Content versus Process Theories - PowerPoint PPT Presentation
1 / 27
Title:
Content versus Process Theories
Description:
The key to success is found in the Serenity Prayer: God Grant Me the Serenity to: ... paraphrase: God Grant Me the Serenity to: Deal with those things I ... – PowerPoint PPT presentation
Number of Views:138
Avg rating:3.0/5.0
Title: Content versus Process Theories
1
Content versus Process Theories
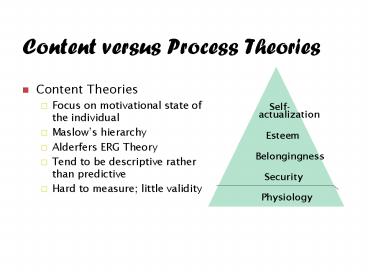
- Content Theories
- Focus on motivational state of the individual
- Maslows hierarchy
- Alderfers ERG Theory
- Tend to be descriptive rather than predictive
- Hard to measure little validity
2
The Two-Factor Theory of Motivation
3
Process Theories
1. What does a company want from employees?
Excellent Performance Achieve Division Goals and
Objectives Contribute to Organizational Goals and
Objectives
Motivation is measured as the amount of effort
people are willing to put into a task (or set of
tasks) or to achieve a prescribed goal.
4
Motivation Made Simple
2. What do Managers Want from an Employee?
Maximum Effort
Excellent Performance
5
Motivation Made Simple
3. How Can Managers Get What They Want?
Maximum Effort
Excellent Performance
Rewards
a. Reward Excellent performance
6
Motivation Made Simple
3. How Can Managers Get What They Want?
b. Make the Job Meaningful to the Employee
Maximum Effort
Excellent Performance
Excellent Performance
a. Reward Excellent performance
7
Motivation Made Simple
3. How Can Managers Get What They Want?
b. Make the Job Meaningful to the Employee
Maximum Effort
Excellent Performance
Rewards
a. Reward Excellent performance
c. Hire Highly Self-Motivated People
8
Motivation Made Simple
3. How Can Managers Get What They Want?
b. Make the Job Meaningful to the Employee
Maximum Effort
Excellent Performance
Rewards
d. Make the job challenging
a. Reward Excellent performance
c. Hire Highly Self-Motivated People
9
Motivation Made Simple
3. How Can Managers Get What They Want?
b. Make the Job Meaningful to the Employee
Maximum Effort
Excellent Performance
Rewards
d. Make the job challenging
a. Reward Excellent performance
e. Make rewards competitive
c. Hire Highly Self-Motivated People
10
Motivation Made Simple
3. How Can Managers Get What They Want?
b. Make the Job Meaningful to the Employee
Maximum Effort
Excellent Performance
Rewards
d. Make the job challenging
a. Reward Excellent performance
e. Make rewards competitive
c. Hire Highly Self-Motivated People
f. Develop Empowered Employees
11
Managing and Motivation
- Management is about SYSTEMS that can be
replicated in other situations and administered
by skilled professionals - Motivation is a process that can be managed,
replicated, and measured for success - The key to success is found in the Serenity
Prayer God Grant Me the Serenity to - Accept the things I cannot Change
- Change the things I can and should be changed,
and - Wisdom to know the difference
- The managers paraphrase God Grant Me the
Serenity to - Deal with those things I cant control
- Identify those things I can change
- Develop the skills and resources to change those
things in a way that works.
12
Managing and Motivation
- A. Some Things I Cannot Change
- Budgets
- Executive leadership
- Customers/Clients
- Employees
- B. Things I Can Change
- The perception of rewards (both monetary and
non-monetary) - The design of a persons job
- How well employees fit their job (both existing
and future) - Challenge (Goal Setting)
- Equity Perceptions
- Employee Perceptions of Empowerment
13
Reward Excellent Performance
- Design a Compensation/Benefit Plan that employees
find attractive (or at least satisficing). - Create a diverse set of non-monetary rewards that
appeals to the widest number of employees - Attach rewards to desired performance levels
- Monitor employee satisfaction with both monetary
and non-monetary rewards. - Do your employees find the compensation adequate?
- Do your employees find the non-monetary rewards
adequate? - E. Research Similar Jobs at Private Companies
and/or other public institutions - Survey employees periodically
- USE THE RESULTS!!!!
14
Job Design
- Analyze Jobs to discover
- the extent to which occupants find them
meaninful, - The extent to which jobholders experience
ownership, - The amount of feedback employees get on a
consistent basis regarding final results
15
Understand Your Employees
Know Who They Are
Personality
Learning Style
Life Situation
16
Challenging Through Goal Setting
17
Competition and Fairness
- Creating a Competitive Environment
- Do Employees enjoy a healthy sense of
competition? - Do employees appreciate performance based
rewards? - Do Employees appreciate recognition (e.g.
employee of the month) that has little or no
financial component? - Are your employees sufficiently similar to allow
for a level playing field? - Manage Equity Perceptions
- Determine who they compare themselves to
- Compare the relationship between
effort/performance and rewards for different
employees - Identify (and correct) areas of perceived inequity
18
Are Your Employees Empowered?
Empowerment is a Cognitive state, not a
management practice
Stage 1
Stage 3
Stage 2
Stage 5
Stage 4
Sources of Self-Efficacy Information Success!!! V
icarious Experience Verbal Persuasion Emotional
Arousal
Conditions Leading to experience of
powerlessness Organizational Factors Supervision
Reward Systems Nature of Job
Strategies Techniques Goal Setting Appraisal
System Modeling Performance based Rewards Job
Enrichment
Empowering Experience Increased Sense Of
Self-Efficacy
Behavioral Effects Initiation Persistence
Five Stages in the Empowerment Process
19
The Experience of Powerlessness
Job Performance Department Goals and
Objectives MCS Goals
In an Ideal World.
20
The Experience of Powerlessness
Budgets
Re-Org!
Effort
Job Performance Department Goals and
Objectives MCS Goals
Empowerment
Politics
21
The Experience of Powerlessness
Resistance rather than Effort
Effort
Job Performance Department Goals and
Objectives MCS Goals
Empowerment
Obstacles
Decreased confidence in self and organization
22
The Experience of Powerlessness
Resistance rather than Effort
Effort
Empowerment
Obstacles
Decreased confidence in self and organization
23
The Experience of Powerlessness
Resistance rather than Effort
Effort
Empowerment
Obstacles
Decreased confidence in self and organization
24
The Experience of Powerlessness
Resistance
Poor Job Performance Failure to Achieve
Departmental and MCS Goals and OBjectives
Powerlessness
Obstacles
Isolation and Competition
25
Stage 2 Building a Base
Motivation as a System is the starting point for
empowering employees
Stage 1
Stage 3
Stage 2
Stage 5
Stage 4
Sources of Self-Efficacy Information Success!!! V
icarious Experience Verbal Persuasion Emotional
Arousal
Conditions Leading to experience of
powerlessness Organizational Factors Supervision
Reward Systems Nature of Job
Strategies Techniques Goal Setting Appraisal
System Modeling Performance based Rewards Job
Enrichment
Empowering Experience Increased Sense Of
Self-Efficacy
Behavioral Effects Initiation Persistence
26
The Experience of Empowerment
Motivation as a System is the starting point for
empowering employees
Stage 1
Stage 3
Stage 2
Stage 5
Stage 4
Sources of Self-Efficacy Information Success!!! V
icarious Experience Verbal Persuasion Emotional
Arousal
Conditions Leading to experience of
powerlessness Organizational Factors Supervision
Reward Systems Nature of Job
Strategies Techniques Goal Setting Appraisal
System Modeling Performance based Rewards Job
Enrichment
Empowering Experience Increased Sense Of
Self-Efficacy
Behavioral Effects Initiation Persistence
27
Psychological Empowerment
Competence
Perceived Control
Empowerment
Resources
Meaning
Impact
Valued