cDNA cloning : survey of tools strategies procedures - PowerPoint PPT Presentation
1 / 32
Title: cDNA cloning : survey of tools strategies procedures
1
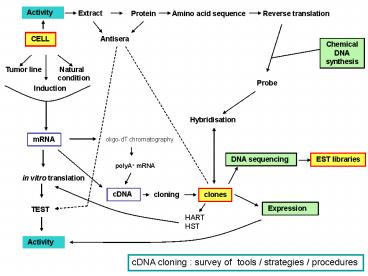
cDNA cloning survey of tools / strategies /
procedures
2
3
Direct selection for a clone containing the R6-5
kanamycin resistance gene (kanR)
4
Direct selection for a trpA gene using a trpA-
strain of E. coli An appropriate mutant strain
must be available.
5
Screening by hybridisation DNA probes RNA
probes oligonucleotide probes mixed probes and
guessmers mismatch probes homologous
probes heterologous probes gt ZOO
blots polyclonal antisera monoclonal antibodies
6
7
Colony hybridization. Probing with a
radioactively labelled or enzymatically,
fluorescently or immunologically tagged probe.
Detection by autoradiography, color,
fluorescence, etc. Similar procedures with
plaque hybridization.
8
Heterologous probing
9
(No Transcript)
10
The amino acid sequence of yeast cytochrome c.
The hexapeptide that is highlighted yellow is
one to illustrate how a nucleotide sequence can
be predicted from an amino acid sequence.
-trp-asp-glu-asn-asn-met- -TGG-GAY-GAR-AAY-AAY
-ATG- 18-mer 2 x 2 x 2 x 2 16
oligonucleotides represent the entire set of
possibilities.
11
The use of a synthetic, labelled or
tagged oligonucleotide to identify a clone of the
yeast cytochrome c gene. From probable to
definite.
12
Antibodies (a) Antibodies bind to foreign
molecules and help to degrade them.
(b) Purified antibodies ("antisera") can
be obtained from (a.o.) a small volume of
blood taken from a rabbit injected with
the foreign protein.
13
Immunoscreening Detection by - labelled
antibody itself or - labelled protein A (as
shown in the figure) or - the use of a second
antibody which binds specifically to the
primary antibody.
14
Plaque screening of clones of fusion proteins
(at LacZ) using antibodies.
15
"Sandwich"-approach in probing with
antibodies.
16
cDNA cloning survey of tools / strategies /
procedures
17
Hybrid arrested translation (HArT)
The plasmid DNA of the cDNA clone that inhibits
the biological activity in the biochemical test
is a good candidate of representing a positive
clone. Sets of DNA's are tested simultaneously,
and subsequently split into smaller numbers,
until individual DNA's can be tested and
analysed.
18
Hybrid selection translation (HST) mRNA is
selected from a total mRNA extract by
hybridisation to an immobilized cDNA plasmid
clone DNA. In vitro translation of the selected
mRNA provides protein product that is analyzed
by a biochemical test.
19
Abundance screening Probing within a cDNA
library to identify an abundant gene (mRNA).
20
Difference screening differential expression
analysis
Making multiple DNA-filters in parallel and
comparing hybridisations with different probes.
Labelled or tagged cDNA copies of mRNAs from
different cells or cell types or different
conditions of growth or induction or other
treatments.
21
Subtractive techniques comparing cell types
mRNA prepared from cell type A. mRNA prepared
from cell type B. cDNA prepared from mRNA of
cell type A, made single-stranded by alkaline
treatment. The cDNA is complementary to mRNA,
also those of cell type B inasmuch as these are
expressed in the latter cell type. gt
renaturation of cDNA(A) with mRNA(B) makes
hydrids, but sequences which are not
common to both cell types remain
single-stranded. mRNA and RNA-DNA hybrids bind
to hydroxyapatite. Cell type A-specific cDNA
can be isolated and either used to make an
A-specific cDNA library, or be used probe to
screen a complete cDNA library of cell type A.
22
Comparing cells of an induced and the
corresponding non-induced stage. Steps in
differential hybridization screening procedures.
/- strategy comparison of signals obtained
with replica filters hybridized with material
derived from cells of the induced and the
non-induced stage, respectively. Dotted lines
strategy with subtracted probes, enriched in
sequences expressed in the induced stage.
Direct identification of "positive" clones.
23
Differential display analysis
Not in 2009-2010
24
RDA
from Primrose Twyman
25
RDA preparing tester and driver DNA
(synthetic) linkers are not phosphorylated
26
RDA
27
28
General basis of SAGE. Anchoring enzyme
NlaIII Tagging enzyme FokI (more details on
following slide)
29
Each mRNA represented by one tag from the
poly(A) tail to the first occurrence of an
NlaIII site. FokI cleaves at 9/13 the 4-nt
extension is filled-in with DNA polymerase.
(the 14/18 fragment is released from the beads
and filled-in to 18-bp fragments) Blunt-end
ligation joins two 18-bp fragments to 36-bp and
cleavage with NlaIII reduces them to 18-bp
with extra 3'-CATG-extensions at both sides.
The tags are pairwise ligated into the vector
and pairs are separated (and thus identified) by
a CATG.
30
Count the number of tags in the
sequenced products.
31
An example of SAGE tag analysis in yeast (S.
cerevisiae)
32
Functional complementation in transgenic mice
using BAC clones.
Not in 2009-2010