Extra-Solar planets - PowerPoint PPT Presentation
1 / 29
Title:
Extra-Solar planets
Description:
Zone around a star where liquid water can exist on the surface of a ... Precession (ASP) ... aligned Apsidal Synchronous Precession. NO close approaches ... – PowerPoint PPT presentation
Number of Views:18
Avg rating:3.0/5.0
Title: Extra-Solar planets
1
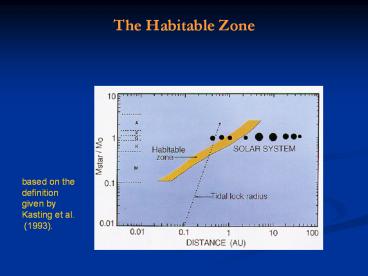
The Habitable Zone
based on the definition given by Kasting et
al. (1993).
2
Habitable Zone
- Zone around a star where liquid water can exist
on the surface of a terrestial-like planet - This zone depends on
- the spectraltype , the mass , the age, . of the
star - the orbit of the planet
- the mass, the composition, the atmosphere , of
the planet - the parameters of other planets in this system
(mass, orbit, )
3
Types of Habitable Zones
- hot-Jupiter type
- Solar system type
- (4) giant planet type habitable moon or trojan
planet
4
Status of Observations
- 164 Extra-solar planetary systems
- 194 Planets near other solar-type stars
- 19 Mulitple planetary systems
- 21 Planets in binaries
5
Facts about Extra-Solar Planetary Systems
- Only 28 of the detected planets have masses lt 1
Jupitermass - About 33 of the planets are closer to the
host-star than Mercury to the Sun - Nearly 60 have eccentricities gt 0.2
- And even 40 have eccentricities gt 0.3
6
Distribution of the detected Extra-Solar Planets
Mercury Earth Mars Venus
Jupiter
7
- Multi-planetary systems
- Binaries
- Single Star and Single Planetary Systems
8
.
9
Sources of uncertainty in parameter fits
- the orbital line-of-sight inclination i is not
known ? - from radial velocities measurements we get
only - a lower limit for the planetary masses
- the relative inclination ir between planetary
orbital planes is usually unknown. - Are the orbital parameters reliable -- using two
body keplerian fits - (the strong dynamical interactions between
planets) - All these leave us a substantial available
parameter space to be explored in order to
exclude the initial conditions which lead to
dynamically unstable configurations
10
Major catastrophe in less
than 100000 years
(S. Ferraz-Mello, 2004)
11
Numerical Methods
Chaos Indicators Fast Lyapunov Indicator (FLI)
C. Froeschle, R.Gonczi, E. Lega (1996) Mean
Exponential Growth factor of Nearby
Orbits (MEGNO) Cincotta Simo (2000)
Long-term numerical integration Stability-Crite
rion No close encounters within the Hill
sphere (i)Escape time (ii) Study of the
eccentricity maximum eccentricity
12
Multi-planetary systems
13
Classification of the known multi-planetary
systems (S.Ferraz-Mello, 2005)
- Class Ia gt Planets in mean motion resonance
(HD82943, Gliese876,HD128311,55Cnc,HD202206) - Class Ib ? Low-eccentricity near-resonant planet
pairs (47Uma) - Class II? Non-resonant planets with significant
secular dynamics (55 Cnc, Ups And, HD12661,
HD169830,HD37124, HD160691) - Class III? Hierarchical planet pairs (HD168443,
HD74156,HD11964,HD38529,55Cnc)
14
MMR 31 21 21 21 73/52
Class II III
Ia III Ia III
III II Ia II
III II II Ib
15
Systems in 21
resonance GJ876 b GJ876c
HD82 b HD82 c HD160 b
HD160 c A AU 0.21 0.13
1.16 0.73 1.5
2.3 e
0.1 0.27
0.41 0.54 0.31
0.8 M .sin i 1.89
0.56 1.63 0.88
1.7 1.0 M_jup
Gliese 876
HD82943
HD160691
16
- Periastra in the same direction
- S - P1 - P2
- S - A1 - A2
- A1 - S - P2
- P1 - S - A2
- Periastra in opposite directions
- S - P1 - A2
- S - A1- P2
- P1 - S P2
- A1 - S A2
- Equivalent in pairs, depending on the resonance
17
HD82943
Aligned
Anti-aligned
18
HD160691 b HD160691 c A AU
1.5 2.3
e 0.31 0.8 M .sin
i 1.7 1.0 M_jup
MEGNO Stability map
Stability condition 21 mean motion
resonance (exact location a_c2.381 AU)
Bois, E., Kiseleva-Eggleton, L., Rambaux,
N., Pilat-Lohinger, E., 2003, ApJ 598, 1312
19
- Planet m sin i a e
w P - HD160691b 1.67 /- 0.11 1.50 /- 0.02
0.2 /- 0.03 294 /- 9 645.5 /- 3
- c 3.1/- 0.71
4.17/- 0.07 0.57/- 0.1 161 /- 8
2986/-30 - d 0.04405
0.09 0 (0.02) 4/- 2
9.55/0.03
20
Stability of thenew system HD160691
21
Due to high eccentricities of the orbits and
despite relatively small semi-major axis, the
relative distances between the two planets may
remain sufficiently large over the whole
evolutionary time scale of The system.
22
- It was shown by several authors
- (e.g. Rivera Lissauer 2000, Laughlin
Chambers 2001, Chiang Murray 2002 Lee Peale
2002, 2003 Ji et al. 2003, 2004, Zhou Sun
2003, Bois et al. 2003) - that the orbits in almost all multi-planet
systems - (except HD38529, HD168443,
HD74156) - are locked in the so-called
- Apsidal Synchronous Precession (ASP)
- meaning that the two orbital planes precess
at the same rate, i.e. the relative apsidal
longitude ?3 of two planetary orbits librates
about 0 (aligned topology) or p (anti-aligned
topology).
, where
23
24
A suitable mechanism for compact multi-planetary
systems
- Low order Mean Motion Resonance
- Favorable relative initial orbital phases of
planets - High planetary eccentricities, especially of the
outer planet - Anti-aligned Apsidal Synchronous Precession
- NO close approaches between planets gt
- NO strong dynamical interactions gt
- STABILITY over long evolutionary timescale
25
- HD 74156
- The orbital parameters were taken from the
- Geneva group of observers
- Masses are Minimum Masses
Mstar 1.05 MSun
HD 74156 b m sini 1.6 Mjup a 0.28 AU e
0.647
HD 74156 c m sin i 8.2 Mjup a 3.82 AU e
0.354
26
e 0.30e0.35e0.40e0.45
27
New Data
HD 74156 b m 1.86 MJup a 0.294 AU e 0.635
HD 74156 c m 6.42 MJup a 3.44 AU e 0.561
28
(in collaboration with Erdi and Sandor)
HD 38529 HD 169830 HD
168443
Mstar 1.39 MSun HD 38529 b m 0.78 MJup a
0.129 AU e 0.29 HD 38529 c m 12.7 MJup a
3.68 AU e 0.36
Mstar 1.4 MSun HD 169830 b m 3.03 MJup a
0.82 AU e 0.327 HD 169830 c m 2.51 MJup a
2.85 AU e 0.0
Mstar 1.01 MSun HD 168443 b m 7.73 MJup a
0.295 AU e 0.53 HD 168443 c m 17.23 MJup a
2.9 AU e 0.2
29
Unstable orbits 21 1.3 AU 31 1 AU SR 0.8
0.9 AU 41 0.82 AU Stable orbits Between
resonances Terrestrial planet is possible!