Business Process Reengineering - PowerPoint PPT Presentation
Title:
Business Process Reengineering
Description:
The Top Ten Ways to Fail at Reengineering (1 of 2) 1. Don't reengineer but say that you are. ... The Top Ten Ways to Fail at Reengineering (2 of 2) 6. Go ... – PowerPoint PPT presentation
Number of Views:103
Avg rating:3.0/5.0
Title: Business Process Reengineering
1
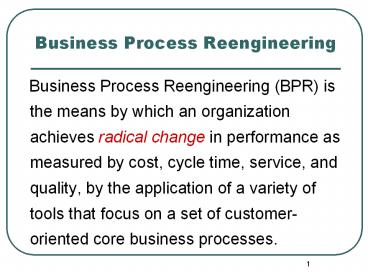
Business Process Reengineering
- Business Process Reengineering (BPR) is the
means by which an organization achieves radical
change in performance as measured by cost, cycle
time, service, and quality, by the application of
a variety of tools that focus on a set of
customer-oriented core business processes.
2
Types of Reengineering
- Type 1 - Process Improvement
- cost-reduction focus
- Type 2 - To achieve parity, or best-in-class
competitive focus - Type 3 - Searching core business for breakpoints
rewriting the rules
3
BPR Process (1 of 2)
- Frame the project
- Create the vision, values and goals
- Redesign the business operation
- Conduct proof of concept
- Andrews Stalick, Business Reengineering The
Survivors Guide
4
BPR Process (2 of 2)
- Plan the implementation
- Obtain implementation approval
- Implement the redesign
- Transition to a continuous improvement state
5
The Dimensions of Business Process Reengineering
- Andrews Stalick (1 of 3)
- Physical/Technical Layer
- Process structure
- Technical structure
- Organization structure
6
The Dimensions of Business Process Reengineering
(2 of 3)
- Infrastructure Layer
- Reward structure
- Measurement systems
- Management methods
7
The Dimensions of Business Process Reengineering
(3 of 3)
- Value Layer
- Organizational culture
- Political power
- Individual belief systems
8
The Top Ten Ways to Fail at Reengineering (1 of 2)
- 1. Dont reengineer but say that you are.
- 2. Dont focus on processes.
- 3. Spend a lot of time analyzing the current
situation. - 4. Proceed without strong executive leadership.
- 5. Be timid in redesign.
- Hammer Champy, The Reengineering Revolution,
1995
9
The Top Ten Ways to Fail at Reengineering (2 of 2)
- 6. Go directly from conceptual design to
- implementation.
- 7. Reengineer slowly.
- 8. Place some aspects of the business off-
- limits.
- 9. Adopt a conventional implementation style.
- 10. Ignore the concerns of your people.
10
Benchmarking
- Benchmarking is the search for the best
practices that will lead to superior performance
of an organization.
11
Benchmarking is NOT
- A cure for all organizational ills
- A means to justify blatant personnel cuts
- A one-shot program
- A process cookbook with no creativity
- A process to conduct industrial espionage
- A one-way information flow
- An improvement tool requiring little cost or
effort
12
Benchmarking Approaches
- Performance benchmarking
- To identify candidates for conducting
benchmarking studies - Process benchmarking
- To identify the best practices
13
Types of Benchmarking ( 1 of 3)
- Internal
- Comparing yourself against a similar process,
product, or service within your own organization
14
Types of Benchmarking (2 of 3)
- Competitive
- Comparing yourself against the toughest external
competitor or against world-class companies in
your industry
15
Types of Benchmarking (3 of 3)
- Generic/Functional
- Comparing yourself against a world-class company
that is not even in your industry, but that uses
a process similar to yours
16
Benchmarking Process ( 1 of 6)
- 1. Getting Organized
- Obtain management buy-in
- Communicate and educate benchmarking concepts
- Plan the overall benchmarking process
- Address fear and concerns
17
Benchmarking Process (2 of 6)
- 2. Preparing to Benchmark
- Identify process to benchmark
- Establish benchmark team
- Understand existing process
- Determine process metrics
18
Benchmarking Process (3 of 6)
- 3. Conduct Research
- Who performs similar processes
- Who performs the best
- What information is needed
- 4. Select the organization to Benchmark
- Establish a relationship
- Reach an agreement on the exchange
19
Benchmarking Process (4 of 6)
- 5. Collect Data and Information
- Identify sources of data/information
- Site visits
- Interviews
- Third parties
- Documents
- Plan and collect data/information
20
Benchmarking Process (5 of 6)
- 6. Analyze and Adapt the Process
- Compare the data/information
- Determine process gaps
- Establish improvement goals
- Design the improved process
- Estimate the improvement
21
Benchmarking Process (6 of 6)
- 7. Implement the New Process
- Train the affected staff
- Implement the process on a trial basis
- Monitor the results
- Adjust and adapt
- Adopt the process
- Celebrate