Normal Red Blood Cells Peripheral Blood Smear - PowerPoint PPT Presentation
1 / 62
Title:
Normal Red Blood Cells Peripheral Blood Smear
Description:
The RBC's demonstrate minimal variation in size (anisocytosis) and shape (poikilocytosis) ... (variation in size) and poikilocytosis (variation in shape) ... – PowerPoint PPT presentation
Number of Views:1651
Avg rating:3.0/5.0
Title: Normal Red Blood Cells Peripheral Blood Smear
1
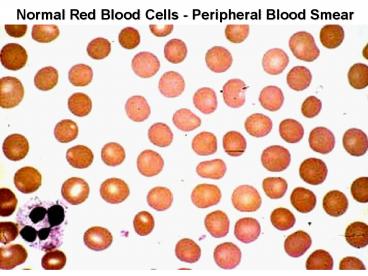
Normal Red Blood Cells - Peripheral Blood Smear
2
Peripheral Blood Cells
A. Erythrocytes B. Large Granular Lymphocyte C.
Neutrophil D. Eosinophil E. Neutrophil F.
Monocyte G. Platelets H. Lymphocyte I. Band
Neutrophil J. Basophil
3
The red blood cells here are normal, happy RBC's.
They have a zone of central pallor about 1/3 the
size of the RBC. The RBC's demonstrate minimal
variation in size (anisocytosis) and shape
(poikilocytosis).
4
Hypochromic Microcytic Anemia (iron deficiency)
5
The RBC's here are smaller than normal and have
an increased zone of central pallor. This is
indicative of a hypochromic (less hemoglobin in
each RBC) microcytic (smaller size of each RBC)
anemia. There is also increased anisocytosis
(variation in size) and poikilocytosis (variation
in shape).
6
Koilonychia - Iron Deficiency
7
Macroovalocytes and Hypersegmented Neutrophil
8
Here is a hypersegmented neutrophil that is
present with megaloblastic anemias. There are 8
lobes instead of the usual 3 or 4. Such anemias
can be due to folate or to B12 deficiency. The
size of the RBC's is also increased
9
Bone marrow -- Megaloblastic anemia --
nuclear/cytoplasmic asynchrony,
10
Markedly hypocellular BM - Aplastic Anemia
11
Breast cancer replacing BM
12
- Spherocytes
- Lab moderate anemia, spherocytes, reticulocytes
- BM - erythroid hyperplasia
- Coombs test - negative
13
Hemoglobin Precipitates -- Heinz bodies G6PD
Deficiency
14
Bite Cell -- G6PD Deficiency Clinical? X linked,
African American Males, only symptomatic during
oxidative stress (meds, fava beans)
15
Sickle Cells -- Clinical stuff microvascular
occulusions lead to tissue infarcts and pain,
autosplenectomy (so no splenomegaly), increased
Salmonella osteomyelitis, some aplastic crises
(Parvovirus)
16
Sickle cell anemia in sickle cell crisis. The
abnormal hemoglobin SS is crystalizes when oxygen
tension is low, and the RBC's change shape to
long, thin sickles that sludge in capillaries,
further decreasing blood flow and oxygen tension.
Persons with sickle cell trait (Hemoglobin AS)
are much less likely to have this happen.
17
Mechanical trauma -- schistocytes
18
Malaria in RBCs -- most common hemolytic anemia
Cyclical hemolysis produces fever and chills,
splenomegaly
19
Activated neutrophil - Dohle body
20
Leukemoid reaction (toxic granulation)
21
Reactive Lymphocyte - Infectious Mononucleosis
22
Normal bone marrow. Note the presence of
megakaryocytes, erythroid islands, and
granulocytic precursors. This marrow is taken
from the posterior iliac crest in a middle aged
person, so it is about 50 cellular, with
steatocytes mixed with the marrow elements.
23
Bone Marrow, Acute Leukemia Age
distributions? ALL -- kids (4 yrs peak
incidence) AML -- Adults
24
Bone marrow acute leukemia Symptoms? Fatigue
(Anemia), Bleeding (thrombocytopenia), Bone pain,
infections, masses, CNS symptoms
25
Lympoblasts -- ALL Diagnostic criteria? 30
lymphoblasts in BM, Tdt, MPO-
26
AML -- myeloblasts with Auer Rod, worse prognosis
than ALL, allogenic Bone Marrow Transplant
curative
27
Myeloblasts -- myeloperoxidase positive
28
Acute Promyelocytic Leukemia (FAB -
M3) Hypergranular promyelocytes, more Auer rods,
DIC from tissue thromboplastin, tx w/retinoic acid
29
Monoblasts -- Acute Myelogenous Leukemia (M5),
nonspecific esterase
30
Non-specific esterase monoblasts
(left) negative control (right)
31
Chronic Myeloid Leukemia Features? WBCgt50,000
with 80 immature, Philadelphia chromosome
32
Chronic Myeloid Leukemia bone marrow Clinical
Course? Slow progressive and then blast phase
(80)
33
Essential Thrombocythemia - Bone marrow with
greatly increased numbers of megakaryocytes
34
Myeloid metaplasia with myelofibrosis - Bone
marrow fibrosis
35
Reactive lymphadenitis - Follicular hyperplasia
36
Reactive lymphadenitis - Sinus histiocytosis
37
Necrotizing lymphadenitis - high power
38
Cat Scratch Disease - Bartonella henselae bacteria
39
Reactive lymphocytes - Infectious Mononucleosis
-- Tcells proliferate, but B cells are infected
40
Follicular lymphoma - lots of follicles, B cells,
common in Europe and America, adults 40yoa
41
Follicular lymphoma, usually diagnosed at a high
stage, when bone marrow is involved, angular
cells cleaved cells
42
Mycosis fungoides - Sezary Syndrome, T cell
lymphoma Early skin lesions (left) Skin plaques
(right)
43
Mycosis Fungoides - Sezary cells in blood
(right) Pautrier abcess in skin (left)
44
Mycosis fungoides - Sezary cells
45
Burkitts Lymphoma -- starry sky pattern due to
macros Endemic type in Tropical Africa
46
Burkitts Lymphoma -- B cells, EBV associated,
myc translocated t(814)
47
(No Transcript)
48
Hodgkins Disease -- cervical and mediastinal
lymphadenopathy, spreads sequentially along lymph
node chain, adolescents and older adults
49
Hodgkins disease -- Nodular Sclerosis type, most
common subtype, dense band s of
collagen/fibrosis, few Reed-Sternberg cells,
young adult females
50
Reed-Sternberg cell -- owl eyes -- Hodgkins
Disease
51
Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia - little cytoplasm
52
These mature lymphocytes are increased markedly
in number. They are indicative of chronic
lymphocytic leukemia, a disease most often seen
in older adults. This disease responds poorly to
treatment, but it is indolent.
53
CLL smudge cell
54
CLL bone marrow
55
Hairy cell leukemia -- single light chain
expressed, (CD19 or CD20), TRAP positive,
splenomegaly, pancytopenia, usually older males
56
Electronmicrographs of a Hairy Cell transmission
EM (left) scanning EM (right)
57
Multiple Myeloma
Stained gel image
Albumin
Tracing of serum protein electrophoresis -
abnormal
M spike
?
?2
?1
?
58
Multiple Myeloma -- Rouleaux
59
Plasma cell myeloma, right is normal , left
filled with plasma cells
60
Plasma cell myeloma, large cytoplasm, IL-6
mediated effects, Symptoms? Bone pain,
pathologic fractures, hypercalcemia, anemia,
amyloidosis
61
Plasma cell myeloma - lytic lesions in the skull
62
Plasmacytoma -- solid tumor of plasma cells,
osseous usually vertebral, soft tissue usually
upper respiratory tract