Symmetric Encryption - PowerPoint PPT Presentation
1 / 14
Title:
Symmetric Encryption
Description:
The encrypted text is larger than a symmetric version. point to multi-point does ... 'I officially notarize the association. between this particular User, and ... – PowerPoint PPT presentation
Number of Views:138
Avg rating:3.0/5.0
Title: Symmetric Encryption
1
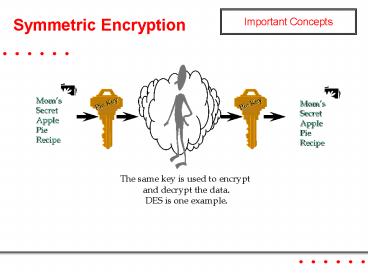
Symmetric Encryption
Important Concepts
Pie Key
The same key is used to encrypt and decrypt the
data. DES is one example.
2
Symmetric Encryption
Important Concepts
- The Advantages
- Secure
- Widely Used
- The encrypted text is compact
- Fast
- The Disadvantages
- Complex Administration
- Requires Secret Key Sharing
- Large Number of Keys
- No non-repudiation
- Keys are Subject to interception
3
Asymmetric Encryption
Important Concepts
One half of a key pair is used to encrypt, the
other half is used to decrypt. RSA is one example.
4
Asymmetric Encryption
Important Concepts
- The Advantages
- Secure
- No secret sharing
- No prior relationship
- Easier Administration
- Far fewer keys
- Supports non-repudiation
- The Disadvantages
- Slower than symmetric key
- The encrypted text is larger than a symmetric
version - point to multi-point does not scale
5
The Combination
Important Concepts
Moms Secret Apple Pie Recipe
Random Symmetric Key
Encrypted
Bills Public Key
To Bill
Digital Envelope
Key Wrapping
6
The Combination
- You get the best of both worlds
- The benefits of Symmetric Key
- Speed
- Compact Encrypted Text
- The benefits of Public Key
- Simpler Key management
- Digital Signature
- Non-Repudiation
7
Digital Certificates
Important Concepts
Certificate
Encrypted
All you need is the CAs public key to verify
the certificate and extract the certified public
key
8
What is a Certificate?
Important Concepts
- A signed packet of identifying attributes
- Identifying Attributes
- Subject Name (the user being identified)
- Public Key
- Issuer Name (trusted source identifying user)
- Validity Period
- Signature
- Specified in
- RFC 2459
- x.509 v 1-3
9
Digital Signatures
Hi level Functionality Non-Repudiation
Encrypted Digest _at_!
Hash
Signers Private Key
10
Digital Signatures
Hi level Functionality Non-Repudiation
Hash Function
match?
Signers Public Key
11
Key Generation
Certificate Issuance
- Standards
- RFC 2510
- Key may be generated by End Entity, RA, or CA
- ANSI x.9.57 - not specified but commonly used
- PKCS 11
- Key may be generated by End Entity, RA, or CA
- RSA (512 - 2048)
- DSA (512 - 2048)
- ECDSA
12
Certificate Creation
Certificate Issuance
- Standards
- PKCS 1
- RFC 2459
- Certificate and CRL Profile
- Specifies the the type and format of a
certificate - essentially x.509 with some modification
- Uses PKCS 1 specifiers
- MD5 with RSA for signature
- SHA-1 with RSA for signature
13
How do you assure that you get a real (and valid)
public key?
X.509 Digital Certificate I officially
notarize the association between this
particular User, and this particular
Public Key
14
How do I validate a certificate?
- For a certificate to be valid, the following
checks must normally succeed - todays date must fall between the starting and
ending validity dates for the certificate - the signature must be valid
- the contents of the certificate must not have
changed - the certificate issuer must be one we trust
- the certificate must not have been revoked