Chemoreceptor Clustering - PowerPoint PPT Presentation
1 / 37
Title:
Chemoreceptor Clustering
Description:
1. Evidence from microscopy that MCPs are clustered. CheA and ... Receptor clustering was observed using fluorescence microscopy to visualize YFP-CheZ clusters ... – PowerPoint PPT presentation
Number of Views:47
Avg rating:3.0/5.0
Title: Chemoreceptor Clustering
1
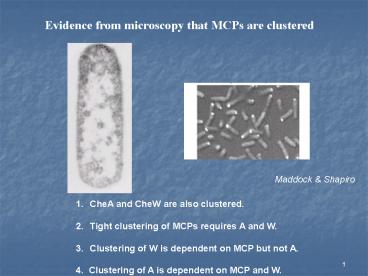
Evidence from microscopy that MCPs are clustered
Maddock Shapiro
- CheA and CheW are also clustered.
- Tight clustering of MCPs requires A and W.
- Clustering of W is dependent on MCP but not A.
- 4. Clustering of A is dependent on MCP and W.
2
Validation by cryo-tomography
Zhang et al., PNAS 2007
3
Why put all receptors in one spot (patch/cluster)?
4
Berg Turner
- Cell pole marked with Tetrazolium Red dye
- Tracked single cells as they ran and tumbled
- Monitored Dye distribution relative to the
flagellar bundle - Result Dye position was randomized during
tumbles - Conclusion Cells swam with either end in front
i.e clusters do not serve as a nose
5
If there is an advantage to localizing
chemoreceptors in patches at only one pole, that
advantage must accrue at some step after signal
detection
6
A trimer of cTsrQ dimers stereo views
Kim et al., Nature 1999
7
Triangular CheA-CheW vault around Tsr
keystone
Shimizu, T. S. et al. Nat. Cell Bio. 2000
Each unit made of 3 MCP dimers, 3 CheA monomers,
and 3 CheW monomers
8
A trimer of cTsrQ dimers stereo views
Kim et al., Nature 1999
9
Chemoreceptor Clustering
Evidence from Genetics
- Ames et al. 2002. Collaborative signaling by
mixed chemoreceptor - teams in Escherichia coli. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci.
USA 99 7060-65.
10
Triangular CheA-CheW vault around Tsr
keystone
Each unit made of 3 MCP dimers, 3 CheA monomers,
and 3 CheW monomers
11
- 80-aa distal tip of receptor mediates ternary
complex formation. This region also contains
contact sites for a t-o-d in the crystal
structure.
12
Questions
- What specific effects do mutations in the trimer
contact sites have on Tsr signaling ability and
at what stage in the signaling pathway do they
act? - Does experimental evidence support the possible
existence of mixed chemoreceptor teams?
13
Experimental Methods
- Mutations were introduced at trimer contact
residues of Tsr - Tsr expression levels were monitored by
immunoblotting with anti-Tsr antibody - Chemotaxis was assessed by observing colony size
in semisolid agar Flagellar rotation monitored
using Ab-tethered cells to measure time spent in
CW rotation
14
Experimental Methods (Cont.)
- Receptor clustering was observed using
fluorescence microscopy to visualize YFP-CheZ
clusters - Complementation studies were undertaken to study
genetic patterns and relationships between Tsr
mutants and wild-type Tsr or Tar chemoreceptors - Dithiobis crosslinking agent was used to
crosslink receptors in order to determine whether
direct contacts exist between heterogeneous
receptor dimers
15
Tsr Trimer Contact Sites
- 11 different residues (6 hydrophobic, 4 polar, 1
central H-bond network) in trimer contact sites
to be studied
16
Falke, 2002
17
Amino Acid Substitutions
18
With one exception, P mutants showed no CW
episodes and no clustering (expected) All but
one A and W mutants showed efficient clustering,
but half of them were lt5 CW defective in
kinase activation. The others were locked Only
two (V398A and R409A) mediated serine
chemotaxis
19
Summary of Clustering and Flagellar Rotation
Results
- Symbols
- Wild-type
- Alanine mutants
- Proline mutants
- Tryptophan mutants
Filled 65 of wt serine chemotaxis Open lt35
of wt serine chemotaxis
20
1. No cluster, no chemotaxis 2. Cluster, but no
kinase activation 3. Kinase activation, but no
regulation (locked)
21
Falke, 2002
22
Testing Interaction by Complementation
- Investigated the effects of mutant Tsr on
wild-type Tsr and Tar in trimers by using the
soft agar assays by co-expressing the proteins in
the same cell, varying the amount of mutant
protein by altering inducer concentrations
23
Results of Complementation
- Four different complementation patterns
- Recessive Mutations have no effect on wild-type
- Dominant Mutations impair wild-type Tsr but do
not affect Tar - Epistasis Mutations impair both wild-type Tsr
and Tar - Rescue Wild-type Tar restores serine chemotaxis
in mutant Tsr
Epistasis An interaction between nonallelic
genes, especially an interaction in which one
gene suppresses the expression of another
24
Complementation Patterns on Soft Agar Plates
A
P
W
A
- Outer ring of the rescuable mutants shows that
serine chemotaxis has been restored
25
Falke, 2002
26
What can the complementation patterns reveal
about nature of defect?
Dominant mutations did not affect Tar function,
so most likely these formed Tsr/Tsr dimers,
spoiling wt subunits through mixed dimer
formation. Epistatic mutations likely spoil a
functional high-order of the dimers Rescuable
mutations also implicate such a high-order of the
dimers
27
Crosslinking
- Epistatic and Rescuable complementation patterns
predict that it should be possible to crosslink
Tsr and Tar in higher-order complexes
Co-express Tsr and Tar-His6 is cells having no
other MCPs. Crosslink. Purify Tar-His6 and see
if Tsr comes along
28
Diagnostic cross-linking sites for the
trimer-of-dimer organization.
A mixed trimer-of-dimers containing one Tsr
molecule (yellow) and two Tar molecules (light
blue). Indicated residues chosen for cysteine
replacements.
29
Crosslinking Results
- The lanes which show Tsr and Tar-H bands that
copurify indicate that these chemoreceptors are
close enough to crosslink (Provides evidence of
mixed complexes of Tsr and Tar dimers)
S soluble membrane fraction E eluted from Ni
resin I377P is dominant, not epistatic no
XL I1377W F373W are epistatic yes XL
30
Conclusions
- Effects of mutations in trimer contact regions
give strong circumstantial evidence that trimer
of dimers is important in signaling - Proline replacements prevented clustering, CheA
activation, and chemotaxis - Alanine and Tryptophan replacements mediated
signaling, but not CheA regulation or chemotaxis - Occurrence of epistatic and rescuable phenotypes
indicate that mixed complexes of Tsr and Tar
dimers are likely - Probable existence of mixed complexes confirmed
from crosslinking experiments
31
Unifying Model of Chemoreceptor Teams
32
Nanodiscs
Boldog, T. et. a. PNAS 2006
33
If there is an advantage to localizing
chemoreceptors in patches at only one pole, that
advantage must accrue at some step after signal
detection
34
Gain
Change in rotational bias/ Change in receptor
occupancy 60
Dennis Bray, PNAS, 2002
35
Triangular CheA-CheW vault around Tsr
keystone
Shimizu, T. S. et al. Nat. Cell Bio. 2000
Each unit made of 3 MCP dimers, 3 CheA monomers,
and 3 CheW monomers
36
2-D Hexagonal network
A 36-fold gain at the receptors indicates that
one receptor molecule can control the activity
of three dozen kinase molecules, implying a
functional network that links one receptor to
multiple copies of the kinase. The response to
attractant stimulation is cooperative Hill
coefficients as high as 10 have been observed
.These properties imply that receptors operate as
allosteric arrays with as many as several dozen
in the cooperative unit.
37
(No Transcript)