging types
Odds Ratio1.9 Conf. Int.1.2-2.9 p0.004
n64
Credo Elucidation of genes affecting AN
phenotypes will enhance cognitive and
pharmacological therapies, leading to a
personalization of the treatment.
n357
DRD2 Distribution of alleles in cases (AN) and
controls
Contact Information M.Brandys, email
m.brandys_at_umcutrecht.nl UMC Utrecht,
Universiteitsweg 100 3584 CG Utrecht, The
Netherlands
The Research Training Network INTACT