Cells of the Nervous System - PowerPoint PPT Presentation
1 / 8
Title:
Cells of the Nervous System
Description:
Sensory neurons (afferent) Cells of the Nervous System. Neurons. Motor neurons (efferent) Sensory neurons (afferent) Interneurons. aka interneuron or intrinsic neuron ... – PowerPoint PPT presentation
Number of Views:42
Avg rating:3.0/5.0
Title: Cells of the Nervous System
1
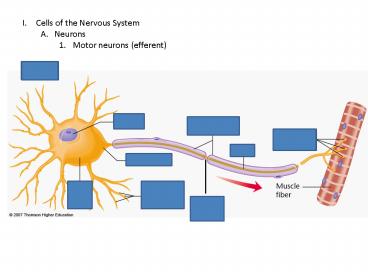
- Cells of the Nervous System
- Neurons
- Motor neurons (efferent)
Node of Ranvier
2
- Cells of the Nervous System
- Neurons
- Motor neurons (efferent)
- Sensory neurons (afferent)
3
- Cells of the Nervous System
- Neurons
- Motor neurons (efferent)
- Sensory neurons (afferent)
- Interneurons
aka interneuron or intrinsic neuron
4
- Cells of the Nervous System
- Neurons
- Glia
- Astrocyte (Astroglia) Star-shaped cells that
provide physical and nutritional support for
neurons - clean up brain debris
- transport nutrients to neurons
- hold neurons in place
- digest parts of dead neurons
- regulate content of extracellular space.
- Microglia Like astrocytes, microglia digest
parts of dead neurons. - Oligodendrocytes Provide the insulation
(myelin) to neurons in the central nervous
system. - Schwann Cells Provide the insulation (myelin)
to neurons in the peripheral nervous system.
Source http//faculty.washington.edu/chudler/glia
.html
5
- Cells of the Nervous System
- Neurons
- Glia
- Differences between neurons glia
- Neurons have TWO processes called axons and
dendrites....glial cells have only ONE. - Neurons CAN generate action potentials...glial
cells CANNOT. However, glial cells do have a
resting potential. - Neurons HAVE synapses that use
neurotransmitters...glial cells do NOT have
chemical synapses. - There are many MORE (10-50 times more) glial
cells in the brain compared to the number of
neurons.
Source http//faculty.washington.edu/chudler/glia
.html
6
II. Nerve Impulse A. Resting Potential
Negative inside, relative to the outside -70mv.
And the sodium-potassium pump keeps it that way.
7
II. Nerve Impulse A. Resting Potential B.
Action Potential
-70mv
30mv
30mv
-80mv
-70mv
Depolarization (internal electrical charge moving
toward a positive charge)
Hyperpolarization (internal electrical charge
moving more negatively, past the resting
potential)
Animation
Channel gating
8
II. Nerve Impulse A. Resting Potential B.
Action Potential C. Saltatory Conduction