India's First Empires - PowerPoint PPT Presentation
1 / 28
Title:
India's First Empires
Description:
Start of the Mauryan Empire. Chandragupta Maurya 321-298 BC: Chandragupta s army of 9,000 elephants and 700,000 soldiers trampled neighboring kingdoms. – PowerPoint PPT presentation
Number of Views:1486
Avg rating:3.0/5.0
Title: India's First Empires
1
India's First Empires
2
Persian King Darius I
- Darius I came through the Khyber Pass and
conquered northwestern India. - For 200 years, Indus Valley was ruled by Persian
satrap, or governor. - First time the Indians felt both the benefits
(unity and order) and burdens of centralized
control.
3
Alexander the Great
- 326 BC Alexander the Great invaded India with
the goal of unifying all of Northern India. - Only stayed for 5 years before giving up on his
goal. - He left generals in his place to keep order among
the people.
4
Chandragupta Maurya
- 321 BC Claimed throne after killing the
unpopular Nanda King. - Start of the Mauryan Empire.
5
Chandragupta Maurya
- 321-298 BC Chandraguptas army of 9,000
elephants and 700,000 soldiers trampled
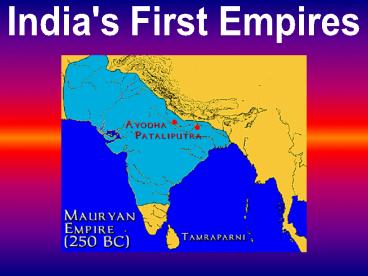
neighboring kingdoms. - United all of North India under his rule.
- Indus Valley, Ganges Valley, and Southern
Himalayas.
6
Chandragupta Maurya
- Divided Empire into 4 provinces.
- Each headed by a royal prince.
- Each split into different districts with
governors who would collect taxes. - Government is the science of Punishment
- -Chandragupta Maurya
7
Chandragupta Maurya
- Chandragupta ruled by force and fear.
- Planted government spies to make sure no one was
planning a revolt. - (Like the one he planned when he killed the Nanda
King!!!) - Trusted no one.
- Made the chef taste his meal before he would eat
it. - Slept in a different room each night in order to
make sure no one would kill him in his sleep.
8
Chandragupta Maurya
- 301 BC Gave up the throne and converted to
Jainism. - Jains taught nonviolence and respect for all
life. - Joined in the Jainist custom of fasting until he
starved to death.
9
Chandraguptas Son
- 301 BC Ruled for 32 years. Little is known about
his rule.
10
(No Transcript)
11
Ashokas Warlike Behavior
- 269 BC Ashoka took the throne of the Mauryan
Empire. - At first he was warlike.
- He waged a bloody war against the neighboring
state of Kalinga. - 100,000 soldiers were slain and even more
civilians perished.
12
Asokas Good Works
- Filled Asoka with remorse and he decided to rule
according to Buddhas teachings of peace to all
beings. - He sent out an apology to the southern tribes and
promised kind treatment in the future.
13
Asokas Good Works
- Ordered huge pillars to be erected inscribed with
a public announcement of his new policies. - Promoted religious tolerance.
- Built roads with wells and rest houses every 9
miles so travelers could rest.
14
(No Transcript)
15
(No Transcript)
16
Asoka
- Instead of spies, Asoka employed officials of
righteousness to look out for the welfare of
Indians of every caste. - They were there to help the unfortunate.
17
(No Transcript)
18
Asoka
- Sent hundreds of Buddhist missionaries to
neighboring lands such as Ceylon. - Thanks to Asoka, Buddhism spread far beyond India
and became a major world religion with millions
of followers.
19
Asokas Death
- 232 BC Last strong ruler of the Mauryan dynasty.
- His policies of toleration and nonviolence failed
to hold the Mauryan Empire together. - 180 BC Mauryan Empire torn apart by rivalry
among local provinces.
20
Start of the Gupta Empire
- Chandra Gupta I married the daughter of an
influential royal family. - 320 AD Chandra Gupta I crowned King of upper
Ganges Valley. - Great King of Kings
21
Start of the Gupta Empire
- His reign brought the Golden Age to India.
- Gupta Dynasty ruled a mighty Empire from 320-467
AD.
22
Samudra Gupta
- Chandra Guptas son.
- 335 AD Crowned King of the Gupta Empire.
- Expanded the Empire through 40 years of conquest.
23
(No Transcript)
24
Daily Life in the Gupta Empire
- First period that historians have a lot of
information about the daily life. - Most Indians lived in small villages.
- Majority were farmers.
- Most families were patriarchal.
- Headed by the eldest male.
- Tax on water.
- Farmers owed a large part of their earnings to
the King.
25
Southern India Daily Life
- The Tamil, were matriarchal.
- Headed by the mother rather than the father.
26
Height of the Gupta Empire
- 3rd Gupta Emperor 375-415 AD
- Chandra Gupta II, created a place that was full
of excitement and growth. - Praised for his heroic qualities.
- Defeated the Shakas
- Enemies to the west. After defeating them he
added their coastal territory to his empire. - This allowed the Guptas to trade with the
Mediterranean world.
27
(No Transcript)
28
Gupta Empire Decline
- 425 AD Chandra Gupta II died.
- New invaders threatened North India
- The Hunas
- Related to the Huns.
- Over the next 100 years, the Gupta Empire broke
into small kingdoms. - Many were overrun by the Hunas.
- 535 AD Empire ended.