Bus Characteristics - PowerPoint PPT Presentation
1 / 17
Title:
Bus Characteristics
Description:
... concessione viene propagato in catena finch l'aspirante master non ... Catena a margherita: tutti i dispositivi condividono una stessa linea di richiesta ... – PowerPoint PPT presentation
Number of Views:57
Avg rating:3.0/5.0
Title: Bus Characteristics
1
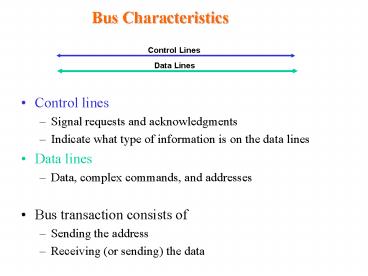
Bus Characteristics
- Control lines
- Signal requests and acknowledgments
- Indicate what type of information is on the data
lines - Data lines
- Data, complex commands, and addresses
- Bus transaction consists of
- Sending the address
- Receiving (or sending) the data
Control Lines
Data Lines
2
Struttura del Bus
- Un bus è composto da 3 gruppi di segnali
- segnali di dato normalmente sono in numero pari
ad un multiplo di 8 possono essere bidirezionali
o unidirezionali (in tal caso è necessario un
numero doppio di linee) - segnali di indirizzo identificano lo slave con
cui il master vuole comunicare (nonché quale
parte dello slave è coinvolta, nel caso della
memoria indicano la locazione da cui leggere o su
cui scrivere dati) possono essere trasmessi
sulle stesse linee dei dati per ridurre le linee
del bus e/o i pin dei dispositivi connessi - segnali di controllo forniscono informazioni di
stato, di temporizzazione, di tipo (dei dati sul
bus).
3
Advantages and Disadvantages of Buses
- Advantages
- Versatility
- New devices can be added easily
- Peripherals can be moved between computer systems
that use the same bus standard - Low Cost
- A single set of wires is shared in multiple ways
- Disadvantages
- It creates a communication bottleneck
- The bus bandwidth limits the maximum I/O
throughput - The maximum bus speed is largely limited by
- The length of the bus
- The number of devices on the bus
- It needs to support a range of devices with
widely varying latencies and data transfer rates
4
Types of Buses
- Processor-Memory Bus (proprietary)
- Short and high speed
- Matched to the memory system to maximize the
memory-processor bandwidth - Optimized for cache block transfers
- I/O Bus (industry standard, e.g., SCSI, USB, ISA,
IDE) - Usually is lengthy and slower
- Needs to accommodate a wide range of I/O devices
- Connects to the processor-memory bus or backplane
bus - Backplane Bus (industry standard, e.g., PCI)
- The backplane is an interconnection structure
within the chassis - Used as an intermediary bus connecting I/O busses
to the processor-memory bus
5
A Two Bus System
Processor-Memory Bus
Processor
Memory
- I/O buses tap into the processor-memory bus via
Bus Adaptors (that do speed matching between
buses) - Processor-memory bus mainly for
processor-memory traffic - I/O busses provide expansion slots for I/O
devices
6
A Three Bus System
Processor-Memory Bus
Processor
Memory
- A small number of Backplane Buses tap into the
Processor-Memory Bus - Processor-Memory Bus is used for processor memory
traffic - I/O buses are connected to the Backplane Bus
- Advantage loading on the Processor-Memory Bus is
greatly reduced
7
I/O System Example (Apple Mac 7200)
- Typical of midrange to high-end desktop system in
1997
Processor
Processor-Memory Bus
Cache Memory
Serial ports
Audio I/O
PCI Interface/ Memory Controller
Main Memory
I/O Controller
I/O Controller
PCI
CDRom
I/O Controller
I/O Controller
SCSI bus
Disk
Graphic Terminal
Network
Tape
8
A Bus Transaction
- A bus transaction includes three parts
- Gaining access to the bus -
arbitration - Issuing the command (and address) - request
- Transferring the data
- action - Gaining access to the bus
- How is the bus reserved by a device that wishes
to use it? - Chaos is avoided by a master-slave arrangement
- The bus master initiates and controls all bus
requests - In the simplest system
- The processor is the only bus master
- Major drawback - the processor must be involved
in every bus transaction
9
Single Master Bus Transaction
- All bus requests are controlled by the processor
- it initiates the bus cycle on behalf of the
requesting device
10
Multiple Potential Bus Masters Arbitration
- Bus arbitration scheme
- A bus master wanting to use the bus asserts the
bus request line - A bus master cannot use the bus until its grant
line has been asserted - A bus master must release the bus after its use
- Bus arbitration schemes usually try to balance
two factors - Bus priority - the highest priority device should
be serviced first - Fairness(equità) - Even the lowest priority
device should never be
completely locked out from using the bus - Bus arbitration schemes can be divided into four
broad classes - Daisy chain arbitration all devices share 1
request line - Centralized, parallel arbitration multiple
request and grant lines - Distributed arbitration by self-selection each
device wanting the bus places a code indicating
its identity on the bus - Distributed arbitration by collision detection
Ethernet uses this
11
Multiple Potential Bus Masters Arbitration
- Schema di arbitraggio del bus
- Un dispositivo master per richiedere lutilizzo
del bus deve asserire la linea di richiesta - Non è possibile utilizzare il bus finchè non
arriva il proprio turno in tal caso viene
asserita la propria linea di concessione del
bus se ve nè una riservata o il segnale di
concessione viene propagato in catena finchè
laspirante master non lo cattura - Ogni master deve rilasciare il bus dopo il suo
utilizzo - Gli schemi di arbitraggio del bus cercano di
bilanciare due fattori - Priorità del dispositivo- Il dispositivo che ha
la più elevata priorità deve essere servito prima - Equità Anche il dispositivo che ha la priorità
minore deve poter accedere al bus(ovvero non ne
deve essere tagliato fuori) - Gli schemi si arbitraggio possono essere
suddivisi in 4 estese classi - Catena a margherita tutti i dispositivi
condividono una stessa linea di richiesta - Centralizzato,parallelo linee di richiesta e
concessione multiple - Distribuito, tramite auto-selezione ogni
dispositivo si identifica attraverso un codice e
ognuno accede al bus solo se non vede codici di
dispositivi aventi priorità maggiore sulle linee
di richiesta - Distribuito tramite rilevamento di
collisioneutilizzato dai dispositivi che
comunicano attraverso il protocollo Ethernet
12
Centralized Parallel Arbitration
Device 1
Device 2
Device N
Control
Data
- Used in essentially all backplane and high-speed
I/O busses
13
Daisy Chain Bus Arbitration
Device 1 Highest Priority
Device N Lowest Priority
Device 2
Grant
Grant
Grant
Release
Bus Arbiter
Request
wired-OR
- Advantage simple
- Disadvantages
- Doesnt assure fairness A low-priority
device may be locked out indefinitely - The daisy chain grant signal also limits the bus
speed(il segnale infatti deve essere propagato
lungo la catena di concessione dai dispositivi
che la condividono)
14
Synchronous and Asynchronous Buses
- Synchronous Bus
- Includes a clock in the control lines
- A fixed protocol for communication that is
relative to the clock - Advantage involves very little logic and can run
very fast - Disadvantages
- Every device on the bus must run at the same
clock rate - To avoid clock skew they cannot be long if they
are fast - Asynchronous Bus
- It is not clocked, so requires handshaking
protocol (req, ack) - Implemented with additional control lines
- Advantages
- Can accommodate a wide range of devices
- Can be lengthened without worrying about clock
skew or synchronization problems - Disadvantage slow(er)
15
Synchronous and Asynchronous Buses
- Synchronous Bus
- Vi è una linea dove viaggia il segnale di clock
tra le linee di controllo - Protocollo fisso di comunicazione basato sul
segnale di clock - Vantaggioè facilmente realizzabile poichè non
richiede un controllo elaborato e pertanto è
anche molto veloce - Svantaggi
- Ogni dispositivo deve comunicare alla stessa
frequenza di clock - Per evitare che ritardi nella propagazione dei
segnali attraverso le linee del bus provochino un
disallineamento del clock, le linee devono essere
corte se si vuole che la frequenza di clock sia
elevata - Asynchronous Bus
- Non è regolato da un segnale di clock, bensì da
un protocollo transazionale(richiede segnalidi
richiesta e conferma) - Implementato con ulteriori linee di controllo
rispetto a quelle del bus sincrono - Vantaggi
- Può essere utilizzato da unampia classe di
dispositivi - Può essere allungato senza preoccuparsi di
ritardi nella trasmissione - Svantaggio più lento (di quello sincrono)
16
Increasing the Bus Bandwidth
- Use separate address lines and data lines
- Address and data can be transmitted in one bus
cycle - Cost more bus lines
- Increase bus width
- By increasing the width of the data bus,
transfers of multiple words require fewer bus
cycles - Example SPARCstation 20s memory bus is 128 bit
wide - Cost more bus lines
- Block transfers
- Allow the bus to transfer multiple words in
back-to-back bus cycles - Only one address needs to be sent at the
beginning - Bus isnt released until the last word is
transferred - Cost (a) increased complexity (b)
decreased response time for request
17
Summary of Bus Options
- Option High performance Low cost
- Bus width Separate address Multiplex address
data lines data lines - Data width Wider is faster Narrower is cheaper
(e.g., 32 bits) (e.g., 8 bits) - Transfer size Multiple words has Single-word
transfer less bus overhead is simpler - Bus masters Multiple Single master (requires
arbitration) (no arbitration) - Clocking Synchronous Asynchronous
- Protocol Pipelined Serial