LOWER - PowerPoint PPT Presentation
1 / 141
Title: LOWER
1
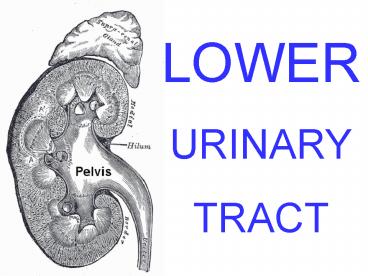
LOWER URINARY TRACT
2
LOWER URINARY TRACT TRANSITIONALEPITHELIUM
UROTHELIUM
MINOR CALYCES MAJOR CALYCES RENAL PELVIS
URETERS BLADDER URETHRA
3
EPITHELIUM
MUSCULARIS PROPRIA
4
EMBRYOLOGY
PRONEPHROS MESONEPHROS METANEPHROS CLOACA MÜLLER
IAN ? WOLFFIAN ?
5
(No Transcript)
6
(No Transcript)
7
(No Transcript)
8
(No Transcript)
9
(No Transcript)
10
(No Transcript)
11
(No Transcript)
12
(No Transcript)
13
(No Transcript)
14
LOWERUrinary Tract
- Ureters(Anomalies, Infl., Neopl.)
- Bladder(Anomalies, Infl., Neopl.)
- Urethra(Anomalies, Infl., Neopl.)
15
(No Transcript)
16
URETERS
- Anomalies (congenital)
- Inflammation/Obstruction (i.e., ureteritis)
- Acute, Chronic
- Neoplasms
- Benign vs. Malignant
- Epithelial vs. stromal (i.e., mesoderm derived)
17
CONGENITAL Ureter Anomalies
- DOUBLE Ureters
- UPJ (Uretero-Pelvic Junction) Obstruction
- Diverticula
- Hydroureter
18
(No Transcript)
19
(No Transcript)
20
(No Transcript)
21
(No Transcript)
22
INFLAMMATION
- The USUAL reasons
- The USUAL patterns, i.e. ?
- Linked to OBSTRUCTION
- GLANDULARIS/CYSTICA
- FOLLICULARIS
23
(No Transcript)
24
(No Transcript)
25
OBSTRUCTIONFACTORS
- INTRINSIC
- CALCULI
- STRICTURES
- TCC, TUMORS
- CLOTS
- NEUROGENIC
- EXTRINSIC
- PREGNANCY
- INFLAMMATION
- ENDOMETRIOSIS
- TUMORS
- SURGERY
26
Sclerosing Retroperitoneal Fibrosis
- 70 Idiopathic
- 30 Drugs (ergot derivatives, beta blockers) or
known retroperitoneal inflammatory conditions,
e.g., Vasculitis, Diverticulitis, Crohns Disease
27
TUMORS
- Benign
- Fibroepithelial Polyp
- Leiomyoma
- Malignant
- Transitional Cell Carcinoma, aka, TCC
- Also aka, UROTHELIAL Carcinoma
28
Which Ureter? Which Part?
29
(No Transcript)
30
(No Transcript)
31
(No Transcript)
32
(No Transcript)
33
LOWERUrinary Tract
- Ureters(Anomalies, Infl., Neopl.)
- Bladder(Anomalies, Infl., Neopl.)
- Urethra(Anomalies, Infl., Neopl.)
34
ANOMALIES
- Diverticula (plural of um)
- Exstrophy
- Vesico-Ureteral Reflux
- Persistent Urachus
- Fistulas Vagina, Rectum, Uterus
35
(No Transcript)
36
(No Transcript)
37
(No Transcript)
38
EXSTROPHY
Developmental Anomaly Very Good Surgical
Correction Rate
39
Vesico-Ureteral Reflux
- Most Common Anomaly
- Very serious in its role in chronic
pyelonephritis and hydronephrosis
40
(No Transcript)
41
ADJECTIVES for CYSTITIS
- Acute
- Chronic
- Hemorrhagic
- Suppurative
- Follicular
- Eosinophilic
- Interstitial
42
(No Transcript)
43
(No Transcript)
44
(No Transcript)
45
(No Transcript)
46
CAUSES for CYSTITIS
- E. coli
- Proteus, Klebsiella, Enterobacter
- Shistosomes (Egypt)
- Chlamydia
- Mycoplasma
- Viruses, e.g., adenoviruses
- ChemoRX
- RadiationRX
47
SYMPTOMS for CYSTITIS
- Frequency
- Urgency
- Hematuria
- Abdominal Pain
- Dysuria
- Systemic Sepsis, i.e., fever, leukocytosis
48
Special Types ofCYSTITIS
- Interstitial cystitis, aka, Hunner Ulcer
- Malacoplakia
49
Interstitial Cystitis
- Womengtgt Men
- Bladder Wall Fibrosis
- Aka, Hunner ulcer
50
(No Transcript)
51
Malacoplakia
- YELLOW Mucosal Plaques
- Why Yellow?
- Chronic bacterial infection
- Michaelis-Gutmann bodies contain Fe and Ca in
macrophages
52
(No Transcript)
53
METAPLASIA
- Glandular(is) (Cystica), from Brunn nests
- Squamous metaplasia
54
(No Transcript)
55
(No Transcript)
56
(No Transcript)
57
(No Transcript)
58
TUMORS
- 95 Epithelial (urothelial), 5 mesenchymal,
i.e., mesodermally derived (mostly smooth muscle) - Benign or Malignant
- Primarily urothelial or transitional, but a few
squamous, from antecedent squamous metaplasia,
and a few adenocarcinomas, from antecedent
glandular metaplasia
59
TCC TUMORS
- MULTIPLE, MULTIPLE, MULTIPLE, i.e., soil theory
- Papillomas vs. Carcinomas
- Grading, I, II, III, or well?poor
- Staging, TNM, based on biologic behavior, really
based on normal anatomy
60
TCC TUMORS
- Causes/Risk Factors
- Arylamines (aniline dyes)
- Cigarettes
- Shitosomiasis
- Longstanding analgesics, same as analgesic
nephropathy drugs, most common NSAIDS - ChemoRX, esp. cyclophosphamides
- Radiation RX
61
Papillomas vs. Carcinomas
- Very few pathologists will have enough guts to
diagnose a transitional papilloma. Why? - PUNLMP, Papillary Urothelial Neoplasm of Low
Malignant Potential? - LOW grade PUC (TCC)?
- HIGH grade PUC (TCC)
62
(No Transcript)
63
LOW Grade
64
(No Transcript)
65
HIGH Grade
66
(No Transcript)
67
(No Transcript)
68
(No Transcript)
69
(No Transcript)
70
BIOLOGIC BEHAVIOR
NORMAL MUCOSA?DYSPLASIA, SEVERE DYSPLASIA,
CARCINOMA IN SITU, INFILTRATION? BASEMENT
MEMBRANE?LAMINA PROPRIA?MUSCULARIS
MUCOSA?MUSCULARIS PROPRIA (i.e., WALL)?SEROSA or
ADVENTITIA?LYMPH NODES?DISTANT METASTASES
TNM
71
TNM example
- Ta----noninvasive, papillary
- Tis---Carcinoma in situ, flat
- T1----Lamina Propria
- T2----Muscularis propria
- T3a---Microscopic beyond the wall
- T3b---Grossly beyond the bladder wall
- T4----Invades adjacent structures
72
Bladder Neck OBSTRUCTION
- Cystocele, MOST common cause in women
- Prostate, MOST common cause in MEN
- Congenital
- Inflammation
- Tumors
- Foreign Bodies, Calculi
- Neurogenic
73
LOWERUrinary Tract
- Ureters(Anomalies, Infl., Neopl.)
- Bladder(Anomalies, Infl., Neopl.)
- Urethra(Anomalies, Infl., Neopl.)
74
URETHRA
- Inflammations
- Gonococcus
- Chlamydia
- Mycoplasma
- Reiters Syndrome
- Caruncle
- Neoplasms
- Transitional
- Squamous
- Glandular
75
(No Transcript)
76
Chapter 21 Male Genital Tract Diseases
77
Male Genital Tract(long version)
- Seminiferous tubules ?
- Straight Tubules ?
- Rete Testis (mediast.) ?
- Efferent Ductules ?
- Epididymis ?
- Vas deferens ?
- Seminal Vesicles ?
- Ejaculatory Ducts ?
- Urethra Prostatic?Spongy
78
(No Transcript)
79
(No Transcript)
80
(No Transcript)
81
(No Transcript)
82
(No Transcript)
83
Efferent Ductules and Epididymis
84
(No Transcript)
85
(No Transcript)
86
(No Transcript)
87
(No Transcript)
88
(No Transcript)
89
LITTRÉ
90
Male Genital Tract(short version)
- Penis Congenital, Inflammation, Tumors
- Testis/Epididymis Congenital, Regressive,
Inflammation, Vascular diseases, Tumors - Prostate Inflammation, Benign Enlargement,
Malignancy
91
Penis Congenital
- Hypospadias
- Epispadias
- Phimosis
92
(No Transcript)
93
(No Transcript)
94
(No Transcript)
95
Penis InflammationBalanoposthitis
- Candida
- Anerobes
- Gardnerella
- Pyogenic
- Role of smegma
96
Penis Neoplasia
- Benign Condyloma Acuminata (caused by HPV), aka
venereal or genital warts - Malignant Squamous cell carcinoma
97
(No Transcript)
98
(No Transcript)
99
Koilocytosis
100
Penis Malignancy
- In-situ Bowens Disease
- Invasive Infiltrating or invasive SQUAMOUS Cell
Carcinoma
101
BOWENs Disease SQUAMOUS cell carcinoma-in-situ
of the skin of the penis
102
(No Transcript)
103
(No Transcript)
104
(No Transcript)
105
Male Genital Tract(short version)
- Penis Congenital, Inflammation, Tumors
- Testis/Epididymis Congenital, Regressive,
Inflammation, Vascular diseases, Tumors - Prostate Inflammation, Benign Enlargement,
Malignancy
106
Male Genital Tract(short version)
- Testis/Epididymis
- Congenital
- Regressive
- Inflammation
- Vascular diseases
- Tumors
107
Male Genital Tract(short version)
- Testis/Epididymis
- Congenital Cryptorchidism 1
- Regressive Atrophy
- Inflammation Mumps, GC, Chlamydia, E. Coli,
Pseudomonas, TB - Vascular diseases Torsion
- Tumors Benign/Malig, Germ Cell/non-Germ Cell
108
Cryptorchidism
- 1 of all births
- 25 bilateral
- Associated with significantly increased incidence
of germ cell tumors
109
Male Genital Tract(short version)
- Testis/Epididymis
- Congenital Cryptorchidism 1
- Regressive Atrophy
- Inflammation Mumps, GC, Chlamydia, E. Coli,
Pseudomonas, TB - Vascular diseases Torsion
- Tumors Benign/Malig, Germ Cell/non-Germ Cell
110
Testicular Atrophy
- atherosclerotic narrowing of the blood supply in
old age - the end stage of an inflammatory orchitis,
whatever the etiologic agent - cryptorchidism
- hypopituitarism
- generalized malnutrition or cachexia
- irradiation
- prolonged administration of female sex hormones,
as in treatment of patients with carcinoma of the
prostate and cirrhosis
111
(No Transcript)
112
Male Genital Tract(short version)
- Testis/Epididymis
- Congenital Cryptorchidism 1
- Regressive Atrophy
- Inflammation Mumps, GC, Chlamydia, E. Coli,
Pseudomonas, TB - Vascular diseases Torsion
- Tumors Benign/Malig, Germ Cell/non-Germ Cell
113
(No Transcript)
114
Male Genital Tract(short version)
- Testis/Epididymis
- Congenital Cryptorchidism 1
- Regressive Atrophy
- Inflammation Mumps, TB, GC, Chlamydia, E. Coli,
Pseudomonas - Vascular diseases Torsion
- Tumors Benign/Malig, Germ Cell/non-Germ Cell
115
(No Transcript)
116
Male Genital Tract(short version)
- Testis/Epididymis
- Congenital Cryptorchidism 1
- Regressive Atrophy
- Inflammation Mumps, GC, Chlamydia, E. Coli,
Pseudomonas, TB - Vascular diseases Torsion
- Tumors Benign/Malig, Germ Cell/non-Germ Cell
117
Testicular TUMORS
- GERM CELL (malig.)
- SEMINOMA
- EMBRYONAL
- CHORIOCARCINOMA
- YOLK SAC
- TERATOMA
- MIXED!!!!!, 60
- NON-GERM (benign)
- CELL, i.e., sex cord
- LEYDIG
- SERTOLI
118
Seminoma (look for germ cells and lymphs)
119
Embryonal Carcinoma, Formerly called
adenocarcinoma, so look for glands and AFP!!!)
120
CHORIOCARCINOMAlook for trophoblast, and HCG!!
121
YOLK SAC TUMOR, aka endodermal sinus tumor
Schiller-Duvall Body
122
TERATOMAMALIGNANT TERATOMATERATOCARCINOMA
neural tissue retina muscle bundles islands of
cartilage clusters of squamous epithelium structur
es reminiscent of thyroid gland bronchial or
bronchiolar epithelium bits of intestinal wall or
brain substance
123
SEX Cord Tumors
- Leydig, tumor cells look like Leydig cells
- Sertoli , tumor cells look like sertoli cells
124
STAGING
- Stage I Tumor confined to the testis,
epididymis, or spermatic cord - Stage II Distant spread confined to
retroperitoneal nodes below the diaphragm - Stage III Metastases outside the retroperitoneal
nodes or above the diaphragm
125
PROSTATE
- INFLAMMATIONS
- BENIGN ENLARGEMENT
- MALIGNANT TUMORS
126
CZ CENTRAL TZ TRANSITIONAL PZ PERIPHAL
127
PROSTATE
- INFLAMMATIONS
- BENIGN ENLARGEMENT
- MALIGNANT TUMORS
128
PROSTATITIS
- ACUTE, usually same as Urinary Tract Pathogens
- CHRONIC, usually A-bacterial, but also often
recurrent or persistent from acute - GRANULOMATOUS, non-TB or TB
129
(No Transcript)
130
(No Transcript)
131
(No Transcript)
132
BENIGN Enlargement
- BPH
- BPH
- Glandular and Stromal Hyperplasia
- Nodular Hyperplasia
- Associated with old age
- Associated with urinary obstruction, frequency,
bladder hypertrophy and bladder trabeculations - By itself, it is NOT premalignant, however.
133
(No Transcript)
134
P.I.N.
135
NUCLEOLI, NUCLEOLI, NUCLEOLI
136
PERINEURAL INVASION
137
(No Transcript)
138
BIOLOGIC BEHAVIOR
- NORMAL PROSTATE ?
- HYPERPLASIA ?
- P.I.N. (Prostatic Intraepithelial Neoplasia), is
like dysplasia leading to adenocarcinoma-in situ
? - INFILTRATION of stroma ?
- CAPSULE ?
- LYMPH NODES ?
- DISTANT, especially BONE ?
139
GRADING
- GLEASON SCORE Predominant pattern (1-5)
Secondary pattern (1-5) - Best Score 2, Worst Score 10
140
STAGING
TNM
141
TID-BITS
- Prostate is 1 most common malignancy in men but
NOT 1 killer. WHY? - 80 over 80
- Every elderly male presenting with widespread
bone metastases is carcinoma of the prostate
until proven otherwise - PSA (Prostate Specific Antigen) has been
controversial as a screening test but is GREAT
for follow up of a known prostate cancer