NADH is not transported DIRECTLY into the matrix - PowerPoint PPT Presentation
1 / 39
Title:
NADH is not transported DIRECTLY into the matrix
Description:
NADH is not transported DIRECTLY into the matrix. 10 H ... b) ADP Pi. c) citrate. d) oligomycin. e) succinate. f) dinitrophenol. g) rotenone. h) cyanide ... – PowerPoint PPT presentation
Number of Views:43
Avg rating:3.0/5.0
Title: NADH is not transported DIRECTLY into the matrix
1
(No Transcript)
2
(No Transcript)
3
(No Transcript)
4
NADH is not transported DIRECTLY into the matrix
5
(No Transcript)
6
For 2H 2NADH O2 ? 2NAD H2O
10 H pumped/2 e- or 10 H pumped /NADH
For 2FADH2 O2 ? 2FAD 2H2O
6 H pumped/2 e- or 6 H pumped /FADH2
7
(No Transcript)
8
see Table 12-1, p373
9
In the e- transport system e- are transferred
from species with lower standard reduction
potential to those with higher standard reduction
potential
10
Complex I transports 4H/2e- NADH H Q
4H(in) ? NAD QH2 4H(out)
11
How are e- transport and H transport coupled? -
protein conformational change - redox loop
mechanism
12
(No Transcript)
13
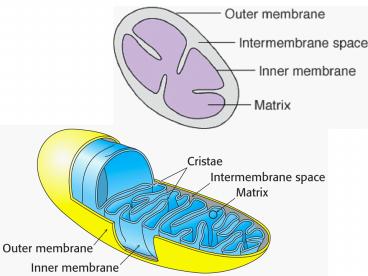
(IMS)
Redox loop mechanism CoQ is reduced (and
therby picks up 2 H) on the matrix side of IMM.
The reduced CoQH2 then moves to the IMS side of
the IMM where it is oxidized (and thereby gives
up 2H).
14
Complex III transports 4H/2e- 2cytc(ox) QH2
2H(in) ? 2cytc(red) Q 4H(out)
15
Intermembrane space
membrane
matrix
16
CoQ-Cytc oxidoreductase (Complex III)
Redox centers in Complex III
17
(No Transcript)
18
Complex IV transports 2H/2e- 2cytc(red) ½O2
4H(in) ? 2cytc(ox) H2O 2H(out)
19
Cytc oxidase (Complex IV)
20
See Fig 12-18
21
oxidative phosphorylation
oxidative refers to electron transport, which
oxidizes upstream cofactors such as NADH and
FADH2 (which, in turn, oxidize nutrients).
22
Intermembrane space (lower pH) Matrix (higher
pH)
ATP synthase (F1F0 ATPase)
23
(No Transcript)
24
(No Transcript)
25
(No Transcript)
26
(No Transcript)
27
X-ray analysis shows 3 different conformations
for the headpiece tight loose open
28
(No Transcript)
29
(No Transcript)
30
Aerobic
Anaerobic
0
e- transport and oxidative phosphorylation
31
4
2
4
3 ATP / NADH or Roughly 3.3 H / ATP
32
(No Transcript)
33
See problems 14-18 in Chapter 12
34
(No Transcript)
35
(No Transcript)
36
(No Transcript)
37
(No Transcript)
38
(No Transcript)
39
Sample Problem
Draw O2 uptake curve that results when the
following are added in the indicated order to a
suspension of mitochondria a) glucose b) ADP
Pi c) citrate d) oligomycin e) succinate f)
dinitrophenol g) rotenone h) cyanide