Angle Modulations - PowerPoint PPT Presentation
1 / 31
Title:
Angle Modulations
Description:
Bessel Functions. From. KMUTT: S. Srakaew. Angle Modulations. Arbitrary FM with ... Properties of Bessel functions. 1. J0( ) varies with the modulation index ... – PowerPoint PPT presentation
Number of Views:37
Avg rating:3.0/5.0
Title: Angle Modulations
1
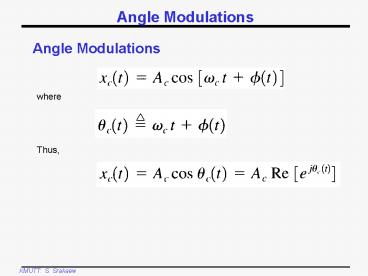
Angle Modulations
Angle Modulations
where
Thus,
2
Angle Modulations
Phase Modulation (PM)
So that
phase modulation index
3
Angle Modulations
Frequency Modulation (FM)
frequency deviation
Since
PM
Therefore,
Thus,
4
Angle Modulations
Frequency Modulation (FM)
Assume that
Therefore,
Thus,
5
Angle Modulations
6
Angle Modulations
Illustrative AM, FM, and PM waveforms
7
Angle Modulations
Narrowband PM and FM
From
we can rewrite xc(t)
where
and
8
Angle Modulations
Narrowband PM and FM
Assume that
so that
Thus,
in which
9
Angle Modulations
Tone Modulation
Assume that
Since
PM
and
FM
Therefore,
modulation index
where
10
Angle Modulations
Narrowband Tone Modulation
From
Therefore,
11
Angle Modulations
Arbitrary FM with Tone Modulation
From
Bessel Functions
12
Angle Modulations
Arbitrary FM with Tone Modulation
Since
Therefore,
13
Angle Modulations
Arbitrary FM with Tone Modulation
14
Angle Modulations
Bessel Functions
15
Angle Modulations
Bessel Functions
16
Angle Modulations
Bessel Functions
17
Angle Modulations
Properties of Bessel functions
1. J0(?) varies with the modulation index
2. The number of sideband lines depends on ?
3. Large ? means large bandwidth
18
Angle Modulations
Tone-modulation line spectra
FM or PM with fm fixed
FM with Amf fixed
19
Angle Modulations
FM phasor diagram
20
Angle Modulations
Transmission Bandwidth
max. deviation(f)
deviation ratio(D)
max. modulating freq(W)
Carsons Rule
BT 2(f W) 2(D1)W for D gtgt 1 or D ltlt1
Majority of FM, 2 lt D lt 10
BT 2(f 2W) 2(D2)W for D gt 2
21
Angle Modulations
Transmission Bandwidth Example
Commercial FM broadcast
A maximum frequency deviation 75
kHz Bandwidth, W 15 kHz
Thus, deviation ration, D 75kHz/15kHz 5 BT
2(52)15 kHz 210 kHz
22
Angle Modulations
FM and PM Generation
- Direct FM and VCO
- Indirect FM
23
Angle Modulations
Direct FM
24
Angle Modulations
Direct FM
25
Angle Modulations
Indirect FM
26
Angle Modulations
FM and PM Detection
- FM-to-AM conversion
- Phase-shift discrimination
- Zero-crossing detection
27
Angle Modulations
FM to AM conversion
28
Angle Modulations
Phase-shift discrimination
29
Angle Modulations
FM and PM Detection
- FM-to-AM conversion
- Phase-shift discrimination
- Zero-crossing detection
30
Assignment 4
1. The signal shown below amplitude modulates a
carrier of frequency 1 MHz
(a) If the modulation is DSBSC, sketch the
modulated waveform and its spectrum. (b) If the
modulation is DSBTC sketch the modulated
waveform. Assume that the amplitude of the
carrier is 1 and the modulation index is 0.5.
(c) The modulated signal of Problem (a) forms
the input to an envelope detector. Sketch
the output of the detector. (d) For the modulated
signal of Problem (b), sketch the output of an
envelope detector.
s(t)
S(f)
1
1
t(msec)
f(kHz)
0.1
-0.1
-0.8
-15-10 -5
5 10 15
2. Consider tone-modulation FM with Ac 100,
Amf 8 kHz, and fm 4 kHz. Draw the line
spectrum for fc 30 kHz and for fc 11 kHz
31
Angle Modulations
Mid-term
- FS
- FT
- Linear Systems (filters)
- Convolution
- AM FM